Healthcare organizations and public health programs aim to improve the health of individuals and the population. The Institute of Medicine (IOM) in the United States defines quality healthcare as care that is safe, effective, patient centered, timely, efficient, and equitable. Quality, simply defined, is the degree of excellence compared with predetermined standards or benchmarks. Quality measures (QMs) used to determine quality and improve care can broadly be categorized as follows: process, outcome, patient perception Perception The process by which the nature and meaning of sensory stimuli are recognized and interpreted. Psychiatric Assessment, organizational structure, and/or system. An example of an outcome-based QM is the number of people who received a service or action (such as breast cancer Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer-related death among women. Breast Cancer screening Screening Preoperative Care) divided by the number of people who should have received the particular service or action based on a predetermined benchmark. A QM is defined as good if it is important, measurable, and feasible. Models for quality improvement have been developed to guide quality-improvement efforts. LEAN, Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA), and 6 Sigma are examples of some of these models. The key to successful quality improvement is an organizational commitment to a culture of continual improvement.
Last updated: Apr 4, 2023
Definitions of quality:
Quality measures in healthcare are developed to:
QMs:
Categories:
A QM is defined as good if it is:
Benchmarking is the process of comparing performance or clinical practice to a predetermined standard (benchmark). The process can be internal or external (local or national).
A clinical practice may decide that all providers in the establishment should aim to achieve low-density lipoprotein Low-density lipoprotein A class of lipoproteins of small size (18-25 nm) and light (1. 019-1. 063 g/ml) particles with a core composed mainly of cholesterol esters and smaller amounts of triglycerides. The surface monolayer consists mostly of phospholipids, a single copy of apolipoprotein B-100, and free cholesterol molecules. The main ldl function is to transport cholesterol and cholesterol esters to extrahepatic tissues. Cholesterol Metabolism cholesterol Cholesterol The principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils. Cholesterol Metabolism levels < 100 for all individuals with diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus visiting their establishment.
Healthcare Effectiveness Data and Information Set (HEDIS):
Healthcare quality is defined by the IOM using 6 domains:
Clinical practice teams embrace QI by having regular Regular Insulin meetings to address quality and performing QI projects. The models and tools for QI help guide these initiatives.
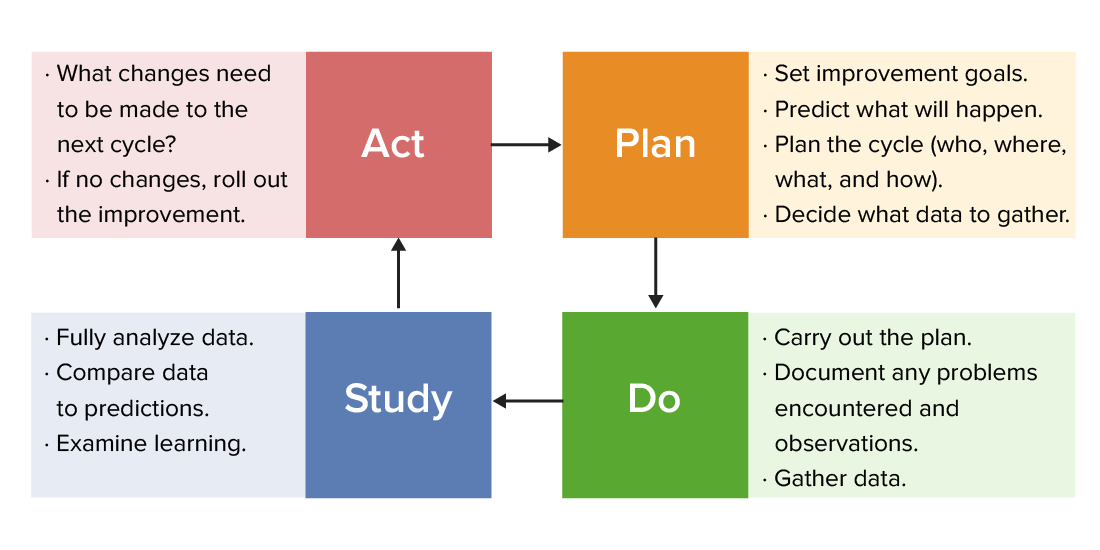
A Plan-Do-Study-Act chart
Image by Lecturio.