Sex-linked inheritance is a form of mendelian inheritance. The term describes traits that are inherited via either the X or the Y chromosome Y chromosome The male sex chromosome, being the differential sex chromosome carried by half the male gametes and none of the female gametes in humans and in some other male-heterogametic species in which the homologue of the X chromosome has been retained. Basic Terms of Genetics. For X-linked recessive X-Linked Recessive Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy transmission, the allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics is recessive and carried on the X chromosome X chromosome The female sex chromosome, being the differential sex chromosome carried by half the male gametes and all female gametes in human and other male-heterogametic species. Basic Terms of Genetics. Males are more likely to express X-linked recessive X-Linked Recessive Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy disorders because they possess only 1 X chromosome X chromosome The female sex chromosome, being the differential sex chromosome carried by half the male gametes and all female gametes in human and other male-heterogametic species. Basic Terms of Genetics. For X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) dominant transmission, the allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics is dominant and carried on the X chromosome X chromosome The female sex chromosome, being the differential sex chromosome carried by half the male gametes and all female gametes in human and other male-heterogametic species. Basic Terms of Genetics. Because of this, only 1 copy of the disease allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics is required for phenotypic expression. X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) dominant disorders are less common than X-linked recessive X-Linked Recessive Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy disorders.
Last updated: Mar 21, 2024
Sex-linked inheritance occurs when genetic traits are inherited on either the X or the Y chromosome Y chromosome The male sex chromosome, being the differential sex chromosome carried by half the male gametes and none of the female gametes in humans and in some other male-heterogametic species in which the homologue of the X chromosome has been retained. Basic Terms of Genetics. There are 2 major sex-linked modes of inheritance: X-linked recessive X-Linked Recessive Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) dominant.
X-linked recessive X-Linked Recessive Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy inheritance:
X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) dominant inheritance:
Children of an unaffected father and a heterozygous ( carrier Carrier Vaccination) mother have the following risks:
| Unaffected father | |||
| x | y | ||
| Heterozygous ( carrier Carrier Vaccination) mother | x | xx (unaffected female) | xy (unaffected male) |
| x | xx ( carrier Carrier Vaccination female) | xy (affected male) | |
Children of an affected father and a heterozygous ( carrier Carrier Vaccination) mother have the following risks:
| Hemizygously affected father | |||
| x | y | ||
| Heterozygous ( carrier Carrier Vaccination) mother | x | xx ( carrier Carrier Vaccination female) | xy (unaffected male) |
| x | xx (affected female) | xy (affected male) | |
Children of an affected father and an unaffected mother have the following risks:
| Hemizygously affected father | |||
| x | y | ||
| Unaffected mother | x | xx ( carrier Carrier Vaccination female) | xy (unaffected male) |
| x | xx ( carrier Carrier Vaccination female) | xy (unaffected male) | |
Children of a hemizygous affected father and a homozygous (affected) mother have the following risks:
| Hemizygously affected father | |||
| x | y | ||
| Homozygously affected mother | x | xx (affected female) | xy (affected male) |
| x | xx (affected female) | xy (affected male) | |

Patterns of X-linked recessive inheritance:
Both maternal and paternal X chromosomes must be affected for females to express the trait. Females are usually carriers of the X-linked recessive trait. With only 1 X chromosome, males are more frequently affected than females. Male-to-male inheritance is impossible because a father can only transmit a Y chromosome to a son.
Note: A few carriers may be mildly affected due to skewed X-chromosome inactivation.
Children of a hemizygous (unaffected) father and a heterozygous (affected) mother have the following risks:
| Unaffected father | |||
| x | y | ||
| Heterozygously affected mother | x | xx (unaffected female) | xy (unaffected male) |
| X | Xx (affected female) | Xy (affected male) | |
Children of a hemizygous (unaffected) father and a homozygous (affected) mother have the following risks:
| Unaffected father | |||
| x | y | ||
| Homozygously affected mother | X | Xx (affected female) | Xy (affected male) |
| X | Xx (affected female) | Xy (affected male) | |
Children of a hemizygous (affected) father and a heterozygous (affected) mother have the following risks:
| Hemizygously affected father | |||
| X | y | ||
| Heterozygously affected mother | X | XX (affected female) | Xy (affected male) |
| x | Xx (affected female) | xy (unaffected male) | |
Children of a hemizygous (affected) father and a homozygous (unaffected) mother have the following risks:
| Hemizygously affected father | |||
| X | y | ||
| Unaffected mother | x | Xx (affected female) | xy (unaffected male) |
| x | Xx (affected female) | xy (unaffected male) | |
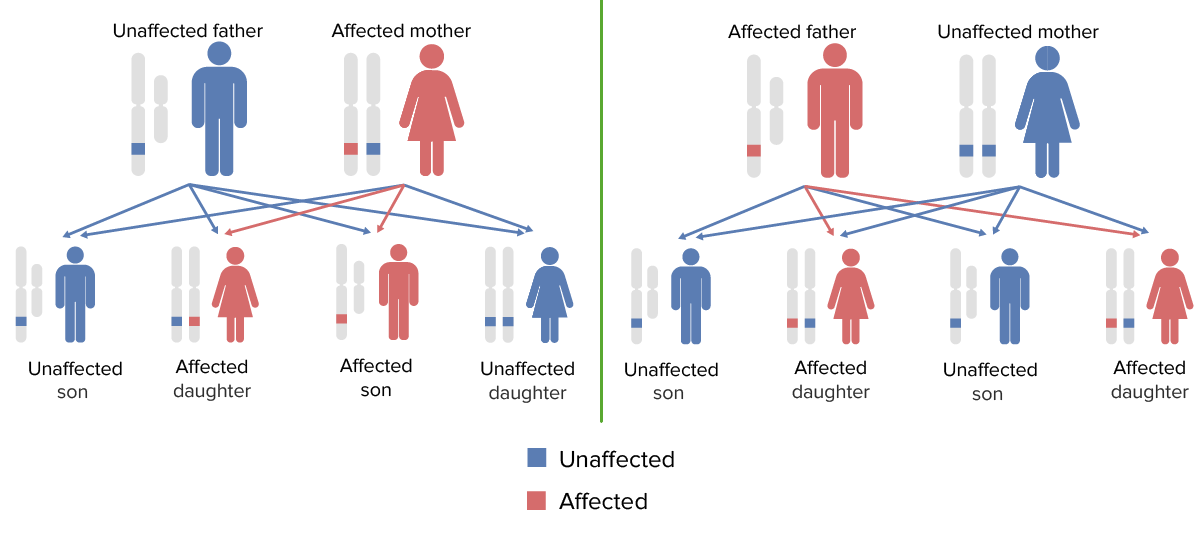
Patterns of X-linked dominant inheritance (a very rare mode of inheritance):
Males and females have an equal probability of expressing the trait.
Note: Some X-linked dominant disorders are embryonic lethal in males; most affect females less severely.