Short stature in children is defined as a height more than 2 standard deviations below the mean for age and gender Gender Gender Dysphoria or growing below the 3rd percentile when plotting height on standardized growth charts. Short stature can be pathological or due to a normal variant in growth pattern. In the majority of cases, short stature in early childhood is due to constitutional growth delay. Management is directed at the underlying cause, and prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas depends on age, etiology, and severity.
Last updated: Oct 6, 2022
Children are diagnosed with short stature if their measured height is 2 standard deviations below the mean for age and sex. “Short stature” is an umbrella term, describing the result of processes that may be either idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis or pathological.
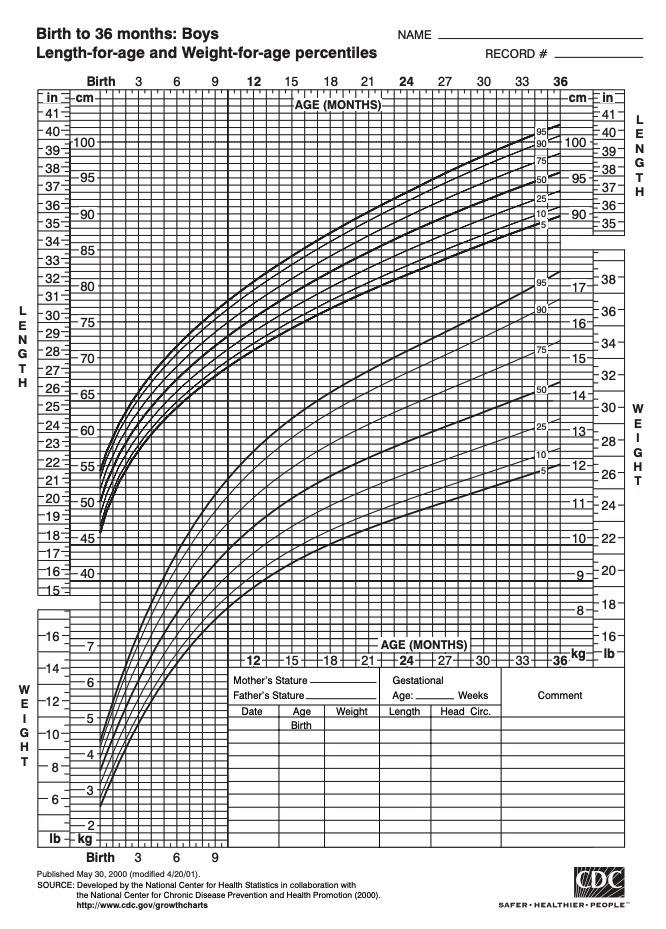
Example of a height-and-weight growth chart for boys from 0 to 36 months of age
Image: “Growthchart for boys” by CDC. License: Public Domain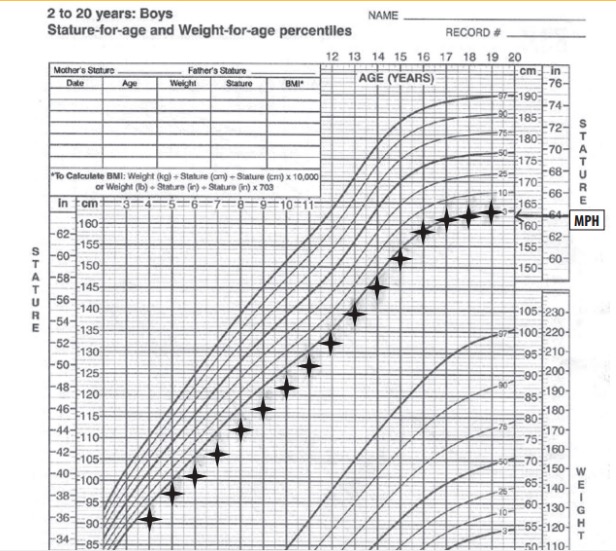
Growth curve showing familial short stature:
Notice how the child height remains parallel to the percentile curves. MPH: midparental height
Idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis: normal variants of patterns of growth that often result in achieving full potential height by adulthood
Pathological:

Formulas for calculation of the expected height of boys and girls
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Syndromes that present with short stature:
Early sexual development ( precocious puberty Precocious puberty Precocious puberty (PP) is the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics due to elevated sex hormones before the age of 6-8 in girls and 9 in boys. Excess hormone secretion may occur only at the level of the sex hormone or may involve the whole hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Precocious Puberty):
Systemic disease:
Bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types age with a hand Hand The hand constitutes the distal part of the upper limb and provides the fine, precise movements needed in activities of daily living. It consists of 5 metacarpal bones and 14 phalanges, as well as numerous muscles innervated by the median and ulnar nerves. Hand: Anatomy X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests:
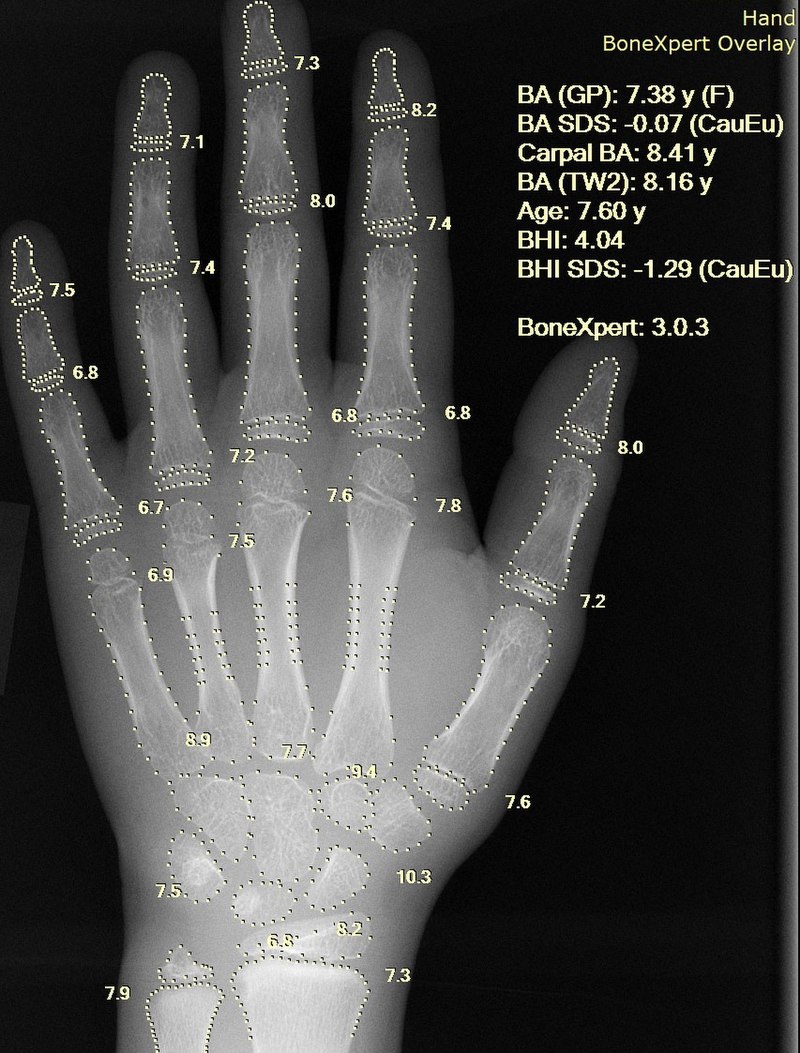
X-ray of a hand, with automatic calculation of bone age by computer software
Image: “X-ray of a hand” by Setzner1337. License: CC0 1.0Labs:
Management of short stature is based on the underlying etiology. Some causes are reversible with intervention, while some others cannot be treated.