Rubella (also known as German measles Measles Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It is highly contagious and spreads by respiratory droplets or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular rash. Measles Virus or three-day measles Measles Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It is highly contagious and spreads by respiratory droplets or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular rash. Measles Virus) is caused by a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology of the Matonaviridae family and the Rubivirus genus. Rubella only infects humans and spreads prenatally via vertical transmission Vertical transmission The transmission of infectious disease or pathogens from one generation to another. It includes transmission in utero or intrapartum by exposure to blood and secretions, and postpartum exposure via breastfeeding. Congenital TORCH Infections or postnatally via droplet contact. Congenital Congenital Chorioretinitis rubella is particularly devastating and is associated with a classic triad of symptoms: cataracts, cardiac defects, and deafness. Infection in children and adults may be mild and present with constitutional symptoms Constitutional Symptoms Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis along with a viral exanthem Exanthem Diseases in which skin eruptions or rashes are a prominent manifestation. Classically, six such diseases were described with similar rashes; they were numbered in the order in which they were reported. Only the fourth (Duke's disease), fifth (erythema infectiosum), and sixth (exanthema subitum) numeric designations survive as occasional synonyms in current terminology. Varicella-Zoster Virus/Chickenpox resembling the measles Measles Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It is highly contagious and spreads by respiratory droplets or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular rash. Measles Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology. Diagnosis is made clinically and confirmed with serum virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology detection and serologic studies. Treatment is supportive and may be targeted depending on the organ system involved. Prevention is achieved through childhood vaccination Vaccination Vaccination is the administration of a substance to induce the immune system to develop protection against a disease. Unlike passive immunization, which involves the administration of pre-performed antibodies, active immunization constitutes the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies. Vaccination with the measles Measles Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It is highly contagious and spreads by respiratory droplets or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular rash. Measles Virus, mumps Mumps Mumps is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. Mumps is typically a disease of childhood, which manifests initially with fever, muscle pain, headache, poor appetite, and a general feeling of malaise, and is classically followed by parotitis. Mumps Virus/Mumps, and rubella ( MMR MMR A DNA repair pathway involved in correction of errors introduced during DNA replication when an incorrect base, which cannot form hydrogen bonds with the corresponding base in the parent strand, is incorporated into the daughter strand. Excinucleases recognize the base pair mismatch and cause a segment of polynucleotide chain to be excised from the daughter strand, thereby removing the mismatched base. Lynch syndrome) vaccine Vaccine Suspensions of killed or attenuated microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa), antigenic proteins, synthetic constructs, or other bio-molecular derivatives, administered for the prevention, amelioration, or treatment of infectious and other diseases. Vaccination.
Last updated: Dec 12, 2023

RNA virus identification:
Viruses can be classified in many ways. Most viruses, however, will have a genome formed by either DNA or RNA. RNA genome viruses can be further characterized by either a single- or double-stranded RNA. “Enveloped” viruses are covered by a thin coat of cell membrane (usually taken from the host cell). If the coat is absent, the viruses are called “naked” viruses. Viruses with single-stranded genomes are “positive-sense” viruses if the genome is directly employed as messenger RNA (mRNA), which is translated into proteins. “Negative-sense,” single-stranded viruses employ RNA dependent RNA polymerase, a viral enzyme, to transcribe their genome into messenger RNA.
Structure:
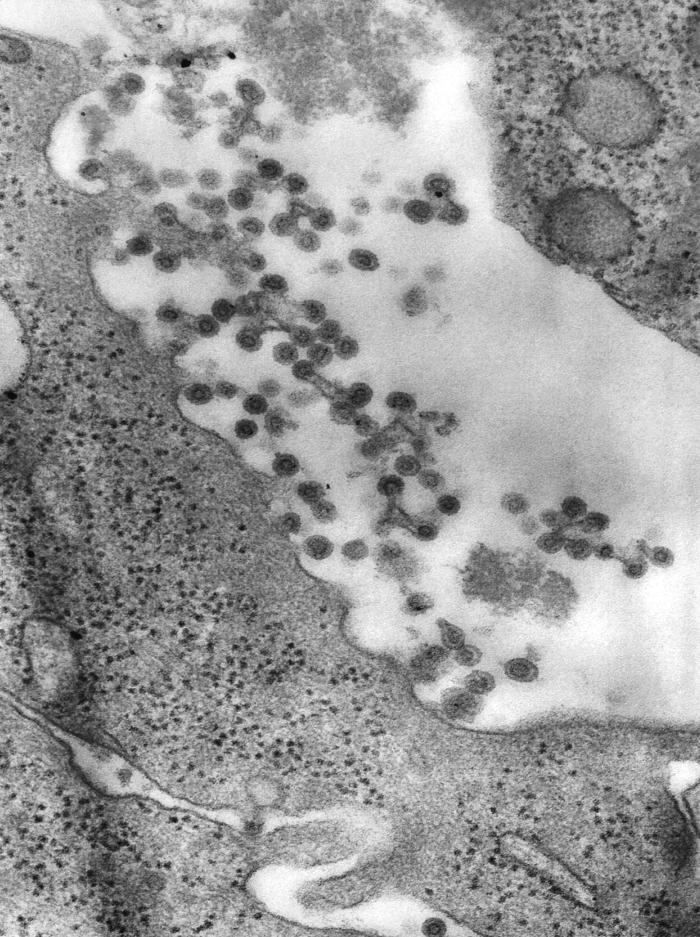
Electron micrograph of virions of the rubella virus
Image: “This transmission electron microscopic (TEM) image revealed the presence of rubella virus virions” by CDC. License: Public DomainPrenatal:
Postnatal:
Postnatal primary infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease with rubella undergo a sequential Sequential Computed Tomography (CT) pathogenic process:
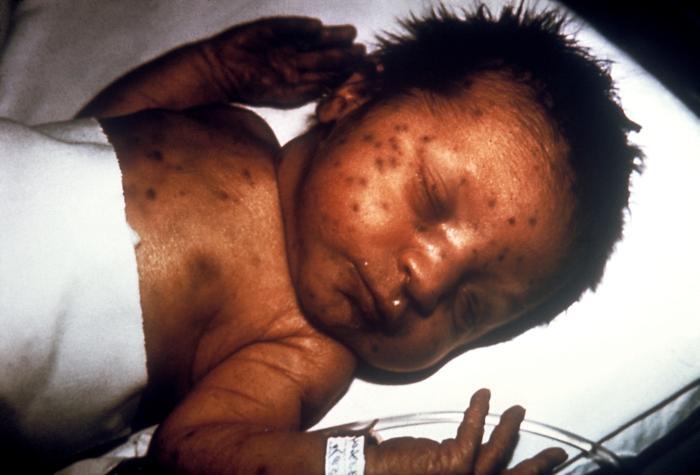
Infant with a “blueberry muffin rash” from congenital rubella
Image: “Infant presented with ‘blueberry muffin’ skin lesions indicative of congenital rubella” by CDC. License: Public Domain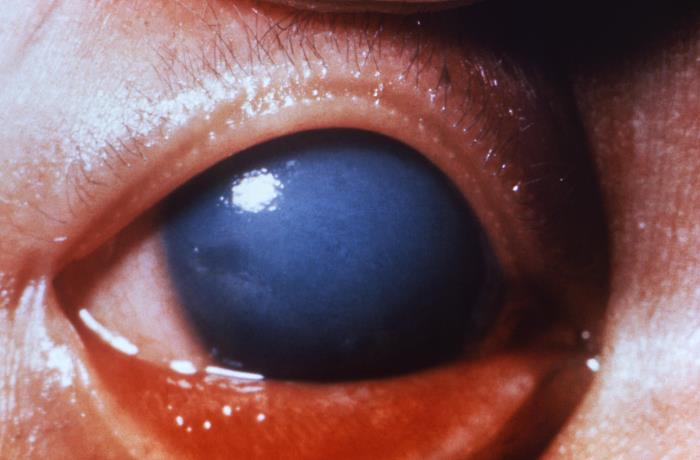
Congenital glaucoma in an infant due to congenital rubella
Image: “This image depicts a close view of the right eye of a 3-year-old infant, who exhibited symptoms of a condition known as congenital glaucoma, due to a case of congenital rubella.” by CDC. License: Public Domain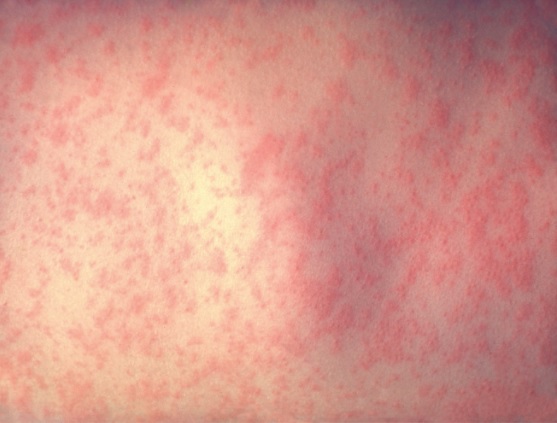
Typical exanthem of rubella infection:
Spread and distribution are similar to measles, however, the lesions are less intensely red and less confluent.
Diagnosis is made clinically and confirmed with serum virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology detection and serologic studies.
Treatment is supportive and targeted based on the organ system involved. Prevention is achieved through MMR MMR A DNA repair pathway involved in correction of errors introduced during DNA replication when an incorrect base, which cannot form hydrogen bonds with the corresponding base in the parent strand, is incorporated into the daughter strand. Excinucleases recognize the base pair mismatch and cause a segment of polynucleotide chain to be excised from the daughter strand, thereby removing the mismatched base. Lynch syndrome or MMRV ( measles Measles Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It is highly contagious and spreads by respiratory droplets or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular rash. Measles Virus, mumps Mumps Mumps is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. Mumps is typically a disease of childhood, which manifests initially with fever, muscle pain, headache, poor appetite, and a general feeling of malaise, and is classically followed by parotitis. Mumps Virus/Mumps, rubella, varicella) vaccination Vaccination Vaccination is the administration of a substance to induce the immune system to develop protection against a disease. Unlike passive immunization, which involves the administration of pre-performed antibodies, active immunization constitutes the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies. Vaccination.
| Number | Other names for the disease | Etiology | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st disease 1st disease Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It is highly contagious and spreads by respiratory droplets or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular rash. Measles Virus |
|
Measles Measles Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It is highly contagious and spreads by respiratory droplets or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular rash. Measles Virus morbillivirus Morbillivirus A genus of the family paramyxoviridae (subfamily paramyxovirinae) where the virions of most members have hemagglutinin but not neuraminidase activity. All members produce both cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies. Measles virus is the type species. Measles Virus |
|
| 2nd disease |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
| 3rd disease |
|
Rubella virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology |
|
| 4th disease |
|
Due to Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess strains that make epidermolytic (exfoliative) toxin |
|
| 5th disease | Erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion infectiosum | Erythrovirus or parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or “slapped cheek syndrome.” Parvovirus B19 (Primate erythroparvovirus Erythroparvovirus Parvovirus B19 1) |
|
| 6th disease |
|
Human herpesvirus 6B or 7 |
|