In the human brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification, information is transmitted in the form of bioelectrical impulses and chemical signaling molecules Signaling molecules Second Messengers. These molecules, called neurotransmitters, are protein molecules used by neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology to emit a specific signal. The signals are picked up in the plasma membrane Plasma membrane A cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates the cell contents from the outside environment. A cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and proteins that function to protect cellular DNA and mediate the exchange of ions and molecules. The Cell: Cell Membrane of adjacent neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology by receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors, which are complexes of protein subunits responsible for sensing relevant stimuli and setting in motion the cellular machinery required to produce the desired response.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
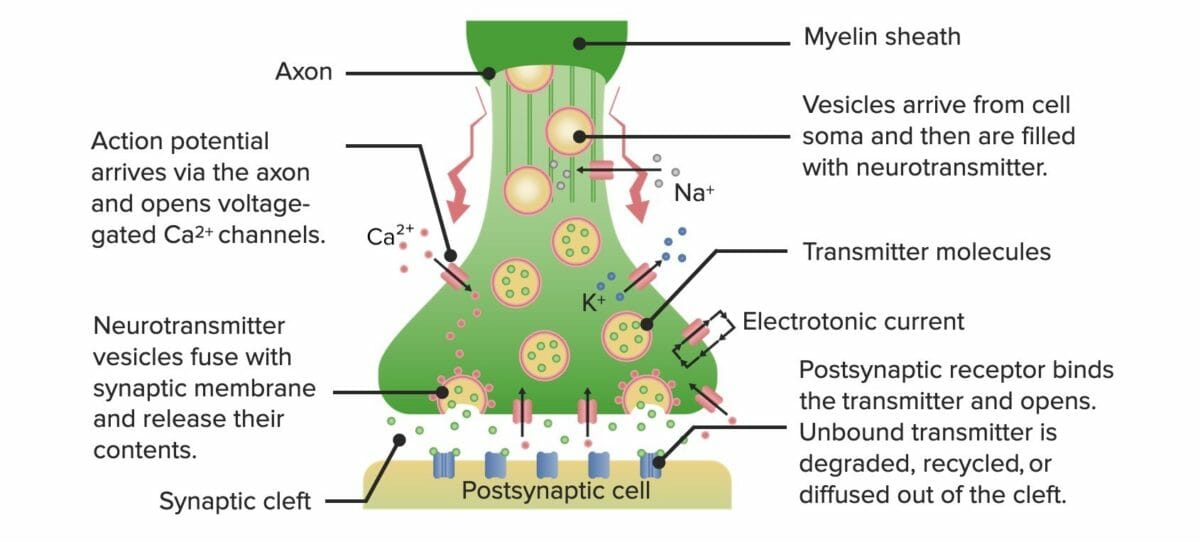
Diagram showcasing the process of neurotransmission
Image by Lecturio.More than 500 unique neurotransmitters have been identified in humans.
| Pathway | Neuron origin | Neuron projection location | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesolimbic | Ventral tegmental area |
|
|
| Mesocortical | Ventral tegmental area | Prefrontal cortex |
|
| Nigrostriatal | Substantia nigra Substantia nigra The black substance in the ventral midbrain or the nucleus of cells containing the black substance. These cells produce dopamine, an important neurotransmitter in regulation of the sensorimotor system and mood. The dark colored melanin is a by-product of dopamine synthesis. Basal Ganglia: Anatomy | Striatum Striatum Striped gray matter and white matter consisting of the neostriatum and paleostriatum (globus pallidus). It is located in front of and lateral to the thalamus in each cerebral hemisphere. The gray substance is made up of the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus (the latter consisting of the globus pallidus and putamen). The white matter is the internal capsule. Basal Ganglia: Anatomy | Locomotor control |
| Tuberoinfundibular | Arcuate nucleus Nucleus Within a eukaryotic cell, a membrane-limited body which contains chromosomes and one or more nucleoli (cell nucleolus). The nuclear membrane consists of a double unit-type membrane which is perforated by a number of pores; the outermost membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. A cell may contain more than one nucleus. The Cell: Organelles | Pituitary Pituitary A small, unpaired gland situated in the sella turcica. It is connected to the hypothalamus by a short stalk which is called the infundibulum. Hormones: Overview and Types gland | Inhibits prolactin Prolactin A lactogenic hormone secreted by the adenohypophysis. It is a polypeptide of approximately 23 kd. Besides its major action on lactation, in some species prolactin exerts effects on reproduction, maternal behavior, fat metabolism, immunomodulation and osmoregulation. Breasts: Anatomy secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies |
| Neurotransmitter | Effect | Site of synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) |
|---|---|---|
| Dopamine | Excitatory and inhibitory | CNS: substantia nigra Substantia nigra The black substance in the ventral midbrain or the nucleus of cells containing the black substance. These cells produce dopamine, an important neurotransmitter in regulation of the sensorimotor system and mood. The dark colored melanin is a by-product of dopamine synthesis. Basal Ganglia: Anatomy, ventral tegmental area, and others |
| Norepinephrine | Excitatory | CNS: locus Locus Specific regions that are mapped within a genome. Genetic loci are usually identified with a shorthand notation that indicates the chromosome number and the position of a specific band along the P or Q arm of the chromosome where they are found. For example the locus 6p21 is found within band 21 of the P-arm of chromosome 6. Many well known genetic loci are also known by common names that are associated with a genetic function or hereditary disease. Basic Terms of Genetics coeruleus, sympathetic nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification, and adrenal medulla Adrenal Medulla The inner portion of the adrenal gland. Derived from ectoderm, adrenal medulla consists mainly of chromaffin cells that produces and stores a number of neurotransmitters, mainly adrenaline (epinephrine) and norepinephrine. The activity of the adrenal medulla is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy |
| Epinephrine Epinephrine The active sympathomimetic hormone from the adrenal medulla. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- adrenergic systems, causes systemic vasoconstriction and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the heart, and dilates bronchi and cerebral vessels. Sympathomimetic Drugs | Excitatory | Adrenal medulla Adrenal Medulla The inner portion of the adrenal gland. Derived from ectoderm, adrenal medulla consists mainly of chromaffin cells that produces and stores a number of neurotransmitters, mainly adrenaline (epinephrine) and norepinephrine. The activity of the adrenal medulla is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy |
| Serotonin |
|
CNS: raphe Raphe Testicles: Anatomy nuclei and enterochromaffin cells |
| Histamine | Excitatory and inhibitory |
|
| Acetylcholine | Excitatory (usually) | Neuromuscular junctions, presympathetic synapses, and preganglionic sympathetic synapses |
