Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory disease of the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions that is associated with capillary hyperreactivity. This condition is predominantly seen in middle-aged women, and is more common in fair-skinned patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may have facial erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion, flushing, telangiectasia Telangiectasia Permanent dilation of preexisting blood vessels creating small focal red lesions, most commonly in the skin or mucous membranes. It is characterized by the prominence of skin blood vessels, such as vascular spiders. Chronic Venous Insufficiency, papules, pustules, phymatous changes, and ocular manifestations. The diagnosis is clinical. Management includes avoidance of triggers Triggers Hereditary Angioedema (C1 Esterase Inhibitor Deficiency), gentle skincare, topical (and/or oral) antibiotics, and laser (or surgical) therapies.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The exact etiology is not understood, but the following may be associated with rosacea:
The precise mechanism is unknown. There are 2 proposed theories:
Rosacea may present as 1 of 4 clinical subtypes. These subtypes are not mutually exclusive, and patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may have features of multiple subtypes with varying symptoms over time.
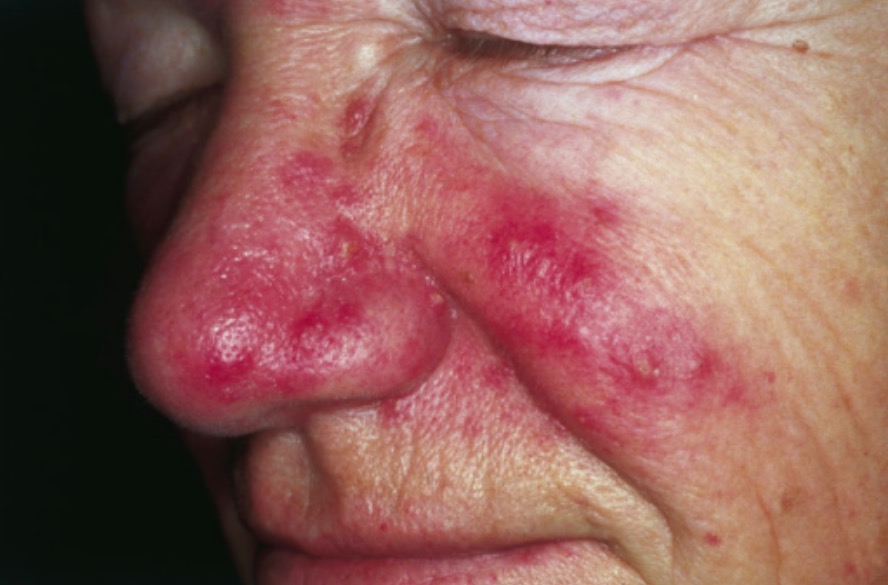
Cutaneous findings of rosacea:
Erythema and telangiectasia are seen over the cheeks, nasolabial area, and nose. Inflammatory papules and pustules can be observed over the nose. The absence of comedones is a helpful tool to distinguish rosacea from acne vulgaris.
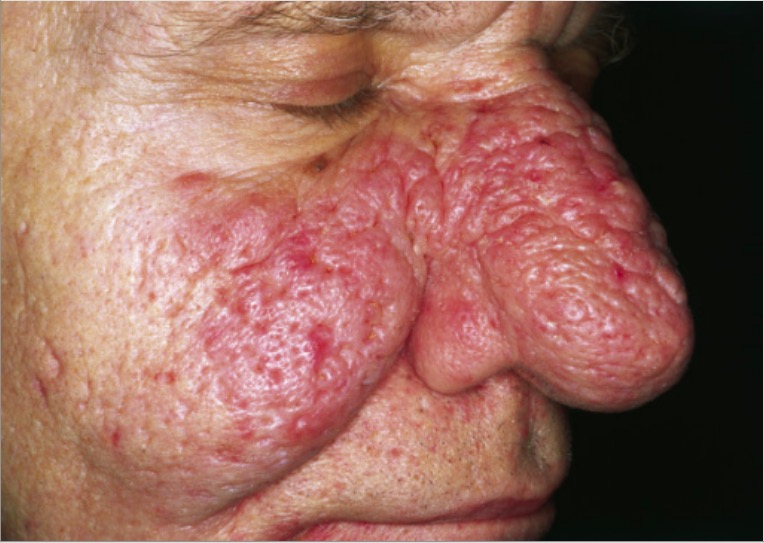
Rhinophyma as a manifestation of rosacea:
An enlarged, bulbous nose is seen due to skin and sebaceous gland thickening resulting in nodular skin contours.
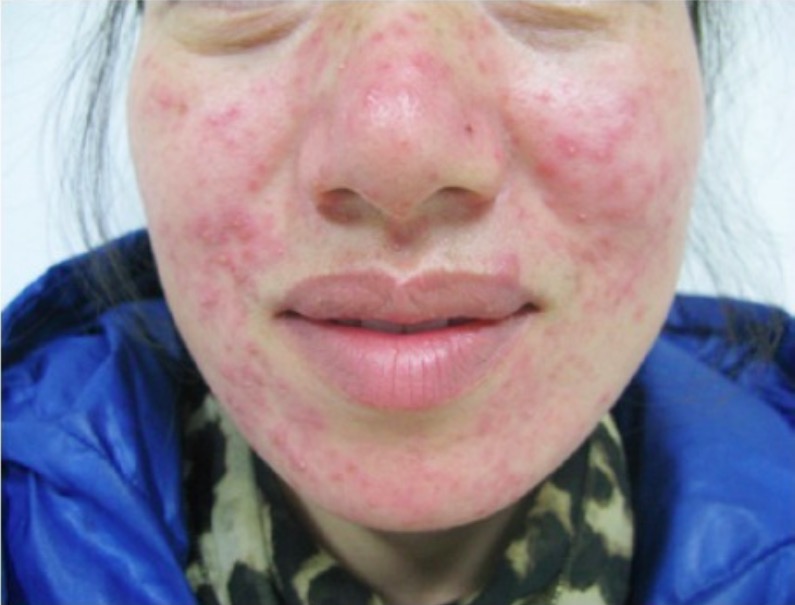
Cutaneous findings of papulopustular rosacea:
Erythema, papules, and pustules are seen on the face.
Rosacea is a clinical diagnosis.
Diagnostic criteria (National Rosacea Society Expert Committee):