Although hepatocellular carcinoma Hepatocellular carcinoma Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) typically arises in a chronically diseased or cirrhotic liver and is the most common primary liver cancer. Diagnosis may include ultrasound, CT, MRI, biopsy (if inconclusive imaging), and/or biomarkers. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases ( HCC HCC Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) typically arises in a chronically diseased or cirrhotic liver and is the most common primary liver cancer. Diagnosis may include ultrasound, CT, MRI, biopsy (if inconclusive imaging), and/or biomarkers. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases) is by far the most common malignant liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy tumor Tumor Inflammation, there are several rare malignant tumors that are important to keep in mind when making a differential diagnosis. These tumors include cholangiocarcinoma; hepatoblastoma and mesenchymal tumors, such as epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EHE); and angiosarcoma. While these conditions differ in their etiology and pathology, they often present similarly, with nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia, weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery, and abdominal discomfort. Diagnosis is by imaging, which can be supported by a biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma. Surgical excision is the only curative approach for these tumors.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Genetic disorders:
Toxins:
Cholangiocarcinoma is associated with work in the following industries:
Precursor/pre-malignant lesions:
Other causes:
Cholangiocarcinoma may be detected incidentally on imaging or may present with symptoms.
Laboratory tests:
Imaging:
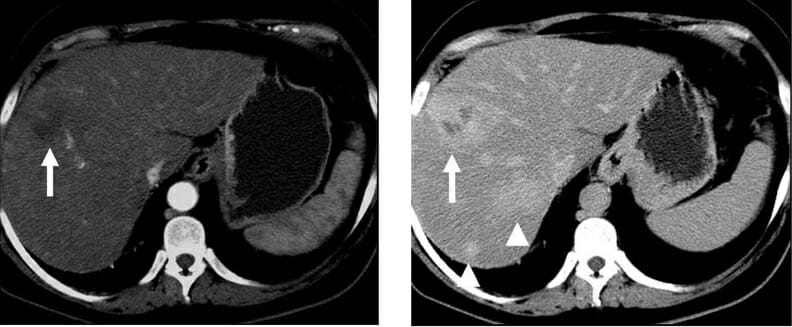
Arterial and portal venous phase CT of cholangiocarcinoma
Image: “Arterial and portal venous phase CT of cholangiocarcinoma” by Kristie Guite, Louis Hinshaw and Fred Lee. License: CC BY 3.0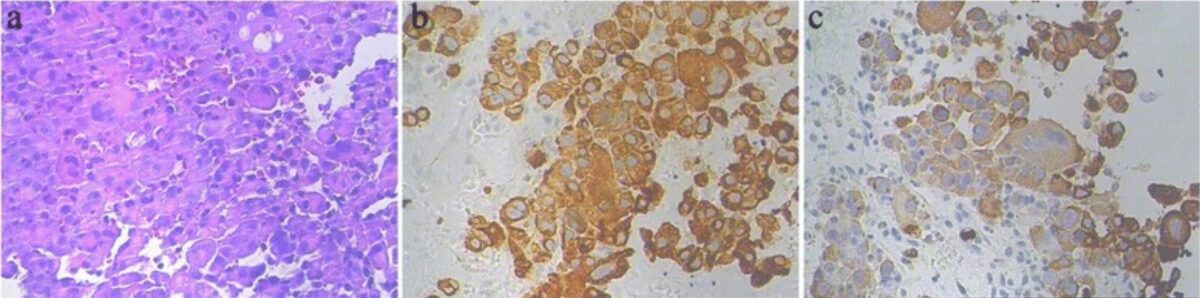
Photomicrographs of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma:
a: markedly atypical epithelial cells (H&E, 200x)
b and c: immunohistochemical stains for the cytokeratins CK7 (b) and CK19 (c), supporting the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma (immunohistochemistry, 200x)
The overall survival rate has greatly improved over the past 4 decades and now stands at 81%.
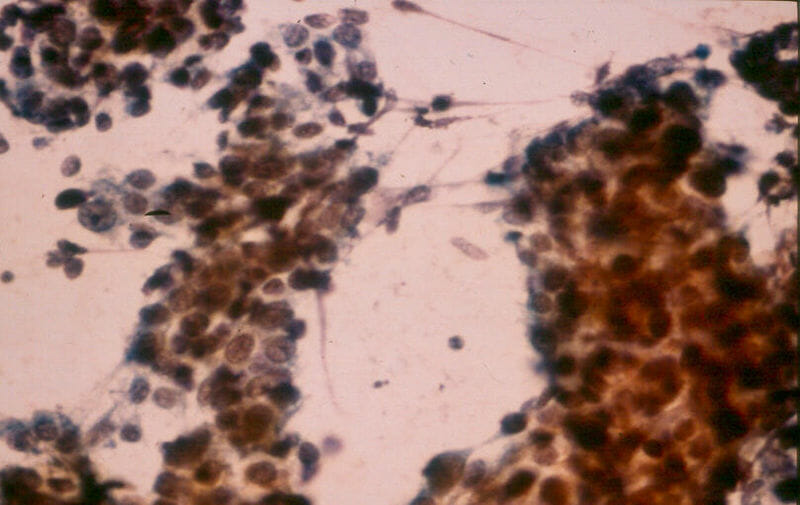
Hepatoblastoma:
characteristic of the embryonal cell type, fine-needle biopsy aspirate consists of small, oval-to-spindle shaped cells with a small amount of cytoplasm and prominent nucleoli
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma is a low-grade malignant vascular neoplasm Vascular neoplasm Neoplasms located in the vasculature system, such as arteries and veins. They are differentiated from neoplasms of vascular tissue (neoplasms, vascular tissue), such as angiofibroma or hemangioma. Hemangioblastoma.
Angiosarcoma is a high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm Vascular neoplasm Neoplasms located in the vasculature system, such as arteries and veins. They are differentiated from neoplasms of vascular tissue (neoplasms, vascular tissue), such as angiofibroma or hemangioma. Hemangioblastoma.
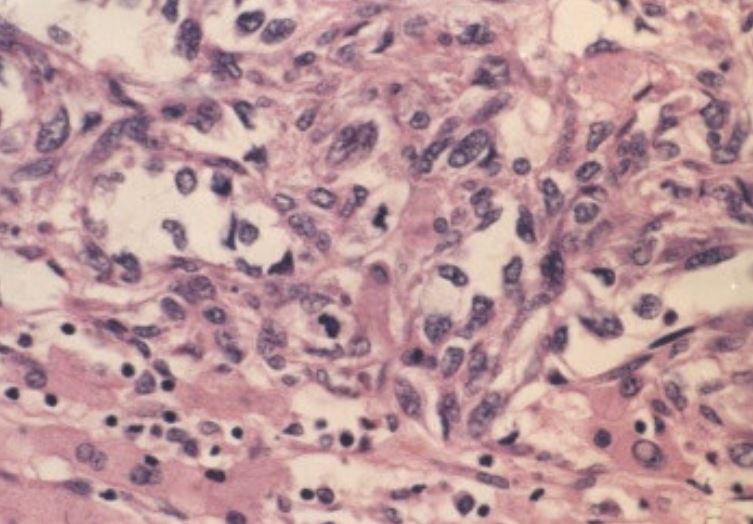
Photomicrograph of hepatic angiosarcoma showing spindle-shaped malignant endothelial cells and neoplastic vascular channels
Scant residual hepatocytes are present (H&E, 400x).
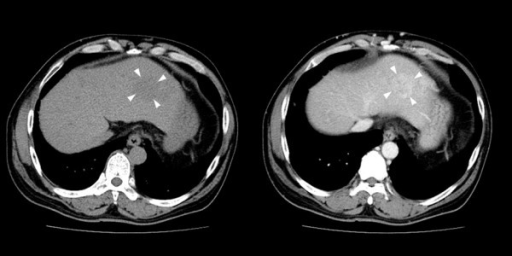
Abdominal CT in an individual with hepatic angiosarcoma:
A low-density mass (3.5 cm) with persistent contrast enhancement in the left hepatic lobe is noted with arrowheads (left: noncontrast phase, right: venous phase). Several enhancing lesions (1–3 cm) in the right lobe of liver S5 are not well-demonstrated in the venous phase nor shown in the figure. Irregular liver surface, splenomegaly, and collateral circulation are noted, indicating cirrhosis.
Risk factors of hepatic angiosarcoma can be remembered as “VAT”:
The following conditions encompass the most important benign Benign Fibroadenoma lesions included in the differential diagnosis of a solid mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast in the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy: