The respiratory system is responsible for eliminating the volatile acid carbon dioxide (CO2), which is produced via aerobic metabolism. The body produces approximately 15,000 mmol of CO2 daily, which is the majority of daily acid production; the remainder of the daily acid load (only about 70 mmol of nonvolatile acids Nonvolatile acids Acid-Base Balance) is excreted through the kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy. When hyperventilation occurs, excess carbon dioxide is blown off and respiratory alkalosis develops. The kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy respond by decreasing serum bicarbonate Bicarbonate Inorganic salts that contain the -HCO3 radical. They are an important factor in determining the ph of the blood and the concentration of bicarbonate ions is regulated by the kidney. Levels in the blood are an index of the alkali reserve or buffering capacity. Electrolytes (HCO3–) through increased HCO3– excretion or decreased excretion of H+. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with an increased respiratory rate Respiratory rate The number of times an organism breathes with the lungs (respiration) per unit time, usually per minute. Pulmonary Examination, dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, light-headedness and potentially psychologic symptoms. Diagnosis involves a thorough history, an exam, and an arterial blood gas measurement. Management focuses on addressing the underlying abnormalities, stabilizing patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship in acute distress, and potentially a small dose of short-acting benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines work on the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor to produce inhibitory effects on the CNS. Benzodiazepines do not mimic GABA, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in humans, but instead potentiate GABA activity. Benzodiazepines.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Respiratory alkalosis refers to the process that results in a decreased level of carbon dioxide (CO2) within the blood.
| Etiology | Examples |
|---|---|
| Physiologic (not pathologic) |
|
| Hypoxia-induced |
|
| Medications |
|
| Intracranial processes |
|
| Psychologic etiologies |
|
| Other processes |
|
Acid–base disorders are classified according to the primary disturbance (respiratory or metabolic) and the presence or absence of compensation Compensation Respiratory Acidosis.
Look at the pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance, PCO2 ( partial pressure Partial pressure The pressure that would be exerted by one component of a mixture of gases if it were present alone in a container. Gas Exchange of CO2), and HCO3– ( bicarbonate Bicarbonate Inorganic salts that contain the -HCO3 radical. They are an important factor in determining the ph of the blood and the concentration of bicarbonate ions is regulated by the kidney. Levels in the blood are an index of the alkali reserve or buffering capacity. Electrolytes) to determine the primary disturbance.
When acidosis Acidosis A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. Respiratory Acidosis or alkalosis develops, the body will try to compensate. Often, compensation Compensation Respiratory Acidosis will result in a normal pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance.
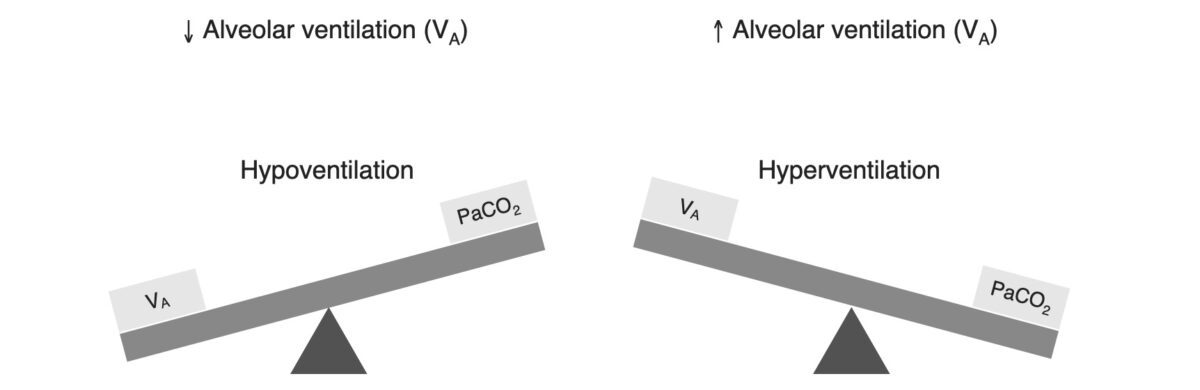
Relationship between alveolar ventilation and PCO2
Image by Lecturio.Respiratory alkalosis is a process that results in a decreased level of carbon dioxide.
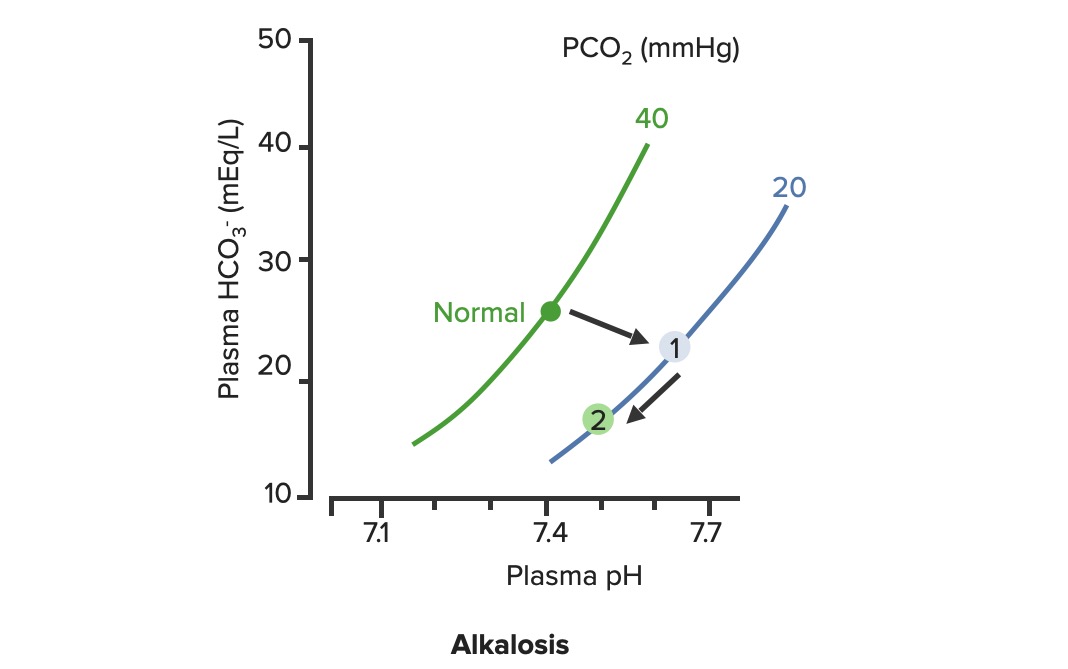
Renal compensation of respiratory alkalosis:
In respiratory alkalosis, the PCO2 is decreased, shifting the PCO2 curve to the right (1). As HCO3– levels are decreased by the kidneys, the pH improves along the PCO2 line (2)
Acute versus chronic respiratory alkalosis is defined by the degree of renal compensation Compensation Respiratory Acidosis.
Diagnosing a respiratory alkalosis typically requires a thorough history and exam and an arterial blood gas measurement.