Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosal lining of the paranasal sinuses that usually occurs concurrently with inflammation of the nasal mucosa (rhinitis), together known as rhinosinusitis. The most common etiology of acute rhinosinusitis is a viral infection; other causes include bacteria or fungi. Clinically, sinusitis presents with facial pain, nasal obstruction, mucopurulent drainage, and decreased olfaction. Diagnosis is usually clinical, and management is supportive; antibiotics are generally not recommended unless symptoms do not improve after 10 days. Chronic sinusitis lasts 12 weeks or longer and may be associated with nasal polyposis or allergic fungal rhinosinusitis. The goal of management in most chronic cases is to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life rather than cure the disorder, which may require surgery.
Last updated: Dec 27, 2025
Viral
Bacterial
General manifestations
Viral sinusitis
Viral sinusitis usually presents in a milder form and lasts 7–10 days.
Bacterial sinusitis
Fungal sinusitis
Fungal sinusitis usually presents chronically, with atypical symptoms ( epistaxis Epistaxis Bleeding from the nose. Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis, dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, and black/brown nasal secretions).
Complications and/or associated conditions
Diagnosis is usually based on clinical symptoms.
To differentiate viral sinusitis from bacterial sinusitis:
Laboratory tests
Culture
Presence of more than 104 colony-forming units/mL on bacterial culture is confirmatory for bacterial sinusitis in children.
Imaging
Biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma
Only needed if infection recurs or if there is no response to different empiric therapies.
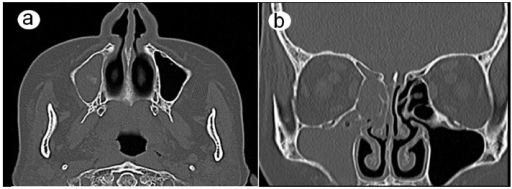
CT scans: (a) the axial plane and (b) the coronal plane show complete opacification in the maxillary, ethmoid, and frontal sinuses on the right side.
Image: “CT scans 6 weeks after the first visit” by Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Nara Medical University, Nara, Japan. License: CC BY 4.0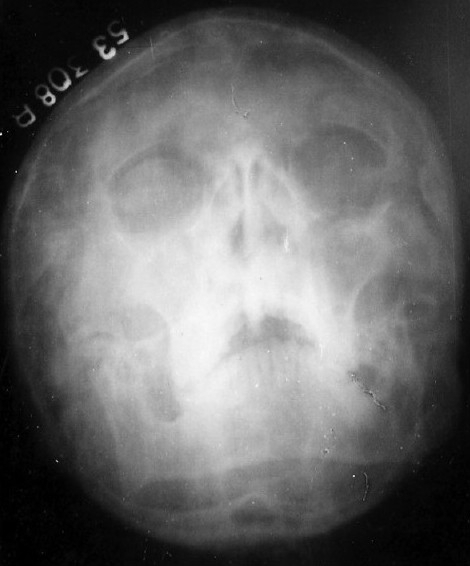
X-ray of paranasal sinuses showing maxillary sinusitis and bilateral hypoplastic frontal sinuses.
Image: “X-ray paranasal sinus showing maxillary sinusitis” by J.L.N. Medical College, Ajmer, India. License: CC BY 2.0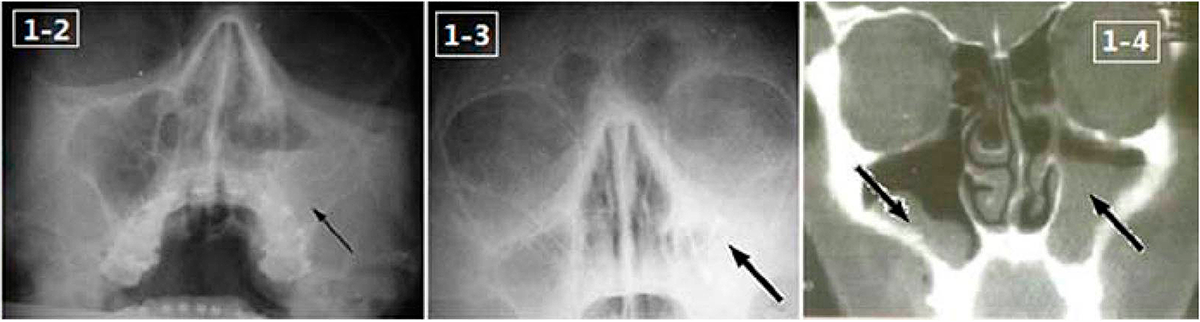
X-ray images in Water’s position (1–2 and 1–3) and magnetic resonance image (1–4) show the opacification of the maxillary sinus and bilateral air-fluid levels.
Image: “Endoscopic image of maxillary sinus mucosa” by Lin Feng, Department of Stomatology, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, P. R. China. License: CC BY 3.0, edited by Lecturio.General supportive care
Viral sinusitis
Bacterial sinusitis
Fungal sinusitis
The following are potential underlying conditions or differential diagnoses of sinusitis: