Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of genetic disorders in which an abnormal Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange molecule ( Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange S) transforms RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology into sickle-shaped cells, resulting in chronic anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, vasoocclusive episodes, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and organ damage. Sickle cell trait, which is the heterozygous condition, is the only 1 of the group that is generally benign Benign Fibroadenoma and rarely associated with serious SCD-like complications. Triggers such as stress and hypoxia Hypoxia Sub-optimal oxygen levels in the ambient air of living organisms. Ischemic Cell Damage can induce or worsen the sickling of RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology. Individuals with SCD are susceptible to infection, infarction of various organs, and bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis aplasia Aplasia Cranial Nerve Palsies; lung involvement in acute chest syndrome can be rapidly fatal. Sickle cells can usually be seen on the peripheral blood smear Peripheral Blood Smear Anemia: Overview and Types, but Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange electrophoresis Electrophoresis An electrochemical process in which macromolecules or colloidal particles with a net electric charge migrate in a solution under the influence of an electric current. Blotting Techniques is needed for diagnosis. The management of painful episodes consists of IV fluids IV fluids Intravenous fluids are one of the most common interventions administered in medicine to approximate physiologic bodily fluids. Intravenous fluids are divided into 2 categories: crystalloid and colloid solutions. Intravenous fluids have a wide variety of indications, including intravascular volume expansion, electrolyte manipulation, and maintenance fluids. Intravenous Fluids and analgesics, and in severe episodes, exchange transfusions may be required. Survival is improved by vaccination Vaccination Vaccination is the administration of a substance to induce the immune system to develop protection against a disease. Unlike passive immunization, which involves the administration of pre-performed antibodies, active immunization constitutes the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies. Vaccination against bacterial infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, prophylactic antibiotics, and aggressive treatment of infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a group of genetic disorders that cause an abnormal Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange molecule ( Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange S) that transforms RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology into sickle-shaped cells, resulting in chronic anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, vasoocclusive episodes, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and organ damage.
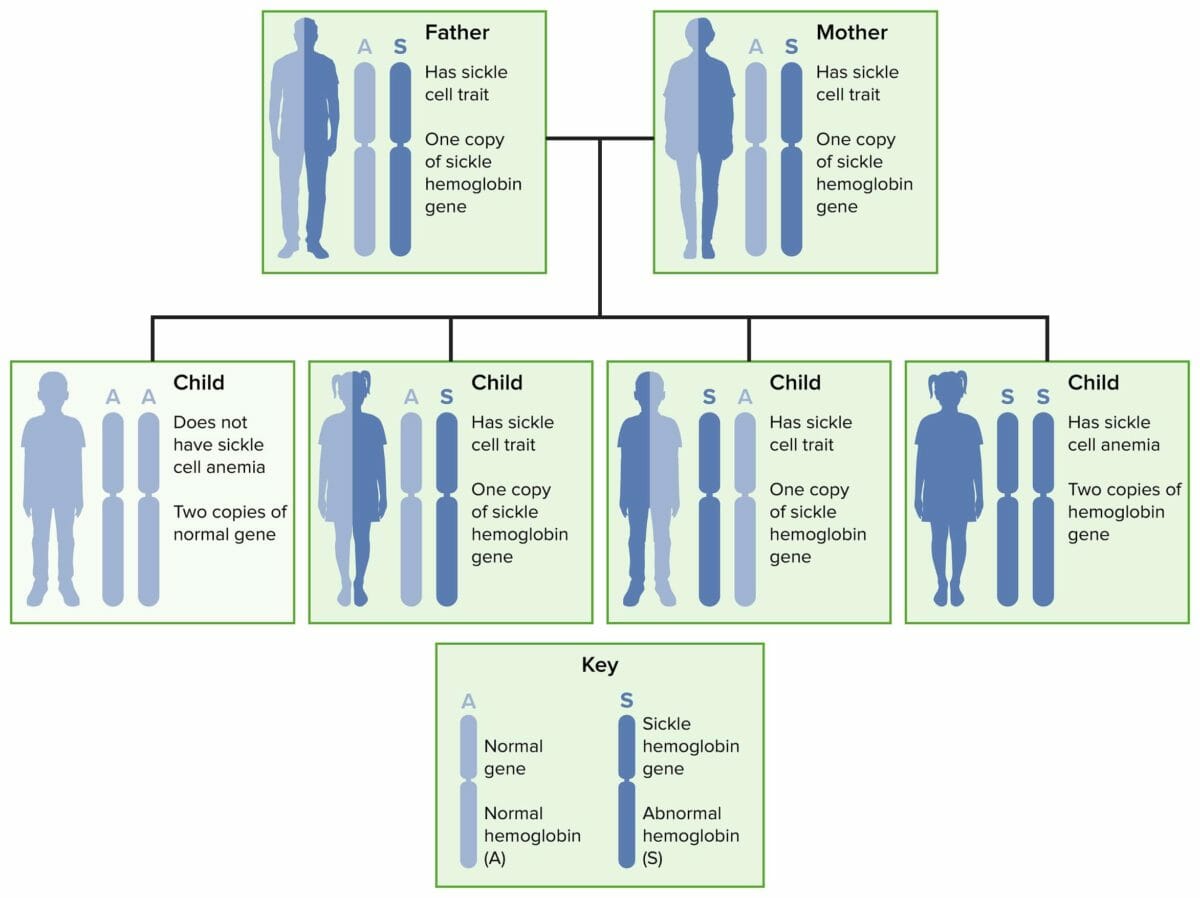
Autosomal recessive inheritance of sickle cell disease and trait
Image by Lecturio.Normal adult hemoglobin molecule (HbA1) consists of 2 pairs of chains called alpha and beta.
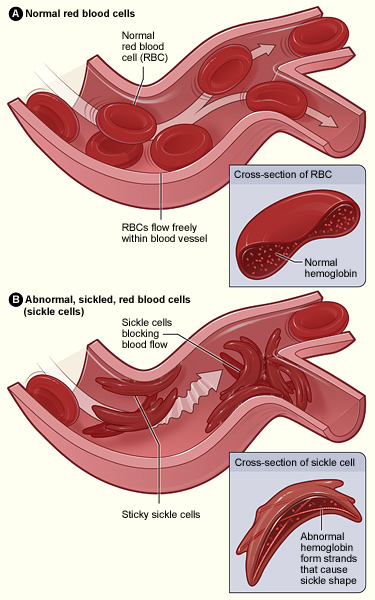
Abnormal hemoglobin results in RBC sickling and adhesion of the sickled cells to endothelium, which is activated by the adherent RBCs. Occlusion of small vessels occurs by an aggregate of sickled RBCs, with platelets and white blood cells (not shown in figure).
Image: “Sickle cell 01” by The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). License: Public DomainMost symptoms result from the anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types and vasoocclusive events seen in individuals with SCD or complications including infection.
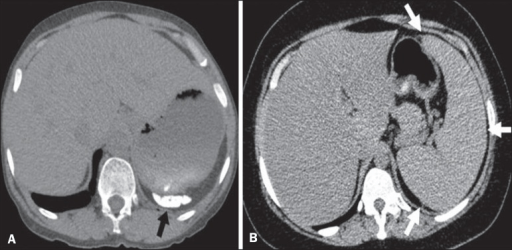
Different patterns of splenic involvement in sickle cell disease:
A: atrophy and calcification of the spleen (arrow)
B: splenomegaly (arrows)
Sickle cell disease is usually diagnosed prenatally or at birth by mandatory neonatal screening Screening Preoperative Care. Methods vary from state to state.
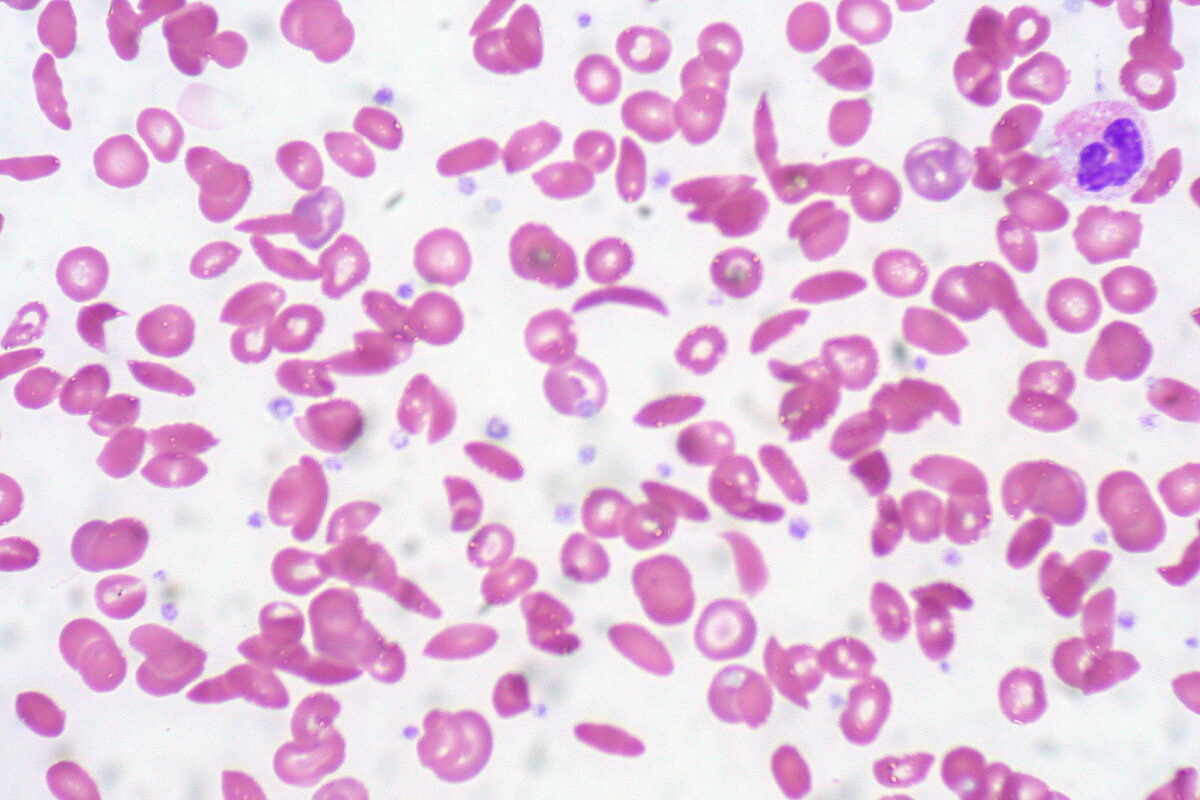
Peripheral blood smear showing a mixture of RBCs, some with round normal morphology and some with sickling (elongation and bending)
Image: “Sickle Cell Anemia” by Ed Uthman. License: CC BY 2.0Treatment of painful episodes includes analgesics and general supportive measures. Transfusions may be needed on occasion if the individual has symptomatic anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, including for the complication of acute chest syndrome.
| Presentation | Management |
|---|---|
| Acute pain Acute pain Intensely discomforting, distressful, or agonizing sensation associated with trauma or disease, with well-defined location, character, and timing. Pain Management episodes/ vasoocclusive events |
|
| Acute splenic sequestration Splenic sequestration Severe Congenital Neutropenia |
|
| Infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease | Prevention:
|
| Priapism Priapism A prolonged painful erection that may lasts hours and is not associated with sexual activity. It is seen in patients with sickle cell anemia, advanced malignancy, spinal trauma; and certain drug treatments. Penile Anomalies and Conditions |
|
| Prophylactic screening Screening Preoperative Care |
|
| Refractory |
|