Stomatitis is a general term referring to inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth, which may include sores. Stomatitis can be caused by infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, autoimmune disorders, allergic reactions Allergic Reactions Type I hypersensitivity reaction against plasma proteins in donor blood Transfusion Reactions, or exposure to irritants. The typical presentation may be either solitary or a group of painful oral lesions. The etiology of the lesion is diagnosed based on appearance and associated symptoms. Treatment involves symptomatic relief, but infectious causes may require antivirals/antibiotics and autoimmune etiologies may require steroid therapy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Stomatitis, sometimes called mucositis, is a broad term referring to inflammatory lesions of the oral mucosa of varied etiologies.
Given the varied etiology, a careful history and physical exam are essential to narrow the diagnosis. Laboratory testing can then confirm findings and clinical suspicion.
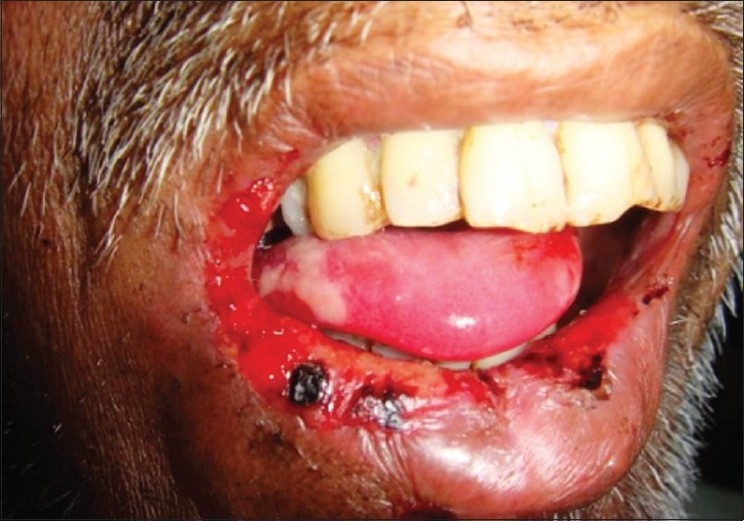
Oral mucositis in a patient who has undergone radiotherapy
Image: “Radiation induced oral mucositis” by Ps SK, Balan A, Sankar A, Bose T. License: CC BY 2.0Management is focused on supportive care, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways reduction, and prevention of secondary infection of the exposed oral mucosa while the underlying cause is treated.