| Glutamate Glutamate Derivatives of glutamic acid. Included under this heading are a broad variety of acid forms, salts, esters, and amides that contain the 2-aminopentanedioic acid structure. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids |
|
CNS: almost every part of the nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification |
| GABA |
|
CNS |
| Glycine Glycine A non-essential amino acid. It is found primarily in gelatin and silk fibroin and used therapeutically as a nutrient. It is also a fast inhibitory neurotransmitter. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids | Inhibitory | CNS: spinal cord Spinal cord The spinal cord is the major conduction pathway connecting the brain to the body; it is part of the CNS. In cross section, the spinal cord is divided into an H-shaped area of gray matter (consisting of synapsing neuronal cell bodies) and a surrounding area of white matter (consisting of ascending and descending tracts of myelinated axons). Spinal Cord: Anatomy, brainstem, and retina Retina The ten-layered nervous tissue membrane of the eye. It is continuous with the optic nerve and receives images of external objects and transmits visual impulses to the brain. Its outer surface is in contact with the choroid and the inner surface with the vitreous body. The outermost layer is pigmented, whereas the inner nine layers are transparent. Eye: Anatomy |
| Enkephalins | Inhibitory ( pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways) | CNS |
| Endorphins | Inhibitory | CNS and PNS |
| Neurokinins | GI tract: modulate motility Motility The motor activity of the gastrointestinal tract. Gastrointestinal Motility, fluid and electrolyte secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies | Intrinsic enteric neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology and extrinsic primary afferent Afferent Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology nerve fibers Nerve Fibers Slender processes of neurons, including the axons and their glial envelopes (myelin sheath). Nerve fibers conduct nerve impulses to and from the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology |
| Receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors | Location | Signaling effector (from 5-HT binding) | Secondary messengers | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1A |
|
Inhibits AC | ↓ cAMP cAMP An adenine nucleotide containing one phosphate group which is esterified to both the 3′- and 5′-positions of the sugar moiety. It is a second messenger and a key intracellular regulator, functioning as a mediator of activity for a number of hormones, including epinephrine, glucagon, and acth. Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors |
|
| 5-HT2A |
|
Activates PLC | ↑ IP3, DAG DAG Second Messengers, Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ |
|
| 5-HT2C |
|
|
↑ IP3, DAG DAG Second Messengers, Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ | Appetite |
| 5-HT3 |
|
Ligand-gated ion channel → influx of Na+, Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ | — |
|
| Receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors | Location | Signaling effector (from dopamine binding) | Involvement in the dopaminergic pathway | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 |
|
Activates AC | Mesocortical |
|
| D1 |
|
Activates AC | Peripheral |
|
| D2 |
|
Inhibits AC |
|
|
| D2 |
|
Inhibits AC | Peripheral |
|
| D3 |
|
Inhibits AC | Mesolimbic |
|
| D3 | Kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy | Inhibits AC | Peripheral | ↓ Renin Renin A highly specific (leu-leu) endopeptidase that generates angiotensin I from its precursor angiotensinogen, leading to a cascade of reactions which elevate blood pressure and increase sodium retention by the kidney in the renin-angiotensin system. Renal Sodium and Water Regulation secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies |
| Receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors | Location | Signaling effector ( glutamate Glutamate Derivatives of glutamic acid. Included under this heading are a broad variety of acid forms, salts, esters, and amides that contain the 2-aminopentanedioic acid structure. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids agonism) | Secondary messengers |
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agonism | Antagonism | ||||
| AMPA | CNS | Ionotropic → influx of Na+ → EPSP → expels Mg2+ from NMDA receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors | — | Fast EPSP | Conduction block |
| NMDA |
|
Ionotropic → EPSP from AMPA → Mg2+ is expelled → influx of Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ → further depolarization Depolarization Membrane Potential | — |
|
|
| mGlur group I | Autoreceptors on glutamatergic neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology | Activates PLC | ↑ IP3, DAG DAG Second Messengers, Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ | Clinical significance unknown | |
| mGlur group II | Inhibits AC | ↓ cAMP cAMP An adenine nucleotide containing one phosphate group which is esterified to both the 3′- and 5′-positions of the sugar moiety. It is a second messenger and a key intracellular regulator, functioning as a mediator of activity for a number of hormones, including epinephrine, glucagon, and acth. Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors | |||
| mGlur group III | Inhibits AC | ↓ cAMP cAMP An adenine nucleotide containing one phosphate group which is esterified to both the 3′- and 5′-positions of the sugar moiety. It is a second messenger and a key intracellular regulator, functioning as a mediator of activity for a number of hormones, including epinephrine, glucagon, and acth. Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors | |||