The Saint Louis encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology (SLEV) is a member of the genus Flavivirus Flavivirus A genus of flaviviridae containing several subgroups and many species. Most are arboviruses transmitted by mosquitoes or ticks. The type species is yellow fever virus. Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus and is the cause of St. Louis encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis. This small, enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology is transmitted by Culex mosquito species and is prevalent in the United States. Most infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are asymptomatic. Symptomatic individuals may have varied presentations, with flu-like symptoms Flu-Like Symptoms Babesia/Babesiosis, aseptic meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis, encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis, or meningoencephalitis Meningoencephalitis Encephalitis. The diagnosis is confirmed with serology Serology The study of serum, especially of antigen-antibody reactions in vitro. Yellow Fever Virus. There is no effective antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B treatment, so management is supportive. Prevention is aimed at local mosquito control and personal protection with insect repellent and protective clothing.
Last updated: Oct 31, 2022

RNA virus identification:
Viruses can be classified in many ways. Most viruses, however, will have a genome formed by either DNA or RNA. RNA genome viruses can be further characterized by either a single- or double-stranded RNA. “Enveloped” viruses are covered by a thin coat of cell membrane (usually taken from the host cell). If the coat is absent, the viruses are called “naked” viruses. Viruses with single-stranded genomes are “positive-sense” viruses if the genome is directly employed as messenger RNA (mRNA), which is translated into proteins. “Negative-sense,” single-stranded viruses employ RNA dependent RNA polymerase, a viral enzyme, to transcribe their genome into messenger RNA.
Transmission electron microscopic image of numerous St. Louis encephalitis virions within an unidentified tissue sample:
This virus is a member of the genus Flavivirus.
St. Louis encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology causes St. Louis encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis ( SLE SLE Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune, inflammatory condition that causes immune-complex deposition in organs, resulting in systemic manifestations. Women, particularly those of African American descent, are more commonly affected. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus).
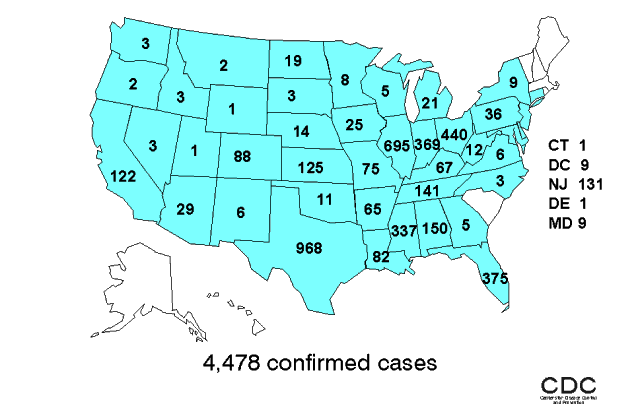
Cases of St. Louis encephalitis in the United States (1964–1998):
Note the distribution of the cases. The disease is most commonly found in the Mississippi River valley, along the Gulf Coast, and in the Southwest.

Close-up photo of a Culex mosquito, the vector for St. Louis encephalitis virus.
Image: “Close-up photo of a Culex mosquito” by CDC. License: Public DomainRisk factors for developing SLEV infection:
The vast majority of infected individuals will be asymptomatic. The incubation Incubation The amount time between exposure to an infectious agent and becoming symptomatic. Rabies Virus period for symptomatic individuals is 4–21 days, and the disease varies in presentation and severity.
General:
Respiratory:
Urinary:
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may present with meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis, encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis, or a combination of the 2 ( meningoencephalitis Meningoencephalitis Encephalitis).
Aseptic meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis (most common):
Encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis:
The diagnosis may be suspected from the history and physical examination.
There are no effective antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B treatments for SLEV, so management is supportive.
| Organism | Tick-borne encephalitis Tick-borne encephalitis Encephalitis caused by neurotropic viruses that are transmitted via the bite of ticks. In europe, the diseases are caused by encephalitis viruses, tick-borne, which give rise to russian spring-summer encephalitis, central european encephalitis, louping ill encephalitis, and related disorders. Powassan encephalitis occurs in north america and russia and is caused by the powassan virus. Aseptic meningitis and rarely encephalitis may complicate colorado tick fever which is endemic to mountainous regions of the Western United States. Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology | Japanese encephalitis virus Japanese encephalitis virus A species of flavivirus, one of the japanese encephalitis virus group, which is the etiological agent of japanese encephalitis found in Asia, southeast Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. Encephalitis | St. Louis encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology | West Nile virus West Nile Virus West Nile virus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus of the genus Flavivirus. Birds are the primary hosts and the disease is most often transmitted by Culex mosquitoes. Most people infected with West Nile virus are asymptomatic. Some patients develop West Nile fever (a self-limited, febrile illness) and a very small proportion of patients develop West Nile neuroinvasive disease. West Nile Virus |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | The structural features are almost identical. | |||
| Region |
|
|
North America |
|
| Transmission | Tick | Mosquito | Mosquito | Mosquito |
| Clinical |
|
|
|
|
| Diagnosis |
|
Serology Serology The study of serum, especially of antigen-antibody reactions in vitro. Yellow Fever Virus | Serology Serology The study of serum, especially of antigen-antibody reactions in vitro. Yellow Fever Virus |
|
| Management | Supportive | Supportive | Supportive | Supportive |
| Prevention |
|
|
Mosquito avoidance measures | Mosquito avoidance measures |