Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a tumor Tumor Inflammation that arises from the lining of the renal tubular system within the renal cortex. Renal cell carcinoma is responsible for 80%–85% of all primary renal neoplasms Neoplasms New abnormal growth of tissue. Malignant neoplasms show a greater degree of anaplasia and have the properties of invasion and metastasis, compared to benign neoplasms. Benign Bone Tumors. Most RCCs arise sporadically, but smoking Smoking Willful or deliberate act of inhaling and exhaling smoke from burning substances or agents held by hand. Interstitial Lung Diseases, hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, and obesity Obesity Obesity is a condition associated with excess body weight, specifically with the deposition of excessive adipose tissue. Obesity is considered a global epidemic. Major influences come from the western diet and sedentary lifestyles, but the exact mechanisms likely include a mixture of genetic and environmental factors. Obesity are linked to its development. The disease usually presents asymptomatically. When symptoms finally arise, the tumor Tumor Inflammation has already grown significantly and/or spread to other tissues. The classic clinical triad of RCC is flank pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, hematuria, and a palpable abdominal renal mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast, but this triad appears in only about 9% of cases. Affected individuals also commonly present with fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever and/or anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types. Renal cell carcinoma is usually diagnosed via CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 "hip" bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy. Localized cases of RCC are commonly treated and cured with surgery, and advanced cases are treated with a combination of immunotherapy and/or molecular targeted therapy Targeted Therapy Targeted therapy exerts antineoplastic activity against cancer cells by interfering with unique properties found in tumors or malignancies. The types of drugs can be small molecules, which are able to enter cells, or monoclonal antibodies, which have targets outside of or on the surface of cells. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy. The long-term prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas for locally advanced or metastatic RCC is often poor.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), also called hypernephroma and renal cell adenocarcinoma, is a type of cancer that originates from the lining of the small tubules of the renal cortex.
The difference between benign Benign Fibroadenoma and malignant masses in the kidney is determined by histologic criteria. According to the morphology, growth pattern, cell of origin, and histochemical and molecular basis, RCCs are classified into several types:
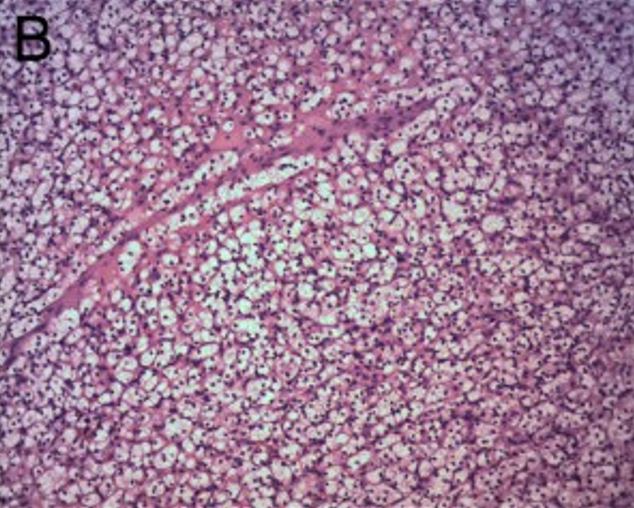
Renal clear cell carcinoma:
The tumor consists of sheet-like, solid clear cells. H&E × 100
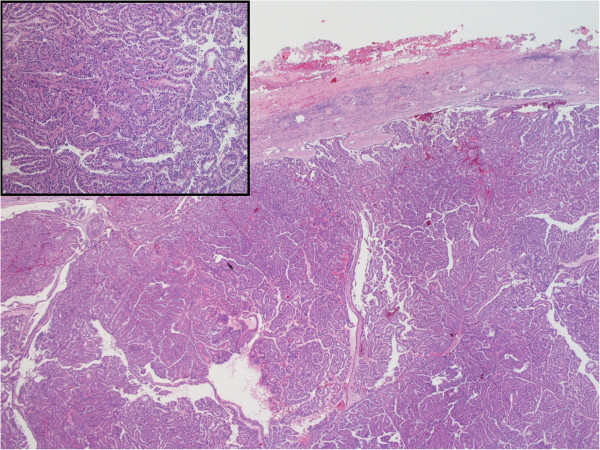
H&E-stained specimen showing characteristic histology of papillary renal cell carcinoma
Image: “Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of the tumor tissue showing characteristic histology of papillary renal cell carcinoma” by Alanee S, Dynda DI, Hemmer P, Schwartz B. License: CC BY 4.0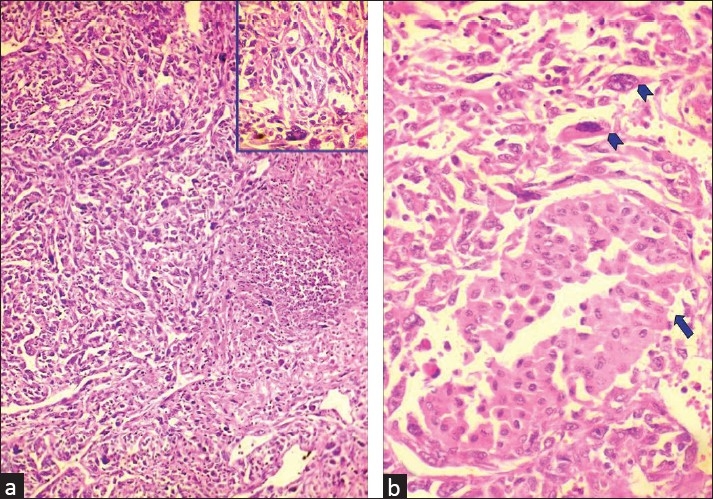
