Pyelonephritis is infection affecting the renal pelvis Renal pelvis Kidneys: Anatomy and the renal parenchyma. This condition arises mostly as a complication of bladder infection that ascends to the upper urinary tract Urinary tract The urinary tract is located in the abdomen and pelvis and consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The structures permit the excretion of urine from the body. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and out through the urethra. Urinary Tract: Anatomy. Pyelonephritis can be acute or chronic (which results from persistent or chronic infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease). Typical acute symptoms are flank pain Flank pain Pain emanating from below the ribs and above the ilium. Renal Cell Carcinoma, fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, and nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics with vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia. The chronic type depends on the underlying pathology. The diagnosis is established via clinical presentation, supported by laboratory findings (in blood and urine). Imaging studies are performed if severe illness is noted or there is no response to initial treatment (antibiotics). CT is the study of choice, given its ability to detect renal abnormalities associated with the infection, including the extent of the disease. Perinephric abscess Perinephric Abscess Imaging of the Urinary System is an infection involving the perinephric space between the kidney and Gerota’s fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis. Perinephric abscess Perinephric Abscess Imaging of the Urinary System can be an extension Extension Examination of the Upper Limbs from pyelonephritis or from hematogenous Hematogenous Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases spread of a systemic infection. The diagnosis is established via CT scan. The treatment includes antibiotics, with abscess Abscess Accumulation of purulent material in tissues, organs, or circumscribed spaces, usually associated with signs of infection. Chronic Granulomatous Disease drainage (which is both diagnostic and therapeutic).
Last updated: May 17, 2024
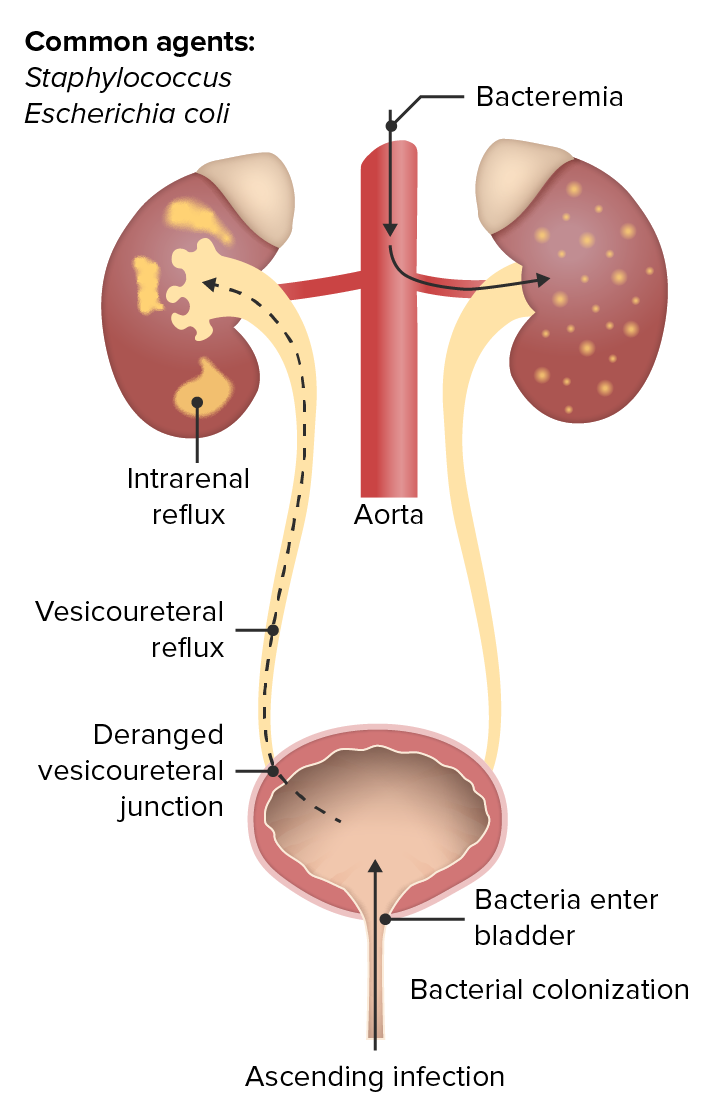
Ascending hematogenous urinary tract infection
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Acute pyelonephritis Acute pyelonephritis Inflammation of the kidney involving the renal parenchyma (the nephrons); kidney pelvis; and kidney calices. It is characterized by abdominal pain; fever; nausea; vomiting; and occasionally diarrhea. Imaging of the Urinary System is the sudden-onset infectious process and inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the kidney(s) from ascending infection Ascending Infection Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Children or hematogenous Hematogenous Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases spread of systemic infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease.
Associated with the development of pyelonephritis and perinephric abscess Perinephric Abscess Imaging of the Urinary System:
Findings suspicious for pyelonephritis:
Blood tests:
Urine studies:
Imaging studies:
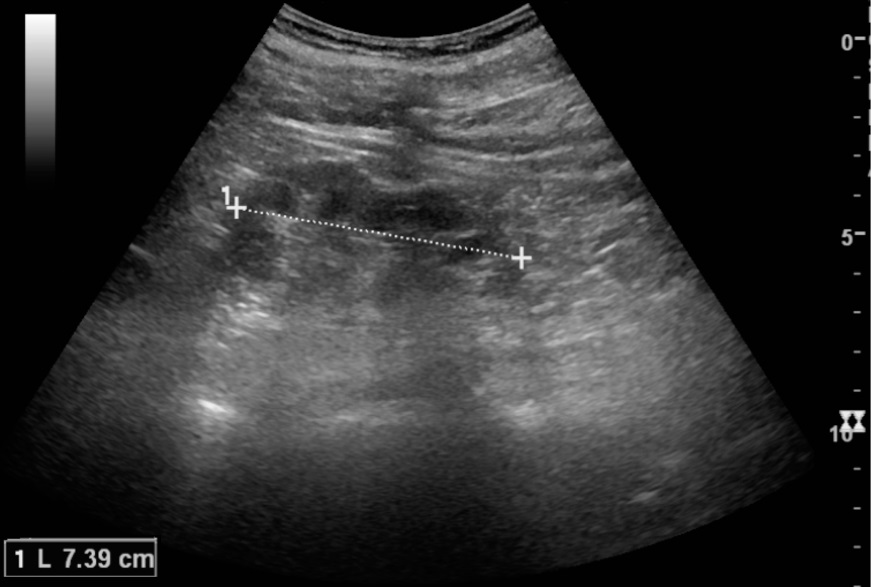
Chronic pyelonephritis illustrated in reduced kidney length (7 cm) and focal cortical thinning:
Normal kidney length is 10–12 cm. Note the kidney measurement as illustrated by the 2 ‘+’ signs and the dashed line.
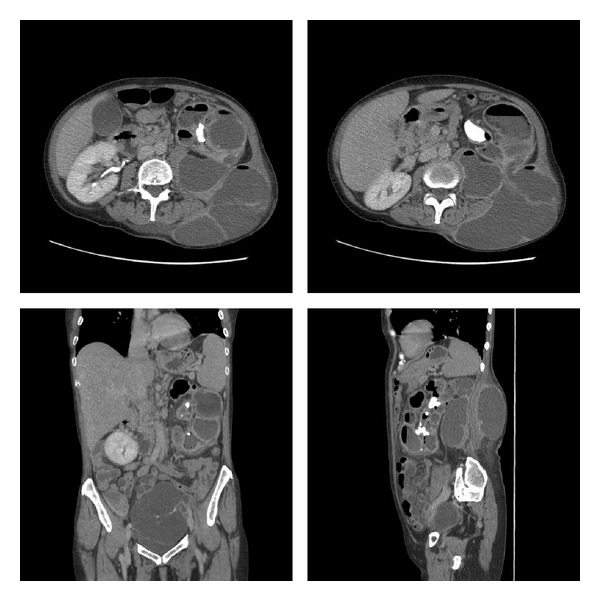
Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis:
CT of the abdomen and pelvis with IV contrast and delayed phase demonstrating a left kidney with parenchyma replaced with multiple large hypodense collections containing fluid and gas, a left staghorn calculus, and communication between the kidney and large flank collection.
Also note the 13.5-by-7.7-cm multiloculated pelvic mass.
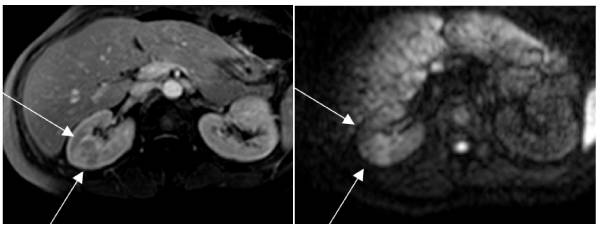
MRI showing pyelonephritis:
Left: T1-weighted sequence showing a large pyelonephritis focus in the right kidney
Right: The same area in diffusion. The large cuneiform lesion is evident because of the intense edema.
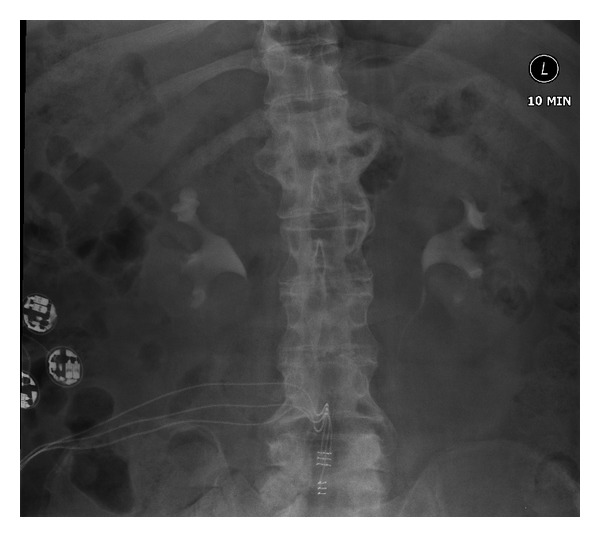
Chronic pyelonephritis:
Intravenous urography shows some blunting of the right upper pole calyx with some reduction in cortical thickness at the right upper pole compatible with chronic pyelonephritis. Otherwise, both pelvicalyceal systems and ureters appear normal.
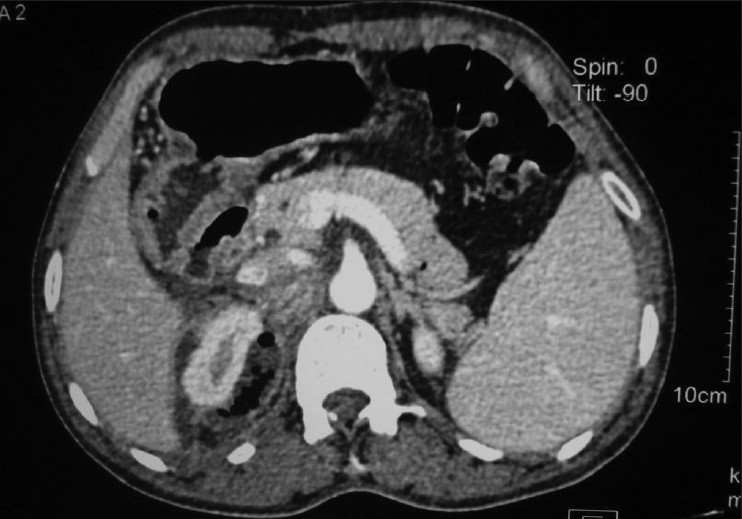
Perinephric abscess: axial CT image through the upper pole of the right kidney showing perinephric abscess reaching posterior to the inferior vena cava
Image: “Axial CT image through the upper pole of the right kidney showing perinephric abscess reaching posterior to IVC.” by Wani NA. License: CC BY 2.0Management depends on the severity of the clinical presentation and risk factors for drug resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing: