Rabies virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology is a single-stranded, negative-sense RNA Negative-sense RNA RNA viruses that have their genetic material encoded in the form of single-stranded, negative-sense RNA. Unlike retroviruses they do not employ DNA intermediates in their life-cycle. Respiratory Syncytial Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology. This bullet-shaped virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology belongs to the family Rhabdoviridae and the genus Lyssavirus. Rabies is a preventable disease most often transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected animal (e.g., bats, raccoons, skunks, and foxes). This life-threatening disease affects the CNS, resulting in severe neurologic manifestations. There are 5 stages of disease in humans: incubation, prodrome Prodrome Symptoms that appear 24–48 hours prior to migraine onset. Migraine Headache, acute neurologic period, coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma, and death. The diagnosis is made with antibody, antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination, or viral RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure detection in tissue biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma, serum, CSF, and saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy. There is no effective treatment for symptomatic disease, so prevention with human rabies immunoglobulin and vaccination Vaccination Vaccination is the administration of a substance to induce the immune system to develop protection against a disease. Unlike passive immunization, which involves the administration of pre-performed antibodies, active immunization constitutes the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies. Vaccination is the mainstay of management.
Last updated: Mar 13, 2025

RNA virus identification:
Viruses can be classified in many ways. Most viruses, however, will have a genome formed by either DNA or RNA. RNA genome viruses can be further characterized by either a single- or double-stranded RNA. “Enveloped” viruses are covered by a thin coat of cell membrane (usually taken from the host cell). If the coat is absent, the viruses are called “naked” viruses. Viruses with single-stranded genomes are “positive-sense” viruses if the genome is directly employed as messenger RNA (mRNA), which is translated into proteins. “Negative-sense,” single-stranded viruses employ RNA dependent RNA polymerase, a viral enzyme, to transcribe their genome into messenger RNA.
Negatively stained Rhabdovirus
Image: “Biological characterization of purified SRV9” by Xu H et al. License: CC BY 4.0, cropped by Lecturio.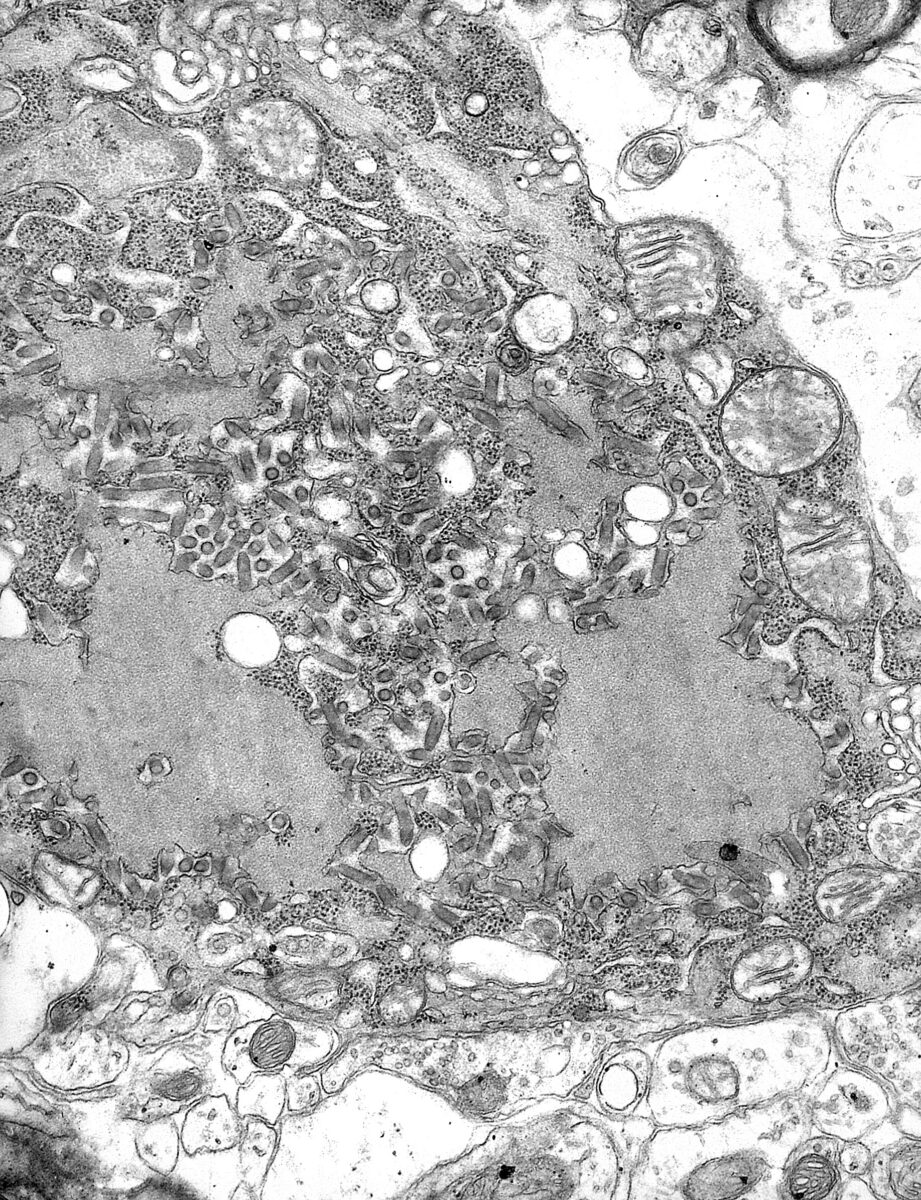
Transmission electron micrograph with numerous rabies virions (small, dark-gray, rod-like or bullet-shaped particles)
Image: “TEM micrograph with numerous rabies virions” by CDC. License: Public Domain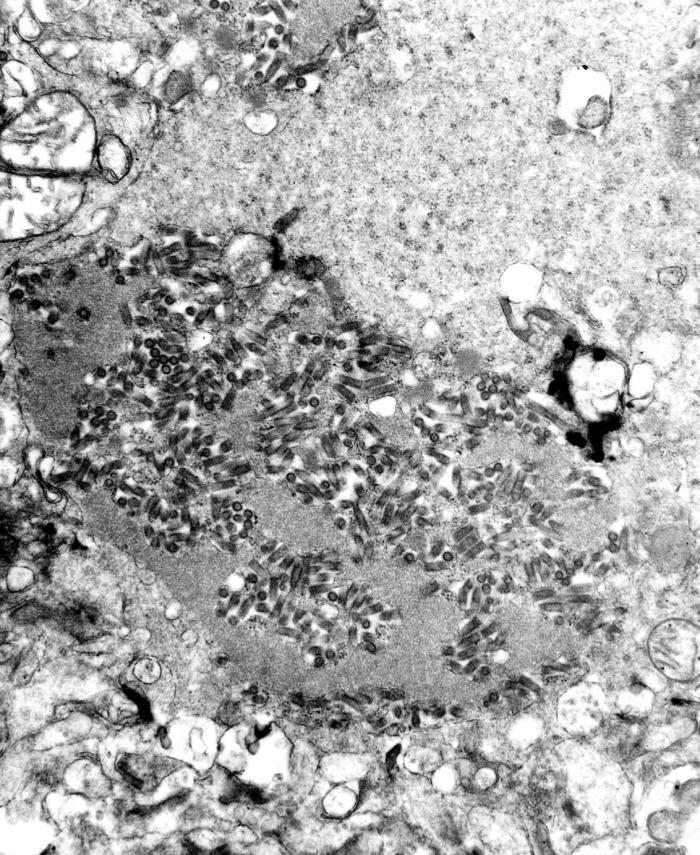
Transmission electron microscopic image showing numerous dark, bullet-shaped, rabies virions within an infected tissue sample
Image: “TEM image revealed the presence of numerous dark, bullet-shaped, rabies virions within an infected tissue sample” by CDC. License: Public DomainRabies virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology causes the disease rabies.
Mammalian species serve as hosts. In the United States, these may include:
Human infection is almost always due to a bite by an infected mammal.
Susceptibility to lethal infection is related to:
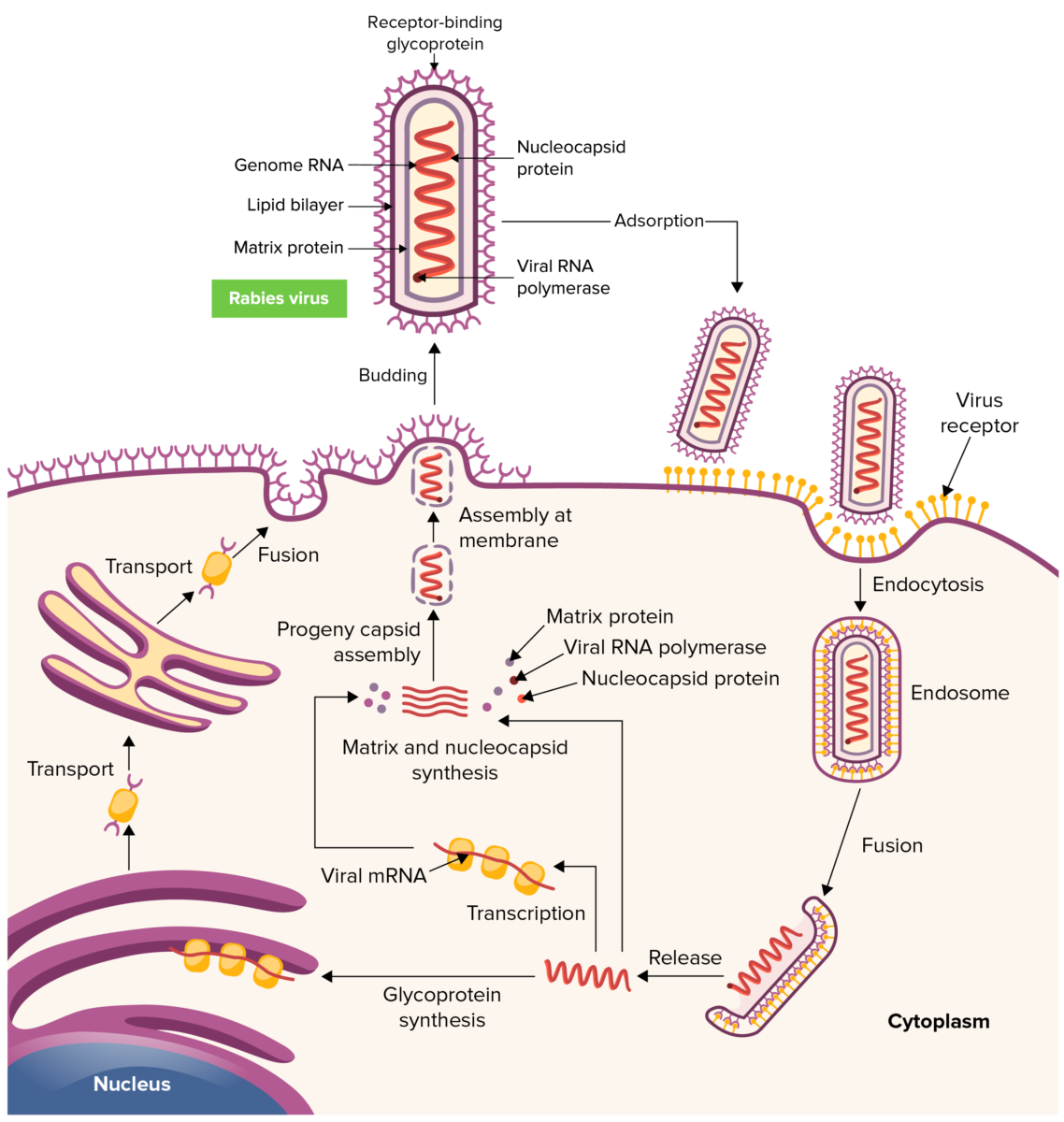
Rabies virus replication cycle
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.05 general stages are recognized in humans: incubation → prodrome Prodrome Symptoms that appear 24–48 hours prior to migraine onset. Migraine Headache → acute neurologic period → coma Coma Coma is defined as a deep state of unarousable unresponsiveness, characterized by a score of 3 points on the GCS. A comatose state can be caused by a multitude of conditions, making the precise epidemiology and prognosis of coma difficult to determine. Coma → death
Acute neurologic period lasts 2–7 days.
Encephalitic form (most common):
Paralytic form:
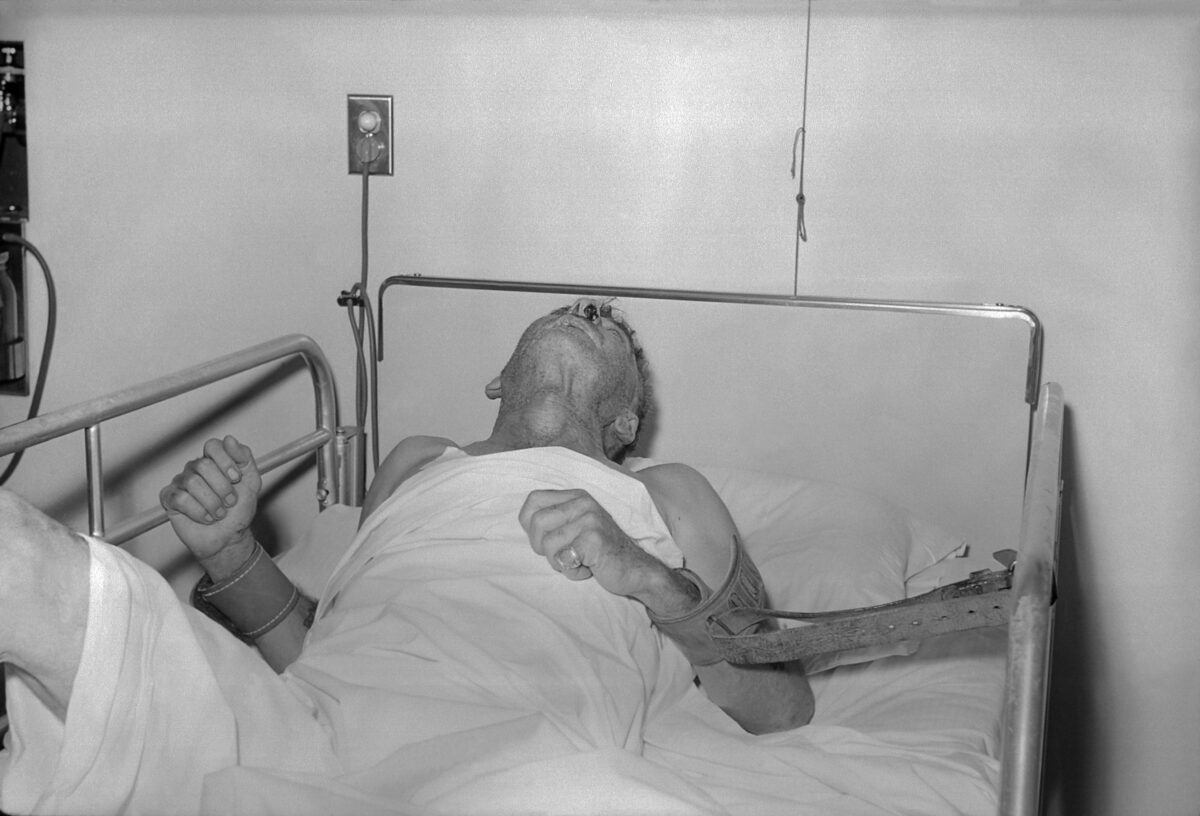
A man with rabies in 1959.
Image: “Rabies patient” by CDC. License: Public DomainThe diagnosis should be suspected in cases of unexplained viral encephalitis Viral encephalitis Inflammation of brain parenchymal tissue as a result of viral infection. Encephalitis may occur as primary or secondary manifestation of togaviridae infections; herpesviridae infections; adenoviridae infections; flaviviridae infections; bunyaviridae infections; picornaviridae infections; paramyxoviridae infections; orthomyxoviridae infections; retroviridae infections; and arenaviridae infections. Encephalitis with a history of an animal bite.
Diagnostic methods:
Specimens that can be tested:
There is no effective treatment for symptomatic rabies, and few patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship survive.
Prevention is the mainstay of care.