Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis Sclerosis A pathological process consisting of hardening or fibrosis of an anatomical structure, often a vessel or a nerve. Wilms Tumor) is an autoimmune condition characterized by diffuse collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology deposition and fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans. The clinical presentation varies from limited skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions involvement to diffuse involvement of internal organs. Diagnosis is established by a combination of physical findings and serology Serology The study of serum, especially of antigen-antibody reactions in vitro. Yellow Fever Virus. There is no curative treatment. Management options are limited and include immunosuppressive medications as well as specific organ- or symptom-directed drugs. The overall 5-year survival of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with scleroderma is about 80%.
Last updated: Mar 28, 2025
Scleroderma, also known as systemic sclerosis Sclerosis A pathological process consisting of hardening or fibrosis of an anatomical structure, often a vessel or a nerve. Wilms Tumor (SS), is an autoimmune disorder Autoimmune Disorder Septic Arthritis in which there is progressive deposition of collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology in the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions and internal organs causing tightening and fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans.
Diffuse and limited cutaneous SS:
Diffuse forms with or without cutaneous involvement Cutaneous involvement Coccidioides/Coccidioidomycosis:
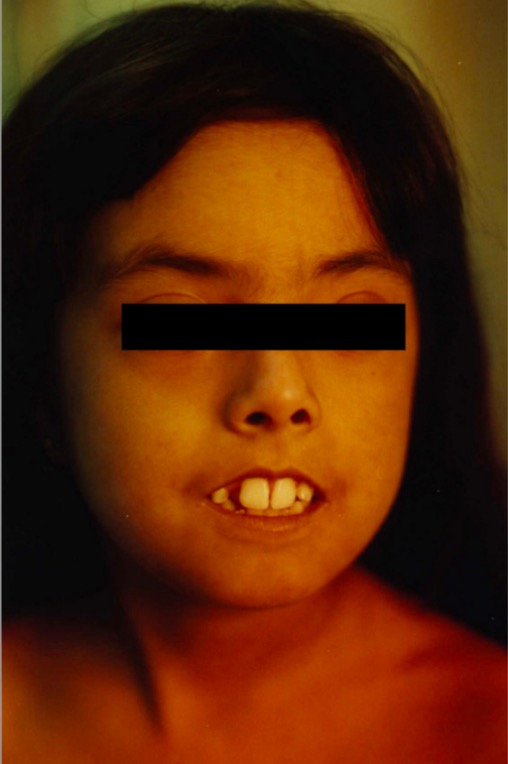
Perioral skin tightening of scleroderma
The patient is unable to close her lips.
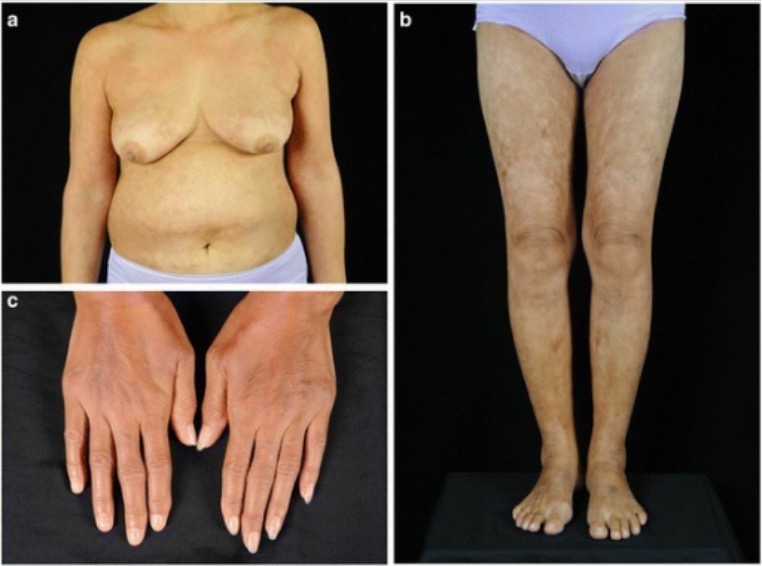
Skin changes noted in SS
a and b: widespread reticulate hyperpigmentation over the trunk and extremities with discrete erythematous indurated plaques over the chest wall and anterior abdomen
c: sclerodactyly with cool periphery of all fingers
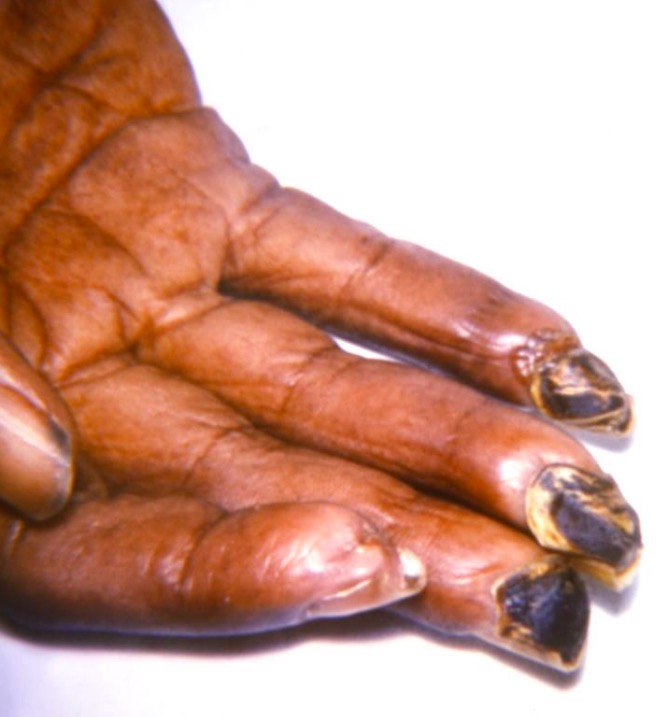
Hand of a scleroderma patient (tight, shiny appearance of the palmar skin)
The fingertips have become gangrenous secondary to ischemia because of arterial vasoconstriction (Raynaud’s phenomenon).
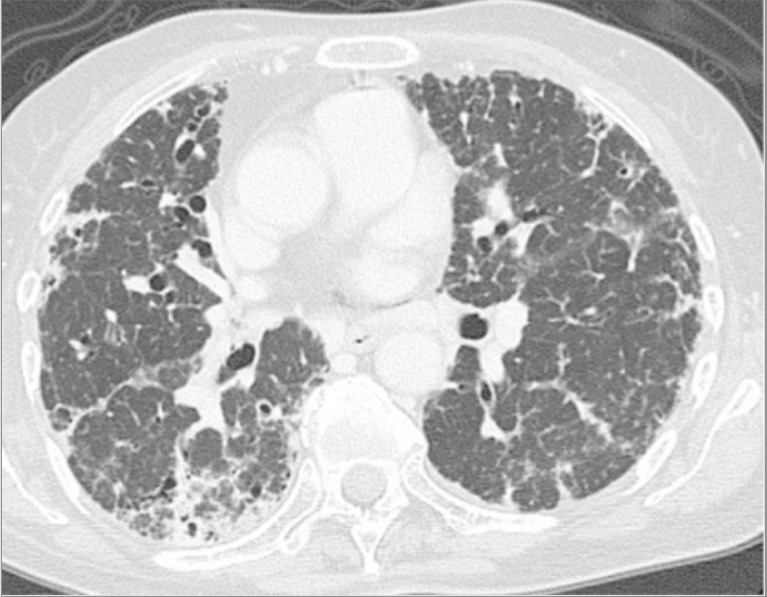
Chest CT scan showing lung fibrosis at the time of diagnosis of progressive systemic sclerosis
Image: “Chest computed tomography scan” by Division of Respiratory Medicine, Mito Medical Center, University of Tsukuba, Mito, Ibaraki 310-0015, Japan. License: CC BY 3.0There is no curative treatment for SS.