Spontaneous abortion, also known as miscarriage, is the loss of a pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care before 20 weeks' gestation. However, the layperson use of the term “abortion” is often intended to refer to induced termination of a pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care, whereas “miscarriage” is preferred for spontaneous loss. Most spontaneous abortions occur within the 1st 12 weeks of gestation and can be caused by several factors such as infection, trauma, and genetic and autoimmune causes. There are different types of spontaneous abortions, including threatened, inevitable, incomplete, complete, and missed abortions. Spontaneous abortions are diagnosed based on history, physical examination, and ultrasound findings. Management options include expectant, medical, or surgical therapy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Spontaneous abortion is the noninduced loss of pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care before 20 weeks’ gestation.
Spontaneous abortion can be classified into the following types (see “Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis” for details):
There are many potential causes for spontaneous abortion.
The diagnosis is made by a combination of history, physical examination, and ultrasound findings.
The types of spontaneous abortions differ based on clinical examination and ultrasound findings.
Threatened abortion:
Inevitable abortion:
Incomplete abortion:
Complete abortion:
Missed abortion:
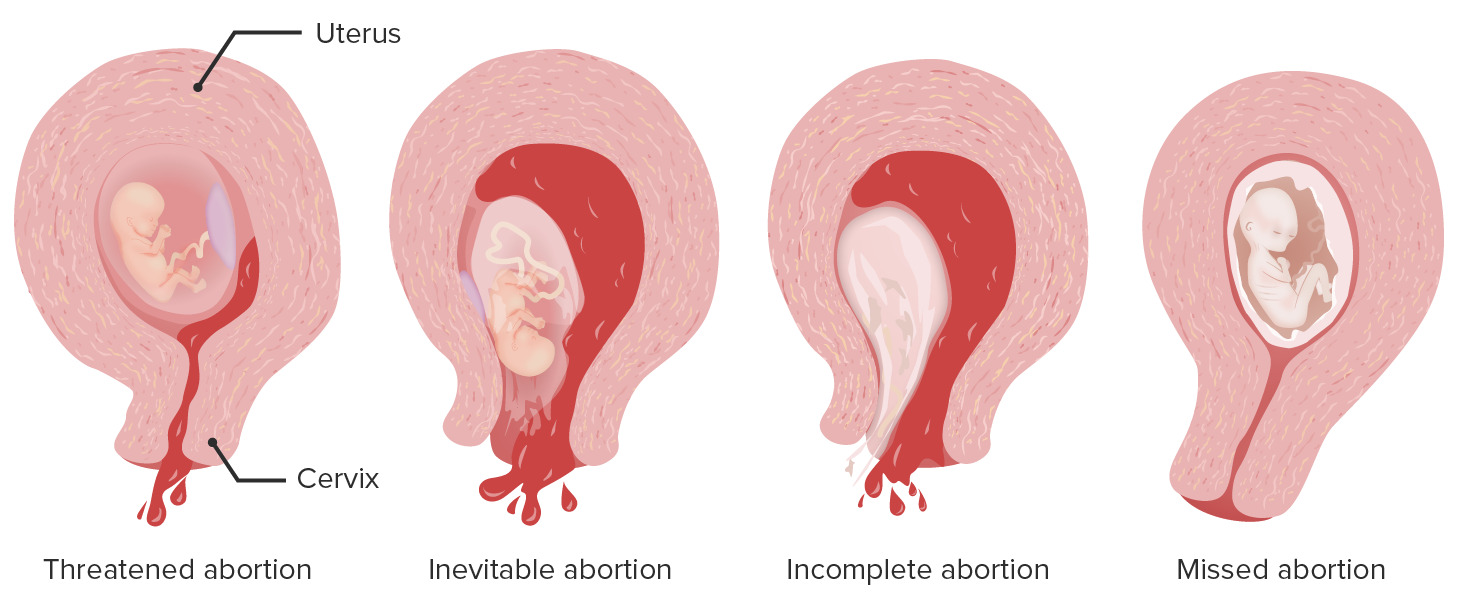
Differences between the types of spontaneous abortion:
Important differentiating factors include the presence or absence of vaginal bleeding, whether the cervical os is dilated or closed, the presence or absence of the products of conception, and fetal cardiac activity.