Sideroblastic anemias are a heterogeneous group of bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis disorders characterized by abnormal iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements accumulation in the mitochondria Mitochondria Semiautonomous, self-reproducing organelles that occur in the cytoplasm of all cells of most, but not all, eukaryotes. Each mitochondrion is surrounded by a double limiting membrane. The inner membrane is highly invaginated, and its projections are called cristae. Mitochondria are the sites of the reactions of oxidative phosphorylation, which result in the formation of ATP. They contain distinctive ribosomes, transfer RNAs; amino Acyl tRNA synthetases; and elongation and termination factors. Mitochondria depend upon genes within the nucleus of the cells in which they reside for many essential messenger RNAs. Mitochondria are believed to have arisen from aerobic bacteria that established a symbiotic relationship with primitive protoeukaryotes. The Cell: Organelles of erythroid precursors. The accumulated iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements appears as granules in a ringlike distribution around the nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles, giving rise to the characteristic morphological feature of a ring sideroblast. Sideroblastic anemias may be due to inherited defects in heme synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) or can be acquired through alcoholism Alcoholism A primary, chronic disease with genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors influencing its development and manifestations. The disease is often progressive and fatal. It is characterized by impaired control over drinking, preoccupation with the drug alcohol, use of alcohol despite adverse consequences, and distortions in thinking, most notably denial. Each of these symptoms may be continuous or periodic. Wernicke Encephalopathy and Korsakoff Syndrome, lead poisoning Lead poisoning Poisoning that results from chronic or acute ingestion, injection, inhalation, or skin absorption of lead or lead compounds. Metal Poisoning (Lead, Arsenic, Iron), medications, or vitamin deficiencies. The anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types is commonly microcytic with low to normal reticulocyte Reticulocyte Immature erythrocytes. In humans, these are erythroid cells that have just undergone extrusion of their cell nucleus. They still contain some organelles that gradually decrease in number as the cells mature. Ribosomes are last to disappear. Certain staining techniques cause components of the ribosomes to precipitate into characteristic 'reticulum' (not the same as the endoplasmic reticulum), hence the name reticulocytes. Erythrocytes: Histology count. Serum iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements levels are typically elevated. A bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis examination showing ring sideroblasts establishes the diagnosis. Management involves treating the underlying condition, avoiding causative medication and/or toxins, and phlebotomy Phlebotomy The techniques used to draw blood from a vein for diagnostic purposes or for treatment of certain blood disorders such as erythrocytosis, hemochromatosis, polycythemia vera, and porphyria cutanea tarda. Hereditary Hemochromatosis in cases of iron overload Iron overload An excessive accumulation of iron in the body due to a greater than normal absorption of iron from the gastrointestinal tract or from parenteral injection. This may arise from idiopathic hemochromatosis, excessive iron intake, chronic alcoholism, certain types of refractory anemia, or transfusional hemosiderosis. Hereditary Hemochromatosis.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Sideroblastic anemias are a heterogeneous group of bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis disorders characterized by abnormal iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements accumulation in the mitochondria Mitochondria Semiautonomous, self-reproducing organelles that occur in the cytoplasm of all cells of most, but not all, eukaryotes. Each mitochondrion is surrounded by a double limiting membrane. The inner membrane is highly invaginated, and its projections are called cristae. Mitochondria are the sites of the reactions of oxidative phosphorylation, which result in the formation of ATP. They contain distinctive ribosomes, transfer RNAs; amino Acyl tRNA synthetases; and elongation and termination factors. Mitochondria depend upon genes within the nucleus of the cells in which they reside for many essential messenger RNAs. Mitochondria are believed to have arisen from aerobic bacteria that established a symbiotic relationship with primitive protoeukaryotes. The Cell: Organelles of erythroid precursors.
The distribution of the iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements is ringlike around the nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles, manifested by the precursors (ring sideroblasts) in the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis.
Congenital Congenital Chorioretinitis disorders:
Acquired:
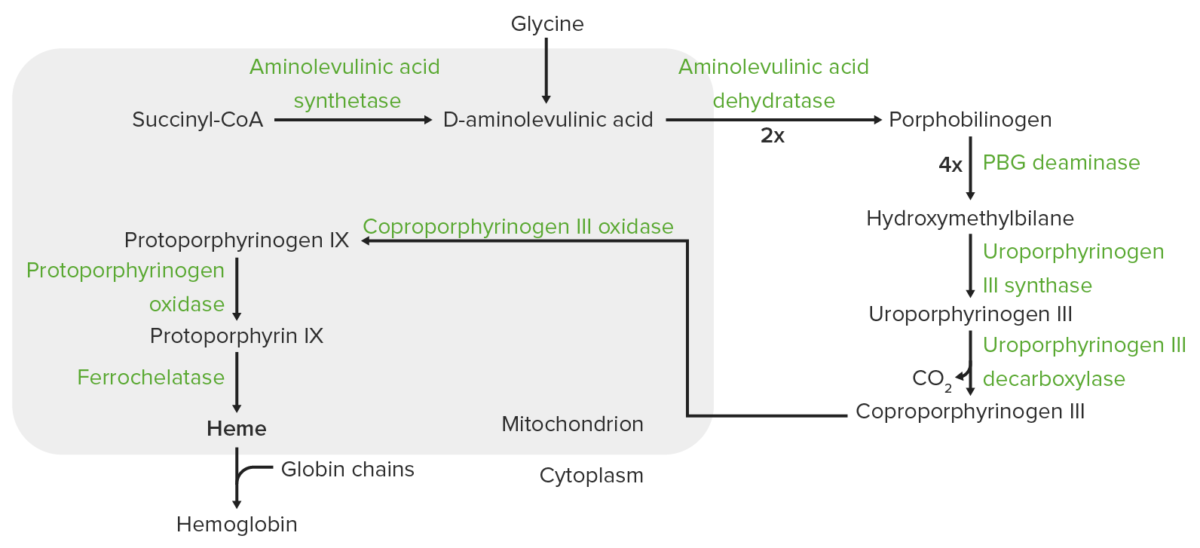
Heme synthesis:
The process of heme synthesis takes place in the mitochondria and cytoplasm.
In the mitochondria, succinyl coenzyme A (CoA) combines with glycine to form aminolevulinic acid.
This reaction is catalyzed by aminolevulinic acid synthase. The aminolevulinic acid exits to the cytoplasm, where 2 aminolevulinic acid molecules condense to produce porphobilinogen (PBG). The subsequent steps lead to the formation of coproporphyrinogen III, which is transported back to the mitochondria. Oxidase facilitates conversion of coproporphyrinogen III to protoporphyrinogen IX, which then is converted to protoporphyrin IX. Ferrous iron is inserted into protoporphyrin IX, forming heme (catalyzed by ferrochelatase).
Defects in heme synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR):
Defects in iron-sulfur cluster (ISC) biogenesis:
Defects in mitochondrial protein synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR):
Dysfunction in erythropoiesis Erythropoiesis The production of red blood cells (erythrocytes). In humans, erythrocytes are produced by the yolk sac in the first trimester; by the liver in the second trimester; by the bone marrow in the third trimester and after birth. In normal individuals, the erythrocyte count in the peripheral blood remains relatively constant implying a balance between the rate of erythrocyte production and rate of destruction. Erythrocytes: Histology:
Clinical presentation varies depending on the underlying disease.
General features of anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types:
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with vitamin B6 deficiency may have:
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with lead poisoning Lead poisoning Poisoning that results from chronic or acute ingestion, injection, inhalation, or skin absorption of lead or lead compounds. Metal Poisoning (Lead, Arsenic, Iron) may have:
Others:
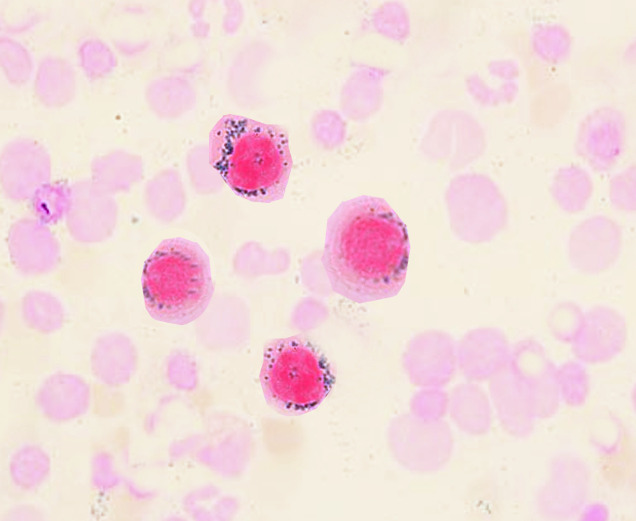
Ring sideroblasts
Image: “Ringed sideroblasts” by S. Bhimji, MD. License: CC BY 4.0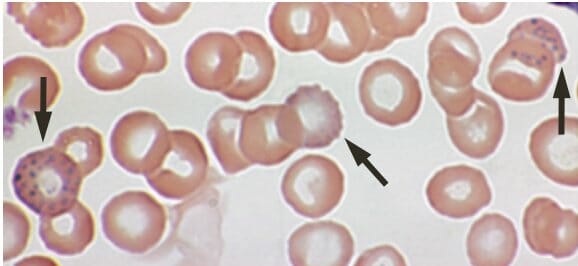
Lead poisoning:
Basophilic stippling on a peripheral blood smear of a 53-year-old with anemia complaining of fatigue and constipation
| CBC finding | Diagnosis | Iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements level | Features or historical setting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types with MCV < 80 | Sideroblastic anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types | ↑ Iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements level | Alcoholic Alcoholic Persons who have a history of physical or psychological dependence on ethanol. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome (Mallory-Weiss Tear), MDS MDS Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are a group of clonal neoplasms with maturation defects characterized by dysplasia, cytopenia, and immature bone marrow precursors. Myelodysplastic syndromes can be idiopathic, or secondary to various injurious exposures such as cytotoxic chemotherapy, ionizing radiation, or environmental toxins. Myelodysplastic Syndromes |
| Iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements deficiency anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types | ↓ Iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements level | Blood loss | |
| Thalassemia Thalassemia Thalassemia is a hereditary cause of microcytic hypochromic anemia and results from a deficiency in either the α or β globin chains, resulting in hemoglobinopathy. The presentation of thalassemia depends on the number of defective chains present and can range from being asymptomatic to rendering the more severely affected patients to be transfusion dependent. Thalassemia | Normal iron Iron A metallic element with atomic symbol fe, atomic number 26, and atomic weight 55. 85. It is an essential constituent of hemoglobins; cytochromes; and iron-binding proteins. It plays a role in cellular redox reactions and in the transport of oxygen. Trace Elements level | Variant dependent (asymptomatic to severe anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types) |
Treatment options depend on the etiology and include: