The respiratory system is responsible for eliminating the volatile acid carbon dioxide (CO2), which is produced via aerobic metabolism. The body produces approximately 15,000 mmol of CO2 daily, which is the majority of daily acid production; the remainder of the daily acid load (only about 70 mmol of nonvolatile acids Nonvolatile acids Acid-Base Balance) is excreted through the kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy. In the setting of hypoventilation, this acid load is not adequately blown off, and respiratory acidosis occurs. Renal compensation Renal compensation Respiratory Alkalosis occurs after 3–5 days, as the kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy attempt to increase the serum bicarbonate Bicarbonate Inorganic salts that contain the -HCO3 radical. They are an important factor in determining the ph of the blood and the concentration of bicarbonate ions is regulated by the kidney. Levels in the blood are an index of the alkali reserve or buffering capacity. Electrolytes levels. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are often asymptomatic, or they may present with neuropsychiatric manifestations or mild dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea. Diagnosis is made with arterial blood gas Arterial blood gas Respiratory Alkalosis measurement. Management involves treating the underlying etiology, stabilizing the patient, and avoiding respiratory sedatives.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Respiratory acidosis is the process that results in an accumulation of carbon dioxide (CO2) due to abnormal gas exchange Gas exchange Human cells are primarily reliant on aerobic metabolism. The respiratory system is involved in pulmonary ventilation and external respiration, while the circulatory system is responsible for transport and internal respiration. Pulmonary ventilation (breathing) represents movement of air into and out of the lungs. External respiration, or gas exchange, is represented by the O2 and CO2 exchange between the lungs and the blood. Gas Exchange in the lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy. In primary respiratory acidosis, the arterial blood gas Arterial blood gas Respiratory Alkalosis will show:
Acid–base disorders are classified according to the primary disturbance (respiratory or metabolic) and the presence or absence of compensation.
Look at the pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance, PCO2 ( partial pressure Partial pressure The pressure that would be exerted by one component of a mixture of gases if it were present alone in a container. Gas Exchange of CO2), and HCO3– ( bicarbonate Bicarbonate Inorganic salts that contain the -HCO3 radical. They are an important factor in determining the ph of the blood and the concentration of bicarbonate ions is regulated by the kidney. Levels in the blood are an index of the alkali reserve or buffering capacity. Electrolytes) to determine the primary disturbance.
When acidosis or alkalosis Alkalosis A pathological condition that removes acid or adds base to the body fluids. Respiratory Alkalosis develops, the body will try to compensate. Often, compensation will result in a normal pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance.
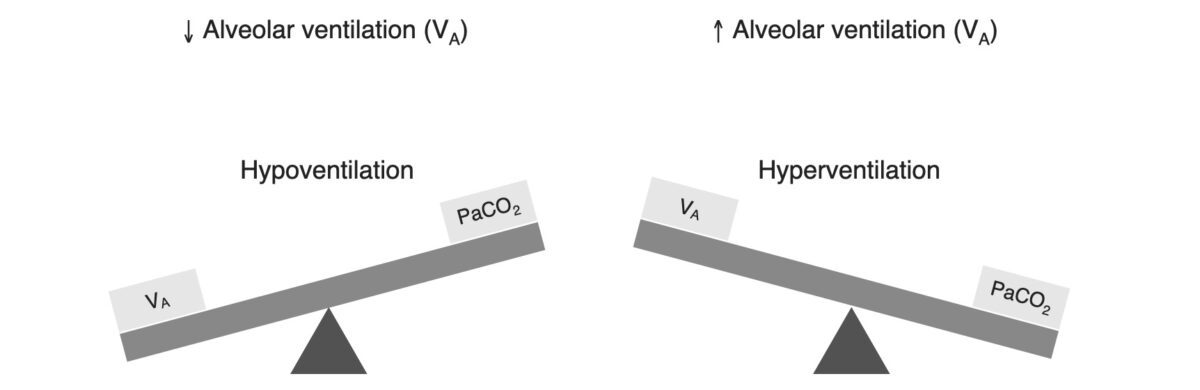
Relationship between alveolar ventilation and PCO2
Image by Lecturio.Respiratory acidosis occurs when the PCO2 is elevated.
| How is CO2 elimination Elimination The initial damage and destruction of tumor cells by innate and adaptive immunity. Completion of the phase means no cancer growth. Cancer Immunotherapy affected? | Disruption of CO2 elimination Elimination The initial damage and destruction of tumor cells by innate and adaptive immunity. Completion of the phase means no cancer growth. Cancer Immunotherapy is caused by disorders of the: |
|---|---|
| “Won’t breathe” | CNS |
| “Can’t breathe” |
|
| Abnormal gas exchange Gas exchange Human cells are primarily reliant on aerobic metabolism. The respiratory system is involved in pulmonary ventilation and external respiration, while the circulatory system is responsible for transport and internal respiration. Pulmonary ventilation (breathing) represents movement of air into and out of the lungs. External respiration, or gas exchange, is represented by the O2 and CO2 exchange between the lungs and the blood. Gas Exchange: “can’t breathe enough” | Lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy |
| Etiology | Examples |
|---|---|
| ↓ Respiratory rate Respiratory rate The number of times an organism breathes with the lungs (respiration) per unit time, usually per minute. Pulmonary Examination: ↓ respiratory drive |
|
| ↓ Tidal volume Tidal volume The volume of air inspired or expired during each normal, quiet respiratory cycle. Common abbreviations are tv or V with subscript t. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing: impaired ability to fully expand the lungs Lungs Lungs are the main organs of the respiratory system. Lungs are paired viscera located in the thoracic cavity and are composed of spongy tissue. The primary function of the lungs is to oxygenate blood and eliminate CO2. Lungs: Anatomy |
|
| ↑ Alveolar dead space Dead space That part of the respiratory tract or the air within the respiratory tract that does not exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with pulmonary capillary blood. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing: impaired ability for gas exchange Gas exchange Human cells are primarily reliant on aerobic metabolism. The respiratory system is involved in pulmonary ventilation and external respiration, while the circulatory system is responsible for transport and internal respiration. Pulmonary ventilation (breathing) represents movement of air into and out of the lungs. External respiration, or gas exchange, is represented by the O2 and CO2 exchange between the lungs and the blood. Gas Exchange |
|
The kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy respond to respiratory acidosis by increasing serum HCO3–.
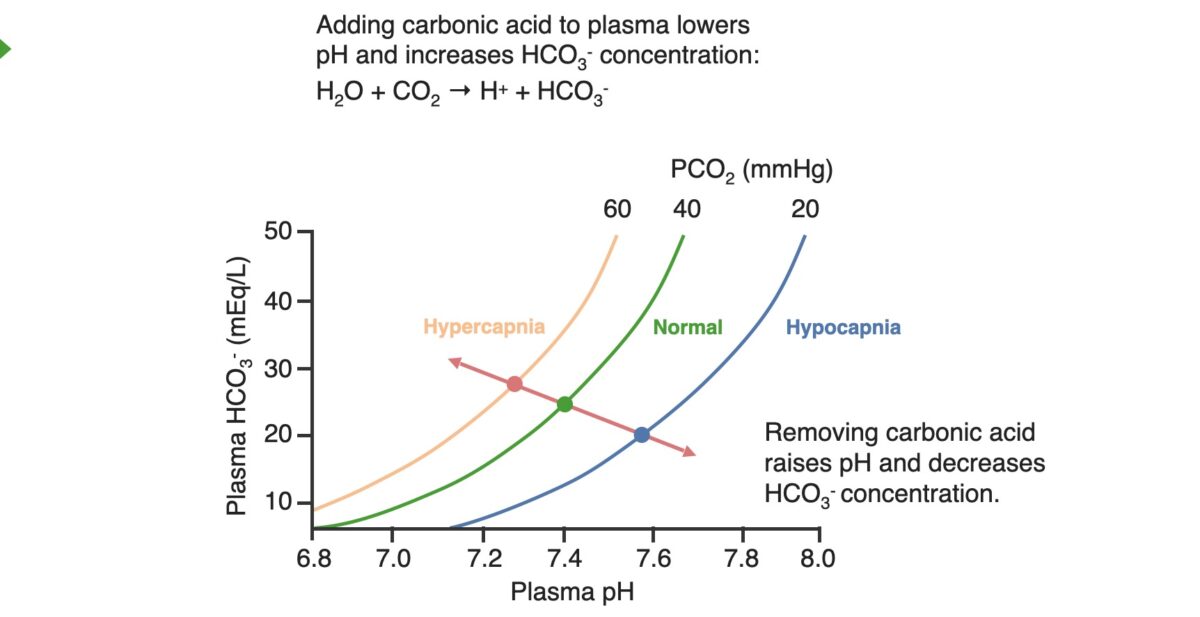
Acid–base diagram showing the relationship between the plasma pH, PCO2, and HCO3–:
The graph shows the shifts in respiratory acidosis (orange line) and respiratory alkalosis (blue line) in relation to normal levels (green line). In respiratory acidosis, patients will be on the orange line, with abnormally low pH levels; to compensate, the kidneys will add HCO3– to the system, causing a shift up and to the right along the orange line, raising the pH level.
In contrast, in respiratory alkalosis, patients will be on the blue line, with abnormally high pH levels; to compensate, the kidneys will remove HCO3– from the system, causing patients a shift down and to the right on the blue line, decreasing the pH level.
The red line is known as the blood-buffer line; the slope of this line represents the buffering power of the blood.
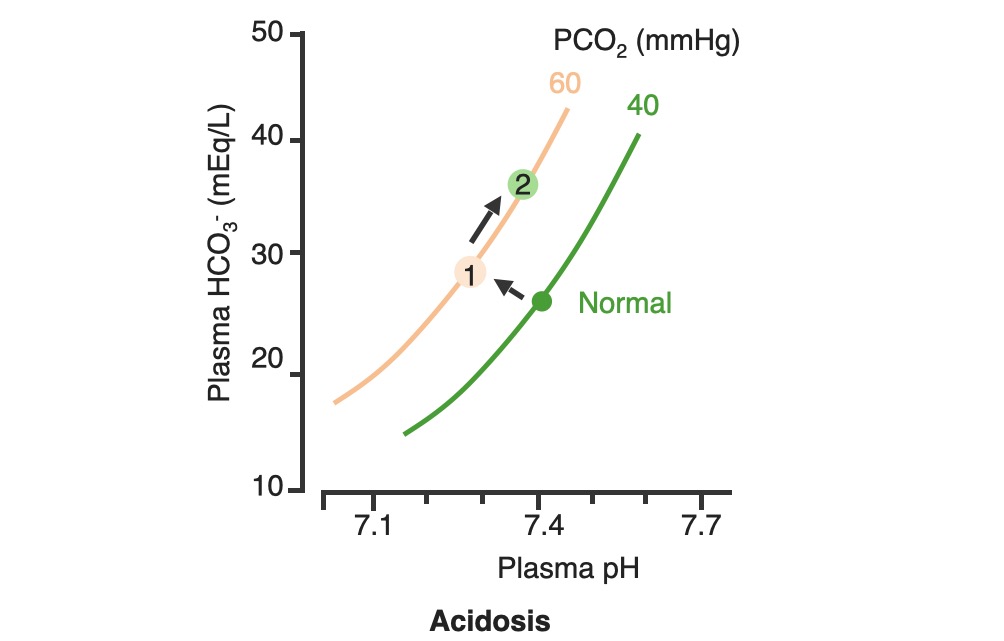
Renal compensation of respiratory acidosis:
In respiratory acidosis, the PCO2 is elevated, shifting the PCO2 curve to the left (1). As HCO3– levels are increased by the kidneys, the pH improves along the PCO2 line (2)
Acute versus chronic respiratory acidosis is defined by the degree of renal compensation Renal compensation Respiratory Alkalosis.
Diagnosing a respiratory acidosis typically requires an arterial blood gas Arterial blood gas Respiratory Alkalosis.