Sjögren syndrome Sjögren Syndrome Rheumatoid Arthritis ( SS SS Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) is an autoimmune condition characterized by diffuse collagen deposition and fibrosis. The clinical presentation varies from limited skin involvement to diffuse involvement of internal organs. Scleroderma) is an autoimmune, inflammatory condition where glandular tissues, such as the salivary and lacrimal glands Lacrimal Glands Dacryocystitis, are infiltrated by lymphocytes Lymphocytes Lymphocytes are heterogeneous WBCs involved in immune response. Lymphocytes develop from the bone marrow, starting from hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and progressing to common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs). B and T lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells arise from the lineage. Lymphocytes: Histology, resulting in decreased tear and saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy production. The disease mainly affects middle-aged women, and is associated with other autoimmune conditions. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may experience symptoms and complications related to dry eyes and mouth. There is a wide range of extraglandular manifestations, including Raynaud phenomenon, neuropathy Neuropathy Leprosy, and cutaneous vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are also at an increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum. Diagnosis is based on the presence of symptoms, and is validated by the clinical examination, serologic studies, or salivary gland Salivary gland Glands that secrete saliva in the mouth. There are three pairs of salivary glands (parotid gland; sublingual gland; submandibular gland). Diseases of the Salivary Glands biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma. A multidisciplinary approach is needed to manage patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship and targets symptomatic relief, with immunosuppressive therapy reserved for severe symptoms.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Sjögren syndrome Sjögren Syndrome Rheumatoid Arthritis ( SS SS Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) is an autoimmune condition characterized by diffuse collagen deposition and fibrosis. The clinical presentation varies from limited skin involvement to diffuse involvement of internal organs. Scleroderma), also known as sicca syndrome, is a chronic autoimmune and inflammatory condition leading to decreased lacrimal and salivary gland Salivary gland Glands that secrete saliva in the mouth. There are three pairs of salivary glands (parotid gland; sublingual gland; submandibular gland). Diseases of the Salivary Glands function, resulting in dry eyes (xerophthalmia) and mouth (xerostomia).
Primary SS SS Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) is an autoimmune condition characterized by diffuse collagen deposition and fibrosis. The clinical presentation varies from limited skin involvement to diffuse involvement of internal organs. Scleroderma:
Secondary SS SS Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) is an autoimmune condition characterized by diffuse collagen deposition and fibrosis. The clinical presentation varies from limited skin involvement to diffuse involvement of internal organs. Scleroderma:
Presents in association with another autoimmune disease:
The overall mechanism for SS SS Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) is an autoimmune condition characterized by diffuse collagen deposition and fibrosis. The clinical presentation varies from limited skin involvement to diffuse involvement of internal organs. Scleroderma is unclear:
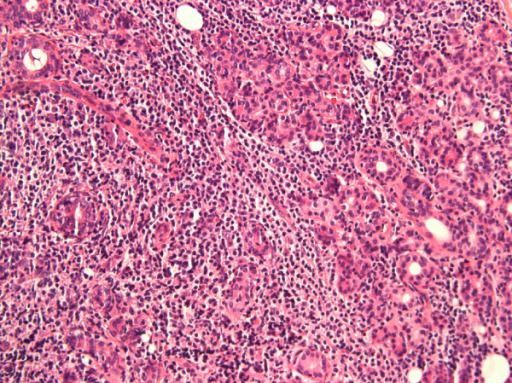
Lymphocytic infiltration of the parotid gland in a patient with SS
Image: “Anti-salivary gland protein 1 antibodies in two patients with Sjogren’s syndrome: Two case reports” by Vishwanath S, Shen L, Suresh L, Ambrus JL. License: CC BY 2.0.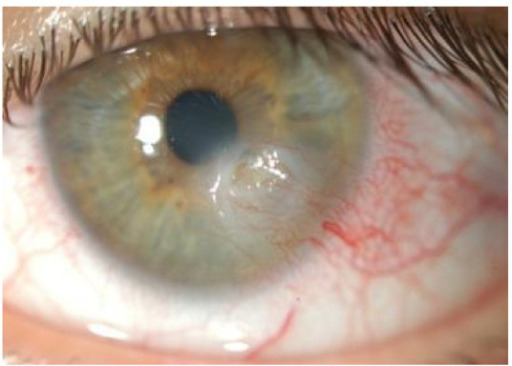
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca with a corneal ulceration in a patient with SS
Image: “Novel aspects of Sjögren’s syndrome in 2012” by Tincani A, Andreoli L, Cavazzana I, Doria A, Favero M, Fenini MG, Franceschini F, Lojacono A, Nascimbeni G, Santoro A, Semeraro F, Toniati P, Shoenfeld Y. License: CC BY 2.0.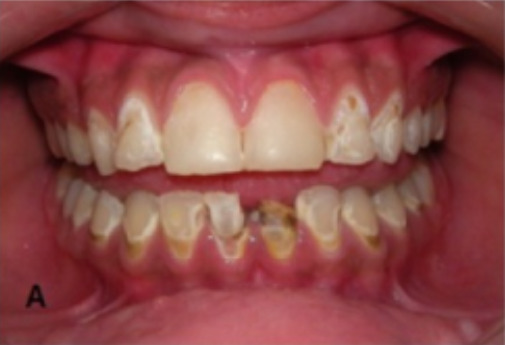
Dental caries in a patient with secondary SS
Image: “Oral Rehabilitation and Management for Secondary Sjögren’s Syndrome in a Child” by Case Reports in Dentistry. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.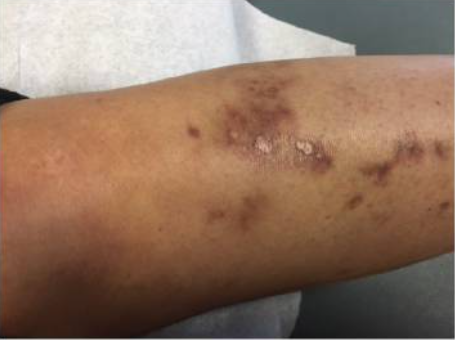
Vasculitic skin changes and ulceration noted in a patient with SS
Image: “Skin Findings in a Patient with Sjogren’s Syndrome” by Case Reports in Rheumatology. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.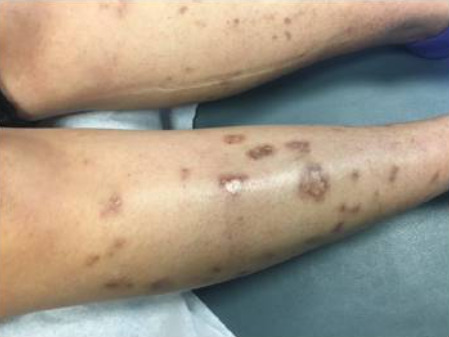
Vasculitic skin changes and ulceration noted in a patient with SS
Image: “Skin Findings in a Patient with Sjogren’s Syndrome” by Case Reports in Rheumatology. License: CC BY 4.0, edited by Lecturio.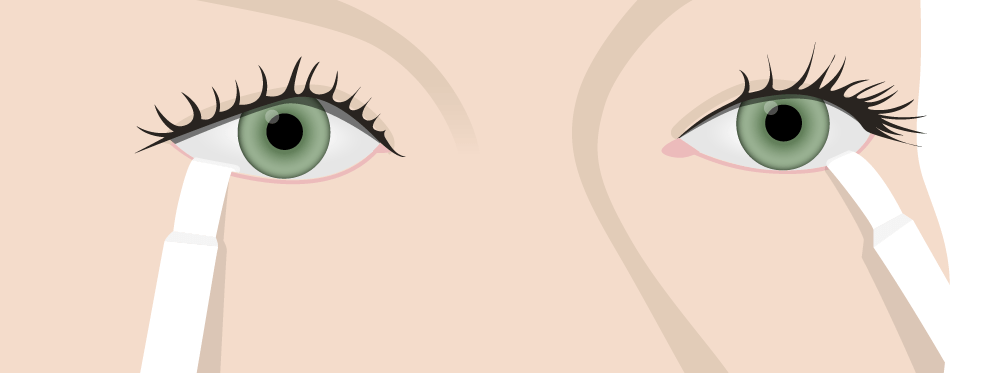
Schirmer test for tear production:
To evaluate for Sjögren syndrome, test strips are placed on the lower eyelid and the extent of wetness is measured after 5 minutes.
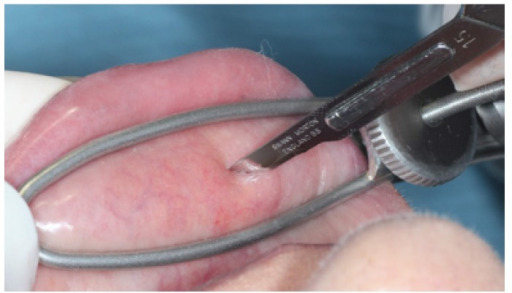
Biopsy of a minor salivary gland on a patient’s lip
Such a biopsy can be done as part of the evaluation for SS.
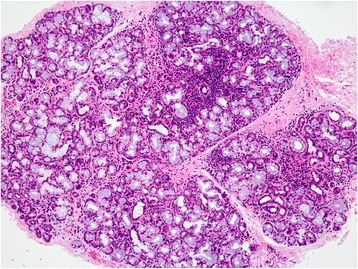
Histologic findings of a minor salivary gland in a patient with SS
Focal lymphocytic aggregation is seen throughout the gland with mild glandular atrophy.
Several criteria have been proposed to aid in the diagnosis of SS SS Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) is an autoimmune condition characterized by diffuse collagen deposition and fibrosis. The clinical presentation varies from limited skin involvement to diffuse involvement of internal organs. Scleroderma. The following is from the American-European Consensus Group (requires 4 of 6 criteria, including a positive biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma or autoantibodies Autoantibodies Antibodies that react with self-antigens (autoantigens) of the organism that produced them. Blotting Techniques):
The differential diagnosis of SS SS Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) is an autoimmune condition characterized by diffuse collagen deposition and fibrosis. The clinical presentation varies from limited skin involvement to diffuse involvement of internal organs. Scleroderma include differentials based on the presenting symptoms as well as other autoimmune disorders: