Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established. Whether the condition is in an acute or chronic state determines the length of antibiotic treatment. The main diagnostic tools are history, physical examination, and work-up investigating the sources of infection (urinalysis and culture). Digital rectal examination is only recommended in patients with chronic prostatitis and not in acute bacterial prostatitis due to the risk of sepsis. Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion and requires multimodal pain management with established patient expectations. The asymptomatic type is an incidental finding that is recognized when a patient has other urologic issues.
Last updated: Dec 16, 2025
Prostatitis Prostatitis Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established. Prostatitis is inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the prostate Prostate The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid. gland that presents as different syndromes:
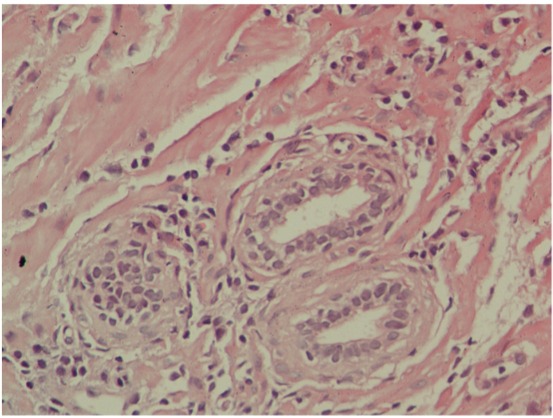
Microscopic appearance of chronic prostatitis:
Numerous small, dark-blue lymphocytes are seen in the stroma between the glands.
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis Chronic bacterial prostatitis Chronic bacterial infection of the prostate with lower urinary tract symptoms Prostatitis are worked up similarly on initial presentation:
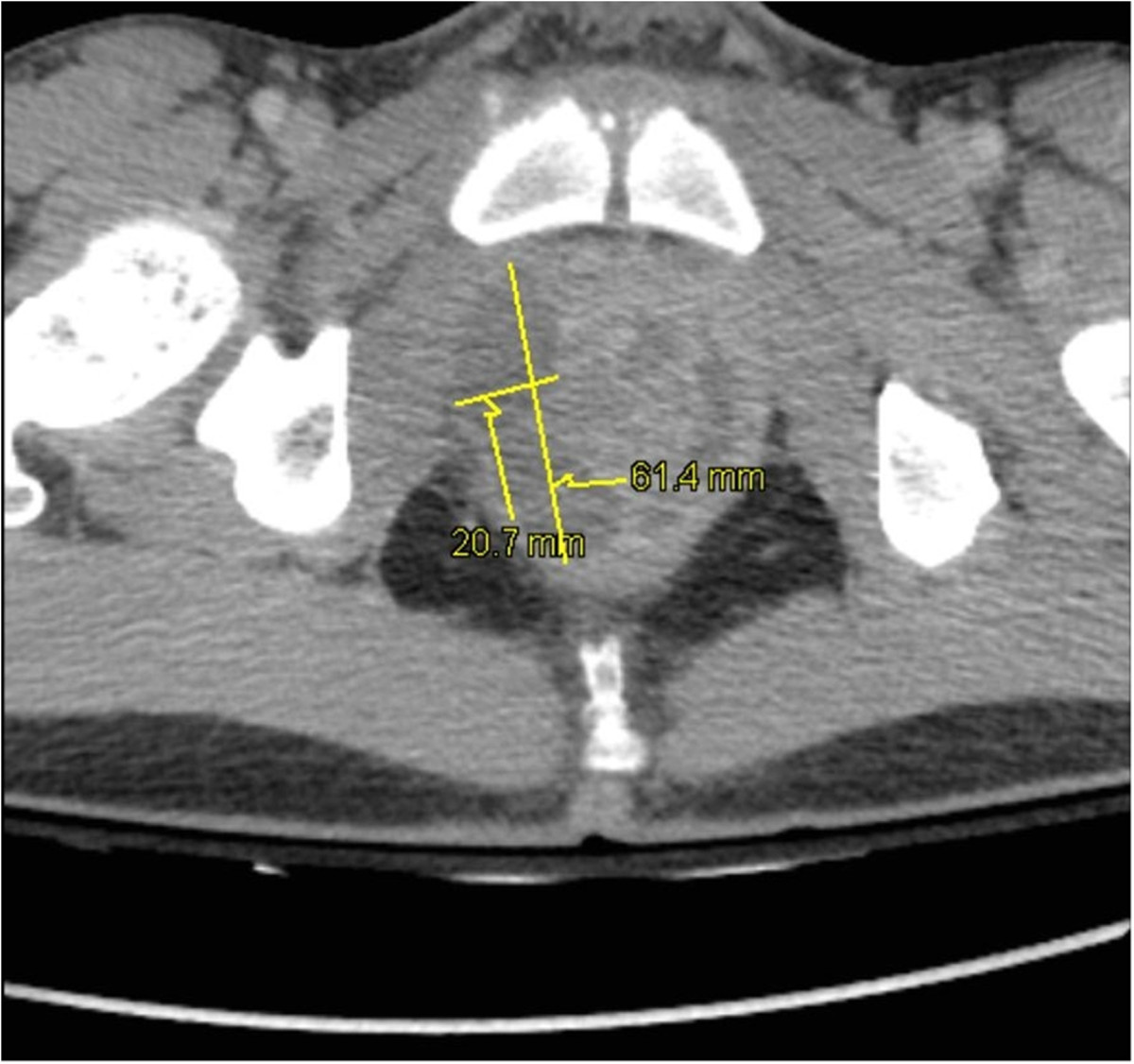
Pelvic CT of prostatic abscesses:
Prostatic hypertrophy and intraprostatic abscesses: 20 × 15 × 33 mm and 64 × 21 × 26 mm in the right lobe and 38 × 10 × 30 mm in the left lobe
CPPS CPPS Chronic lower pelvic pain and inflammation of the prostate gland ≥ 3 months. May or may not be associated with infection Prostatitis is a diagnosis of exclusion:[4,7,8]
Additional tools (validated questionnaires) for chronic bacterial prostatitis Chronic bacterial prostatitis Chronic bacterial infection of the prostate with lower urinary tract symptoms Prostatitis and CPPS CPPS Chronic lower pelvic pain and inflammation of the prostate gland ≥ 3 months. May or may not be associated with infection Prostatitis:[4,8]
Treatment protocols may vary based on locale. The following recommendations are based on North American, UK, and European guidelines.
Acute bacterial prostatitis Acute bacterial prostatitis Acute bacterial infection of the prostate with lower urinary tract symptoms Prostatitis:[4–7,9]
Chronic bacterial prostatitis Chronic bacterial prostatitis Chronic bacterial infection of the prostate with lower urinary tract symptoms Prostatitis:[4,8,9]
Chronic prostatitis Prostatitis Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established. Prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways:[4,8,9]
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis Non-infectious, nonspecific prostate gland inflammation Prostatitis:[7]
Acute bacterial prostatitis Acute bacterial prostatitis Acute bacterial infection of the prostate with lower urinary tract symptoms Prostatitis, uncomplicated:
Acute bacterial prostatitis Acute bacterial prostatitis Acute bacterial infection of the prostate with lower urinary tract symptoms Prostatitis, complicated (requiring hospitalization Hospitalization The confinement of a patient in a hospital. Delirium), treated with parenteral antibiotics (see table for specific options for dosing):
| Factors considered | Antibiotic regimen | Alternative regimen |
|---|---|---|
| Not severely ill and without resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing factors | ||
| Severely ill and without resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing risk factors | ||
| Any severity, with fluoroquinolone resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing and ESBL-producing E. coli (transrectal manipulation) | ||
| Any severity, Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas spp. (transurethral manipulation) | (add aminoglycoside if clinically unstable) |
|
| Any severity, fluoroquinolone resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing | (add aminoglycoside if clinically unstable) |
Chronic bacterial prostatitis Chronic bacterial prostatitis Chronic bacterial infection of the prostate with lower urinary tract symptoms Prostatitis and CPPS CPPS Chronic lower pelvic pain and inflammation of the prostate gland ≥ 3 months. May or may not be associated with infection Prostatitis antibiotic-naive:[4,8,9]
Diagnosis Codes:
These codes are used to diagnose
prostatitis
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established.
Prostatitis, or
inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function.
Inflammation of the
prostate
Prostate
The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid.
gland. The codes distinguish between acute, chronic, and unspecified forms.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | N41.0 | Acute prostatitis Prostatitis Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established. Prostatitis |
| ICD-10-CM | N41.1 | Chronic prostatitis Prostatitis Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established. Prostatitis |
Evaluation & Workup:
These codes are for a
urinalysis
Urinalysis
Examination of urine by chemical, physical, or microscopic means. Routine urinalysis usually includes performing chemical screening tests, determining specific gravity, observing any unusual color or odor, screening for bacteriuria, and examining the sediment microscopically.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Children and
urine culture
Urine culture
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs), which are essential tests to identify the presence of
bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases.
Bacteriology and determine the appropriate antibiotic for treating bacterial
prostatitis
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established.
Prostatitis.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 81001 | Urinalysis Urinalysis Examination of urine by chemical, physical, or microscopic means. Routine urinalysis usually includes performing chemical screening tests, determining specific gravity, observing any unusual color or odor, screening for bacteriuria, and examining the sediment microscopically. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Children, by dip stick or tablet reagent |
| CPT | 87086 | Culture, bacterial; quantitative colony count, urine |
Medications:
This code is for a fluoroquinolone antibiotic like
ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin
A broad-spectrum antimicrobial carboxyfluoroquinoline.
Fluoroquinolones, which is a common treatment for bacterial
prostatitis
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established.
Prostatitis due to its excellent
penetration
Penetration
X-rays into
prostate
Prostate
The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid.
tissue.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 2551 | Ciprofloxacin Ciprofloxacin A broad-spectrum antimicrobial carboxyfluoroquinoline. Fluoroquinolones (ingredient) |