Septic arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis is an infection of the joint due to direct inoculation, contiguous extension Extension Examination of the Upper Limbs, or hematogenous Hematogenous Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases spread of infectious organisms into the joint space. This process causes an acute, inflammatory, monoarticular arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis. A variety of organisms have been implicated, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess. Previously damaged joints (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis) are at the highest risk of infection. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with a swollen, warm, and tender joint, most commonly involving the knee. Positive cultures from arthrocentesis are diagnostic, with antibiotic therapy tailored to the specific organism. Repeated joint aspiration, or surgical drainage, is required in some cases. If the joint space is infected with a prosthetic in place, debridement Debridement The removal of foreign material and devitalized or contaminated tissue from or adjacent to a traumatic or infected lesion until surrounding healthy tissue is exposed. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and prosthesis removal may also be required.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The majority of septic arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are monomicrobial. Common organisms include:
| Risk factors | Infectious agents |
|---|---|
| No specific risk factor | S. aureus S. aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Staphylococcus |
| Prosthetic joint replacement |
|
| Chronic disease, autoimmune disorder, skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions infection, trauma, elderly | S. pyogenes (group A beta-hemolytic strep) |
| Young, sexually active | N. gonorrhoeae N. gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria |
| Trauma | S. epidermidis S. epidermidis A species of staphylococcus that is a spherical, non-motile, gram-positive, chemoorganotrophic, facultative anaerobe. Mainly found on the skin and mucous membrane of warm-blooded animals, it can be primary pathogen or secondary invader. Staphylococcus |
| Sickle cell anemia Sickle cell anemia A disease characterized by chronic hemolytic anemia, episodic painful crises, and pathologic involvement of many organs. It is the clinical expression of homozygosity for hemoglobin S. Sickle Cell Disease |
|
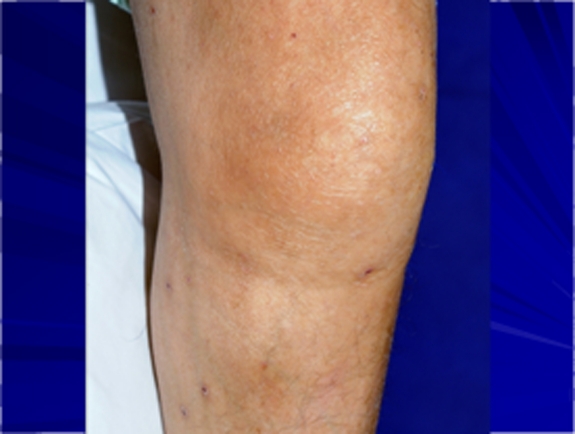
Knee swelling and mild erythema in a patient with septic arthritis
Image: “Troublesome Tuberculosis: A Case Report on Multi-focal Tuberculous Osteomyelitis in An Immunocompetent Patient” by Lynn MM, Kukanesen JR, Khan AW. License: CC BY 2.0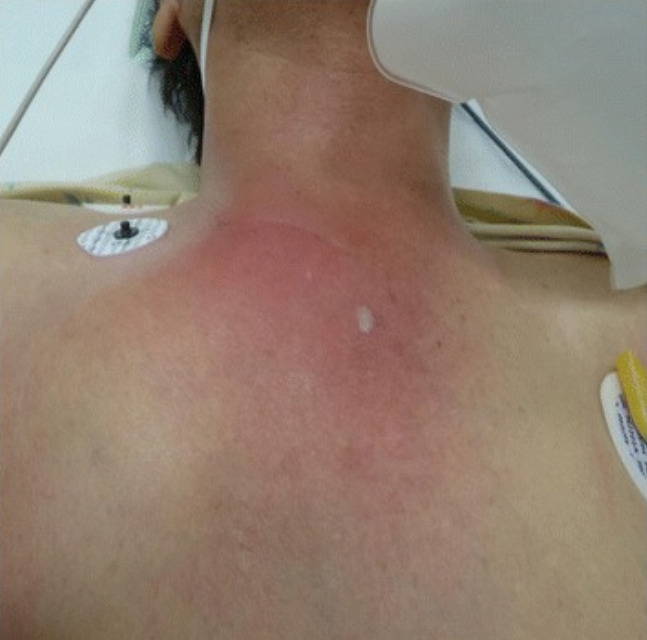
Significant erythema and swelling over the right sternoclavicular joint, which is concerning for septic arthritis
Image: “Sternoclavicular joint septic arthritis with chest wall abscess in a healthy adult: a case report” by Tanaka Y, Kato H, Shirai K, Nakajima Y, Yamada N, Okada H, Yoshida T, Toyoda I, Ogura S. License: CC BY 4.0The diagnosis of septic arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis is made with synovial fluid analysis Synovial Fluid Analysis Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Laboratory studies that support the diagnosis:

X-ray showing soft-tissue swelling of the right ankle in an 8-month-old patient with septic arthritis
Image: “Polyarticular Septic Arthritis Caused by Haemophilus influenzae Serotype f in an 8-Month-Old Immunocompetent Infant: A Case Report and Review of the Literature” by Ali RA, Kaplan SL, Rosenfeld SB. License: CC BY 3.0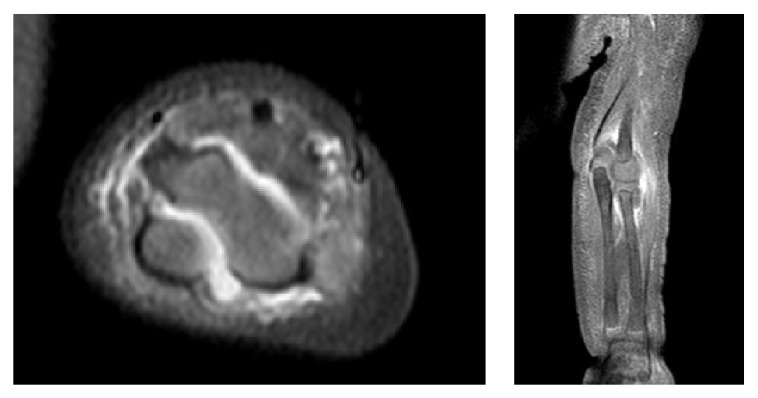
MRI showing a large effusion between the humerus and olecranon process in a pediatric patient with septic arthritis
Image: “Polyarticular Septic Arthritis Caused by Haemophilus influenzae Serotype f in an 8-Month-Old Immunocompetent Infant: A Case Report and Review of the Literature” by Ali RA, Kaplan SL, Rosenfeld SB. License: CC BY 3.0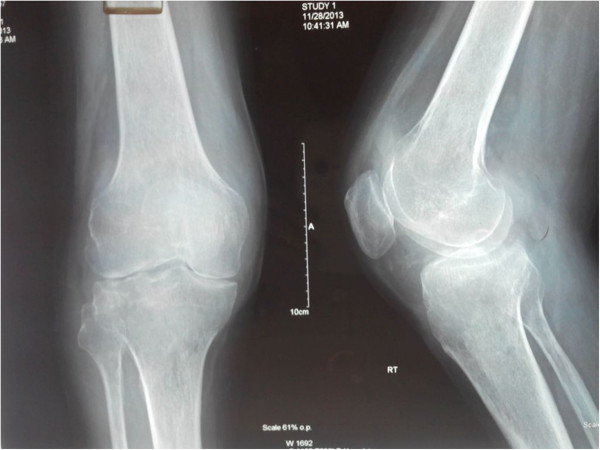
X-ray of the knee demonstrating mild periarticular osteopenia and significant joint-space narrowing in a patient with septic arthritis
Image: “Disseminated Aspergillus flavus following septic arthritis in an immunocompetent patient: a case report” by Tiwari V, Khatri K, Khan SA, Nath D. License: CC BY 4.0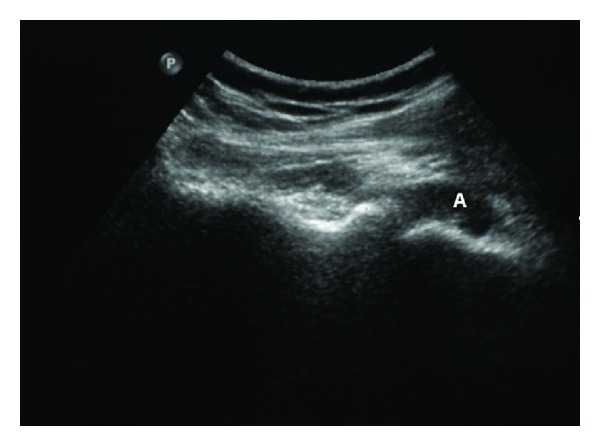
Ultrasound of the right shoulder glenohumeral articulation showing a distended posterior aspect of joint capsule by fluid (A) in a patient with septic arthritis
Image: “Streptococcus agalactiae Septic Arthritis of the Shoulder and the Sacroiliac Joints: A Case Report” by Imam YZ, Sarakbi HA, Abdelwahab N, Mattar I. License: CC BY 3.0Antibiotic selection Selection Lymphocyte activation by a specific antigen thus triggering clonal expansion of lymphocytes already capable of mounting an immune response to the antigen. B cells: Types and Functions is based on the initial Gram stain Gram stain Klebsiella and tailored based on culture data.
Duration of therapy depends on additional factors:
Joint drainage:
Surgical debridement Debridement The removal of foreign material and devitalized or contaminated tissue from or adjacent to a traumatic or infected lesion until surrounding healthy tissue is exposed. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with prosthesis: