Prostatitis is inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate Prostate The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid. that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established. Whether the condition is in an acute or chronic state determines the length of antibiotic treatment. The main diagnostic tools are history, physical examination, and work-up investigating the sources of infection ( urinalysis Urinalysis Examination of urine by chemical, physical, or microscopic means. Routine urinalysis usually includes performing chemical screening tests, determining specific gravity, observing any unusual color or odor, screening for bacteriuria, and examining the sediment microscopically. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Children and culture). Digital rectal examination Digital Rectal Examination A physical examination in which the qualified health care worker inserts a lubricated, gloved finger of one hand into the rectum and may use the other hand to press on the lower abdomen or pelvic area to palpate for abnormalities in the lower rectum, and nearby organs or tissues. The method is commonly used to check the lower rectum, the prostate gland in men, and the uterus and ovaries in women. Prostate Cancer Screening is only recommended in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with chronic prostatitis and not in acute bacterial prostatitis due to the risk of sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock. Chronic pelvic pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways syndrome is a diagnosis of exclusion and requires multimodal pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways management with established patient expectations. The asymptomatic type is an incidental finding that is recognized when a patient has other urologic issues.
Last updated: May 29, 2025
Prostatitis is inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the prostate Prostate The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid. gland that presents as different syndromes:
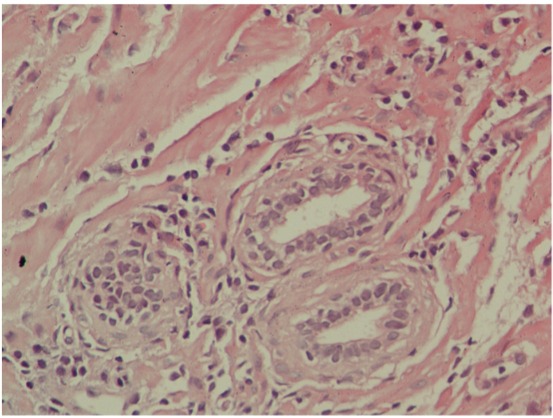
Microscopic appearance of chronic prostatitis:
Numerous small, dark-blue lymphocytes are seen in the stroma between the glands.
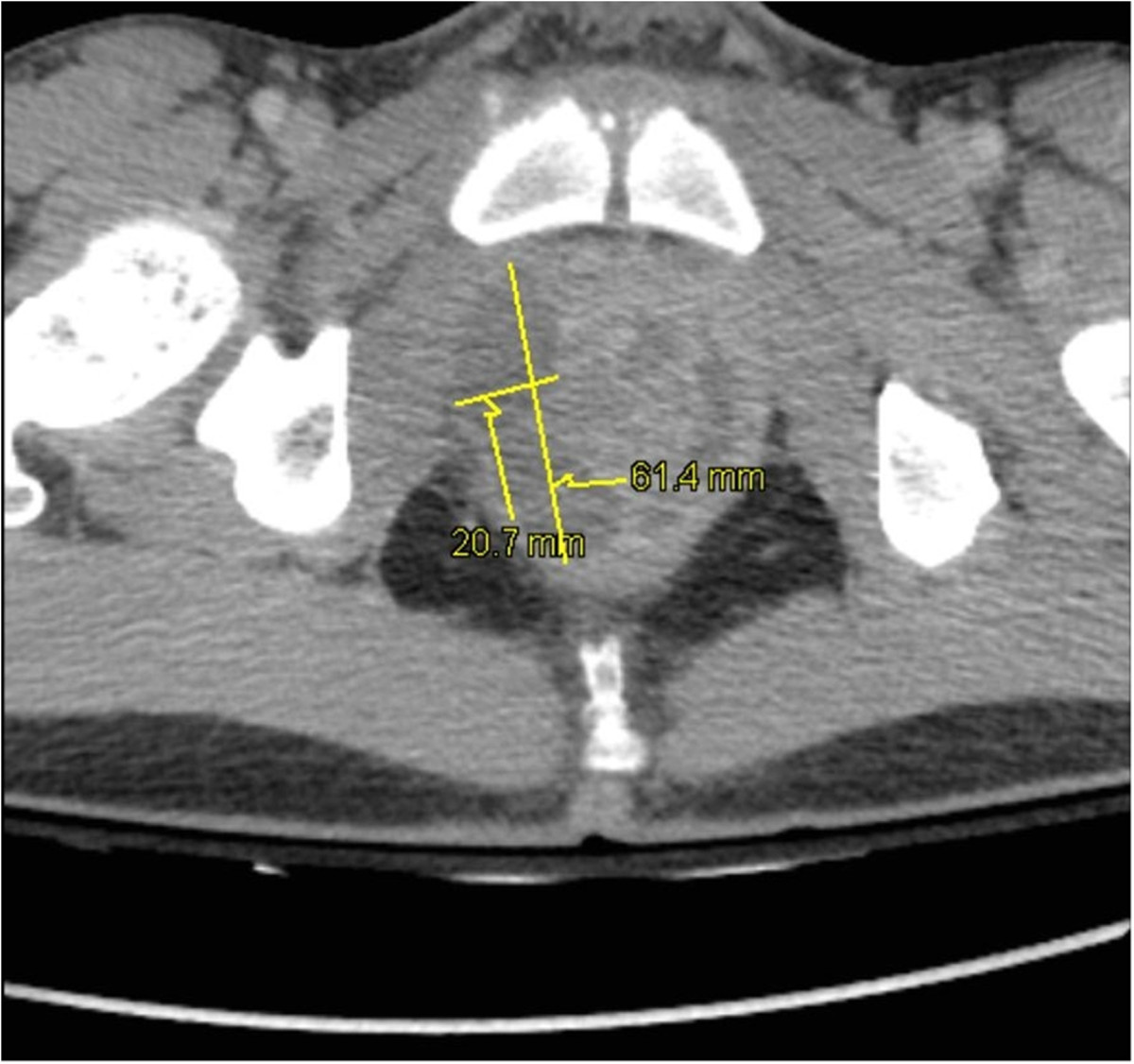
Pelvic CT of prostatic abscesses:
Prostatic hypertrophy and intraprostatic abscesses: 20 × 15 × 33 mm and 64 × 21 × 26 mm in the right lobe and 38 × 10 × 30 mm in the left lobe