Rocky Mountain spotted fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever (RMSF) is a bacterial infection caused by the obligate intracellular parasite Rickettsia rickettsii Rickettsia rickettsii A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria that is the etiologic agent of rocky mountain spotted fever. Its cells are slightly smaller and more uniform in size than those of rickettsia prowazekii. Rickettsia. Transmission occurs through an arthropod vector, most commonly the American dog tick ( Dermacentor Dermacentor A widely distributed genus of ticks, in the family ixodidae, including a number that infest humans and other mammals. Several are vectors of diseases such as tularemia; rocky mountain spotted fever; colorado tick fever; and anaplasmosis. Rickettsia variabilis). Rocky Mountain spotted fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever is prevalent in the southeastern United States. Early signs and symptoms of RMSF are nonspecific and include a high fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, severe headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess, and rash. The rash is characteristic in that it begins peripherally and moves centrally, and also appears on the hands and soles. A high clinical suspicion is required for diagnosis, and empiric treatment with doxycycline is recommended within 5 days of symptom onset.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Rocky Mountain spotted fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever (RMSF) is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology Rickettsia rickettsii Rickettsia rickettsii A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria that is the etiologic agent of rocky mountain spotted fever. Its cells are slightly smaller and more uniform in size than those of rickettsia prowazekii. Rickettsia, which is usually transmitted by ticks Ticks Blood-sucking acarid parasites of the order ixodida comprising two families: the softbacked ticks (argasidae) and hardbacked ticks (ixodidae). Ticks are larger than their relatives, the mites. They penetrate the skin of their host by means of highly specialized, hooked mouth parts and feed on its blood. Ticks attack all groups of terrestrial vertebrates. In humans they are responsible for many tick-borne diseases, including the transmission of rocky mountain spotted fever; tularemia; babesiosis; african swine fever; and relapsing fever. Coxiella/Q Fever.
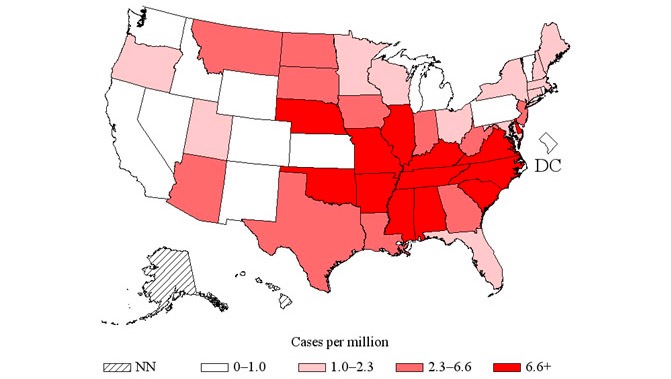
Distribution of spotted fever rickettsiosis in the United States, of which RMSF is a type, 2014
Image: “US distribution of spotted fever rickettsiosis” by CDC. License: Public Domain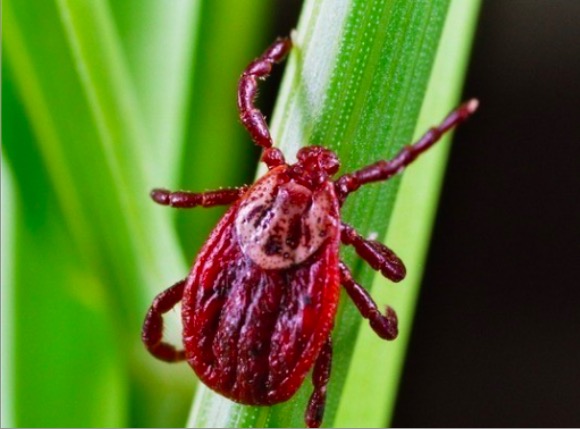
Adult Dermacentor tick
Image: “Adult Dermacentor spp. tick” by Center for Infectious Diseases and Travel Medicine, University Hospital Freiburg, Hugstetter Strasse, Germany. License: CC BY 2.0Symptoms usually occur within 2–14 days of exposure to an infected tick bite. Initial symptoms may be vague and non-specific ( fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, generalized malaise Malaise Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus). Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may not be aware of tick exposure.
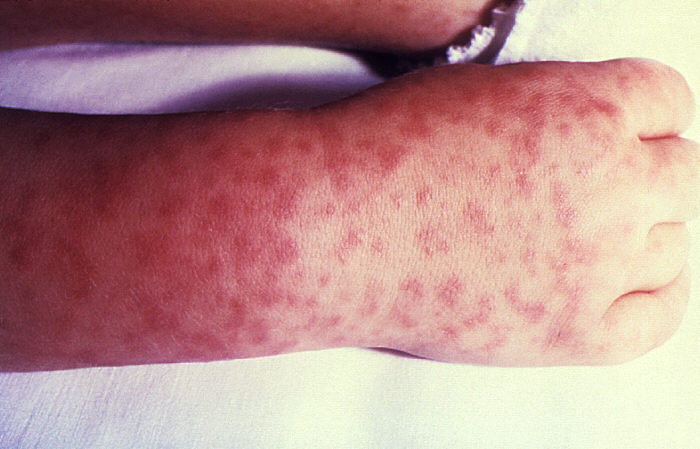
Classical RMSF rash, maculopapular and not sparing the soles and palms
Image: “Child’s right hand and wrist” by CDC. License: Public Domain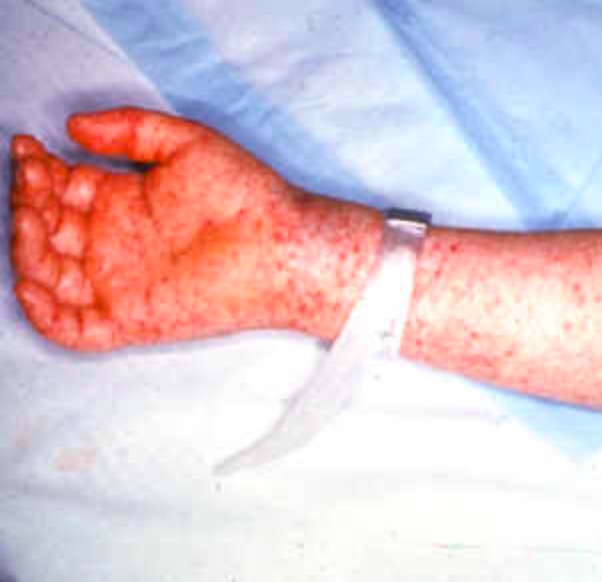
Classical RMSF rash, maculopapular and not sparing the soles and palms
Image: “Rocky mountain spotted fever” by CDC. License: Public DomainComplications of untreated infection may include:
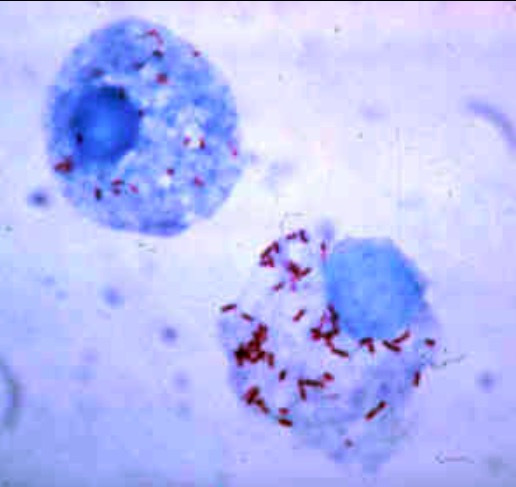
Giemsa-stained R. rickettsii in the cells of a tick
Image: “Gimenez stain” by CDC. License: Public Domain