Sarcomatoid chromophobe renal cell carcinoma:
a. Microphotograph demonstrating sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma with giant cell tumors and necrosis (H&E x 100) (inset shows giant cell tumor among pleomorphic cells (H&E x 400))
b. Microphotograph showing chromophobe renal cell carcinoma (arrow) admixed with sarcomatoid areas with bizarre cells and giant cells (arrowheads)
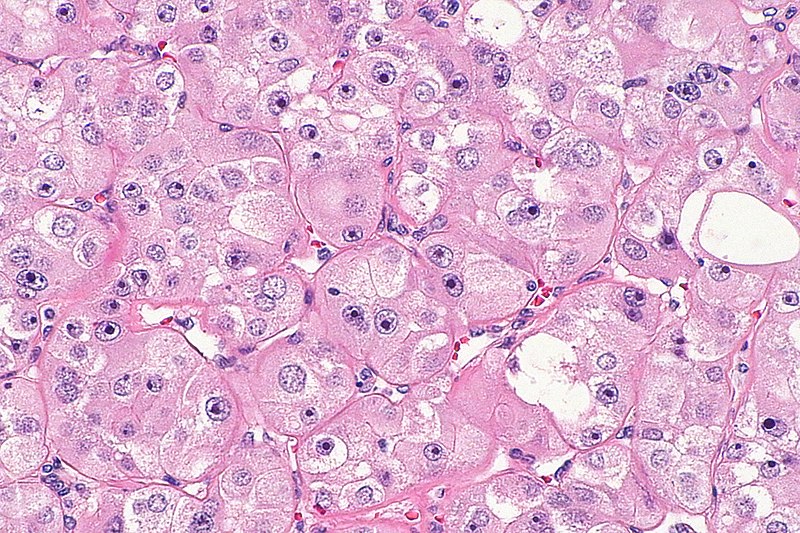
High-grade oncocytic renal tumor
Image: “High-grade oncocytic renal tumour — high mag” by Nephron. License: CC BY-SA 4.0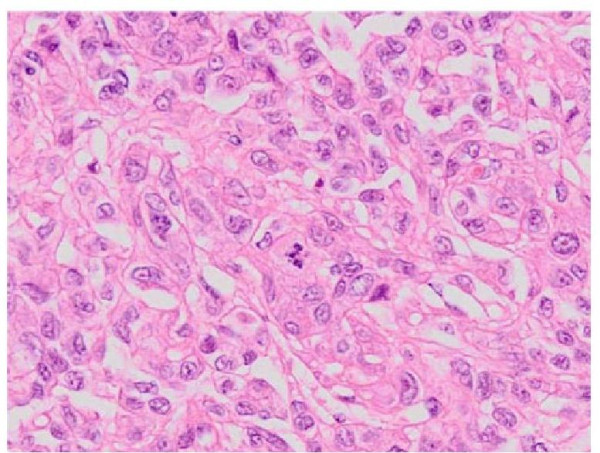
H&E-stained tissue sections demonstrating collecting duct carcinoma
Image: “Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue sections from the nephrectomy specimens demonstrating collecting duct carcinoma” by Tazi EM, Essadi I, Tazi MF, Ahellal Y, M’rabti H, Errihani H. License: CC BY 2.0Many cases present asymptomatically, leading to further progression of the diseases. Symptoms arise when the tumor Tumor Inflammation has reached a significant size, invaded adjacent structures, or developed distant metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis.
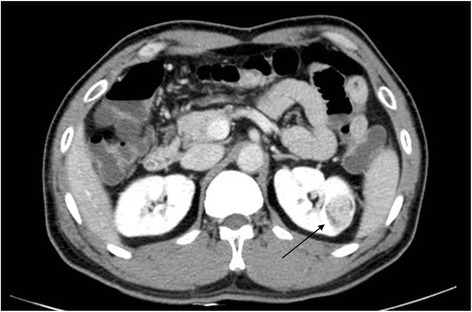
A CT scan showing renal cell carcinoma (arrow)
Image: “Fig1: CT scan of renal cell carcinoma (Arrow)” by June-Hee Lee et al. License: CC BY 4.0 CC BY 1.0RCCs vary greatly in the extent of disease at presentation.
| Stage | Definition | Subdivision |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor Tumor Inflammation stage | ||
| T0 | No evidence of primary tumor Tumor Inflammation | |
| T1 | < 7 cm in the greatest dimension, confined to the kidney |
|
| T2 | > 7 cm in the greatest dimension, confined to the kidney |
|
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Extends into major veins Veins Veins are tubular collections of cells, which transport deoxygenated blood and waste from the capillary beds back to the heart. Veins are classified into 3 types: small veins/venules, medium veins, and large veins. Each type contains 3 primary layers: tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia. Veins: Histology or perinephric tissues, but not into the adrenal gland or beyond the Gerota fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis (anterior perirenal fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis) |
|
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Invades beyond the Gerota fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis and/or into the adrenal gland | |
| Regional lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 – 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy | ||
| N0 | No metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis to regional lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 – 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy | |
| N1 | Metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis to regional lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 – 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy | |
| Distant metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis | ||
| M0 | No distant metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis | |
| M1 | Metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis to distant lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 – 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy and/or organs | |