Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is an inflammatory disease that causes fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans and strictures of the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy ducts. The exact etiology is unknown, but there is a strong association with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship typically present with an insidious onset of fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia, pruritus Pruritus An intense itching sensation that produces the urge to rub or scratch the skin to obtain relief. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema), and jaundice Jaundice Jaundice is the abnormal yellowing of the skin and/or sclera caused by the accumulation of bilirubin. Hyperbilirubinemia is caused by either an increase in bilirubin production or a decrease in the hepatic uptake, conjugation, or excretion of bilirubin. Jaundice, which can progress to cirrhosis Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a late stage of hepatic parenchymal necrosis and scarring (fibrosis) most commonly due to hepatitis C infection and alcoholic liver disease. Patients may present with jaundice, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cirrhosis can also cause complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, and hepatorenal syndrome. Cirrhosis and complications related to biliary obstruction. The diagnosis is established with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Liver transplantation Liver transplantation The transference of a part of or an entire liver from one human or animal to another. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases is the only definitive treatment and is indicated in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with advanced liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease characterized by intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy duct inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation and fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans, forming multifocal Multifocal Retinoblastoma bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy duct strictures.
The cause of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is unknown, but the disease is associated with:
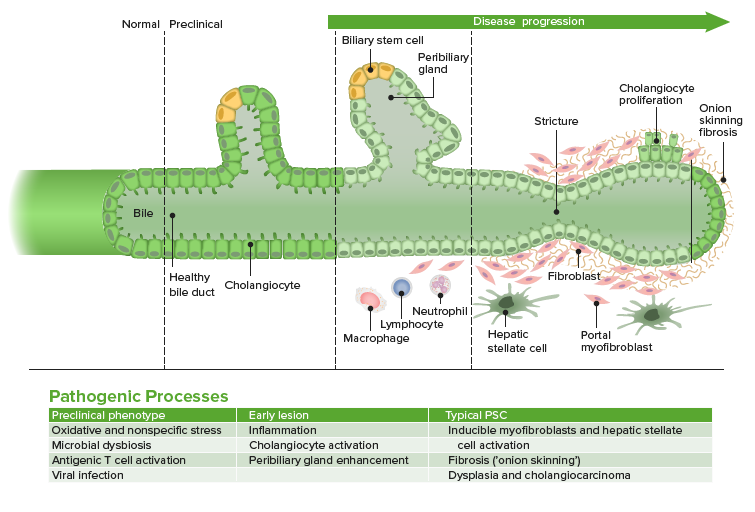
Progression of cholangiocyte activation, inflammation, and fibrosis in PSC. This starts with a predisposed phenotype, and may be triggered by a stressor.
Image by Lecturio.Though many patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are asymptomatic, others may present with:
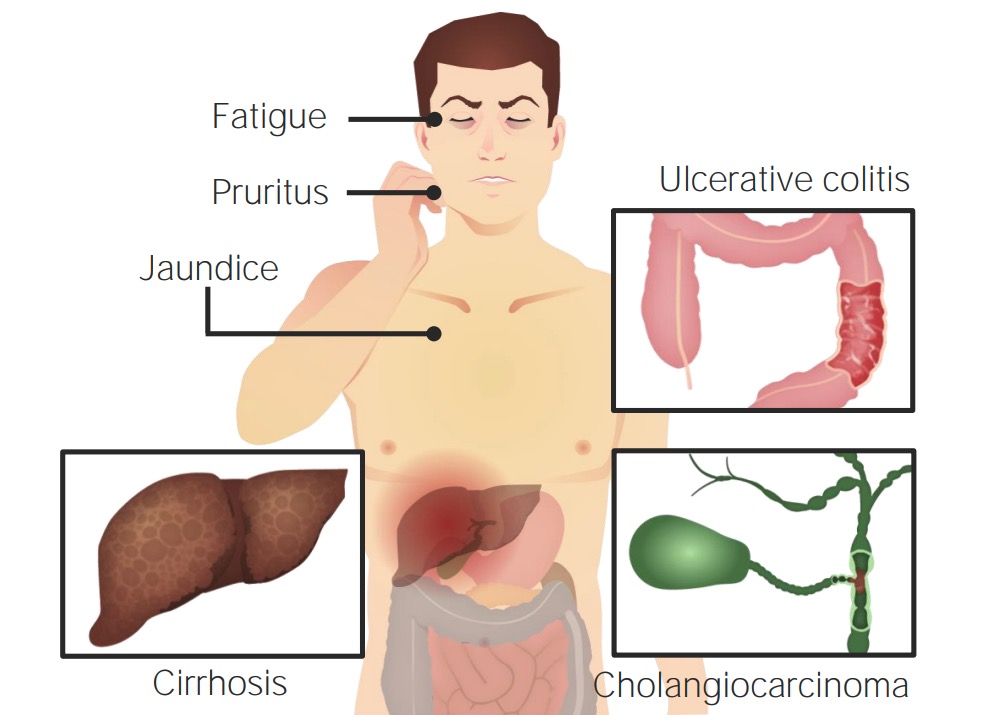
Common presentations in PSC are fatigue, pruritis, jaundice, and cirrhosis. Patients may have concurrent IBD, and PSC is associated with an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma.
Image by Lecturio.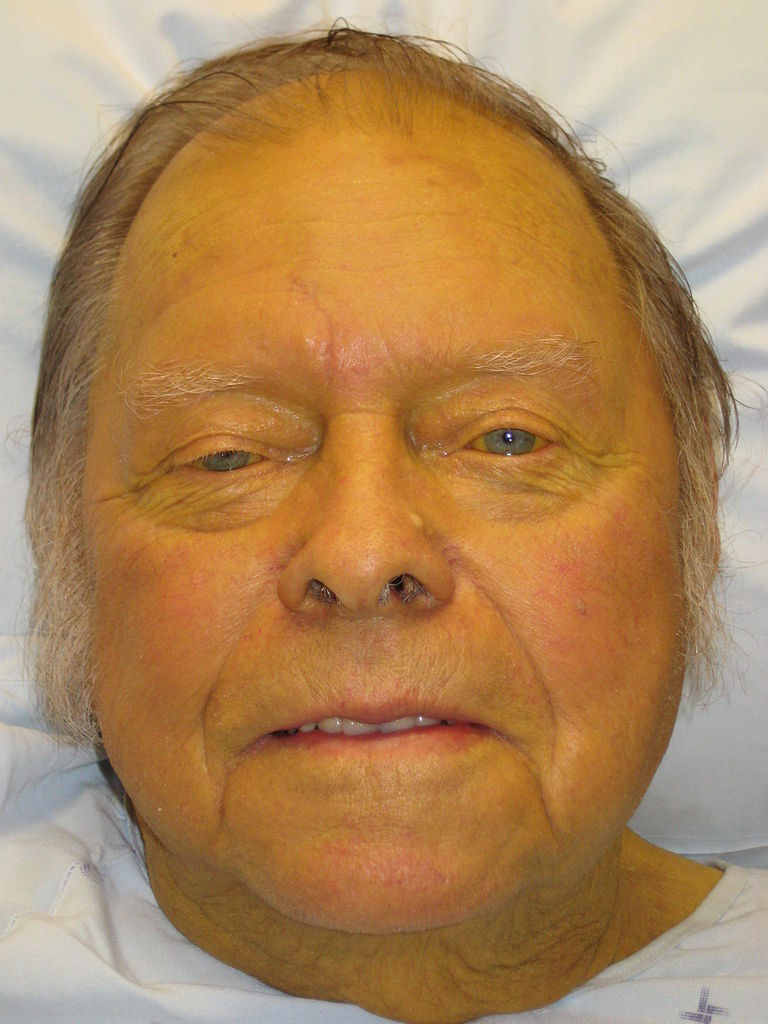
Jaundice: yellow discoloration of the skin due to bilirubin deposition
Image: “Jaundice08” by James Heilman, MD. License: CC BY 3.0.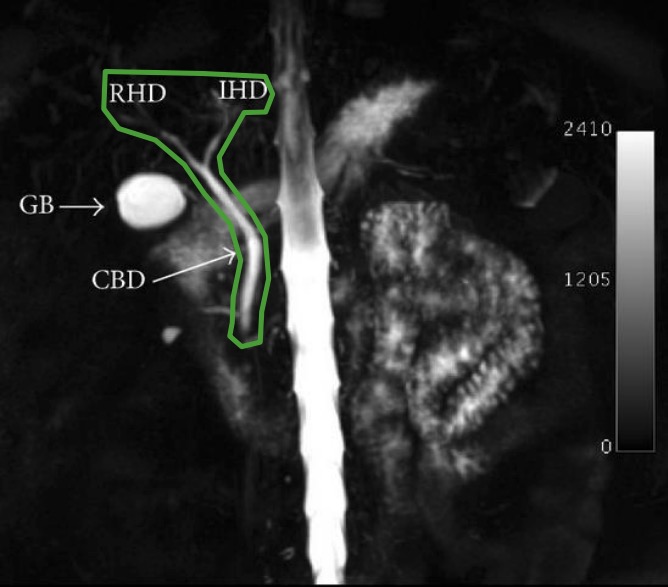
Normal common bile duct and hepatic duct anatomy
Image: “MRCP” by Shamir O. Cawich et al. License: CC BY 3.0, edited by Lecturio.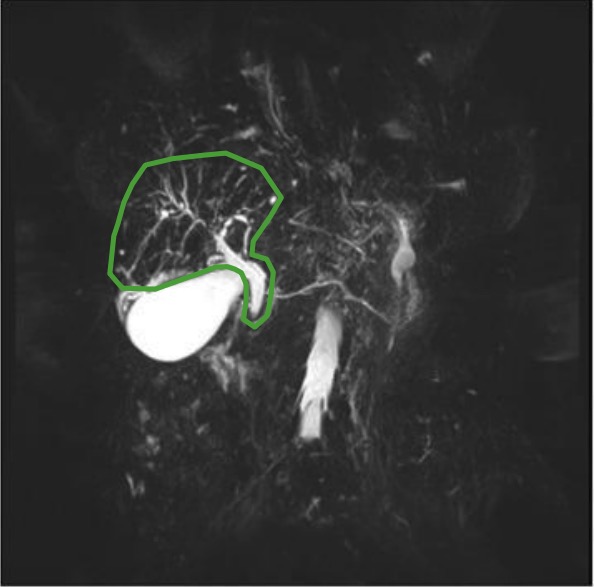
“Beaded” ducts, a prominent common bile duct, and irregular hepatic ducts in PSC
Image: “MRCP with beaded ducts” by Shamir O. Cawich et al. License: CC BY 3.0, edited by Lecturio.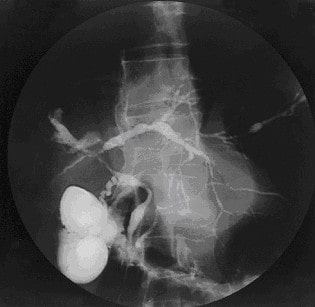
An ERCP of a patient with PSC: The ERCP shows narrowing and dilatation of both intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts, resulting in a “beaded” appearance.
Image: “Cholangiogram of primary sclerosing cholangitis” by the Department of Gastroenterology, John Radcliffe Hospital, Headington, Oxford, OX3 9DU, UK. License: CC BY 2.0.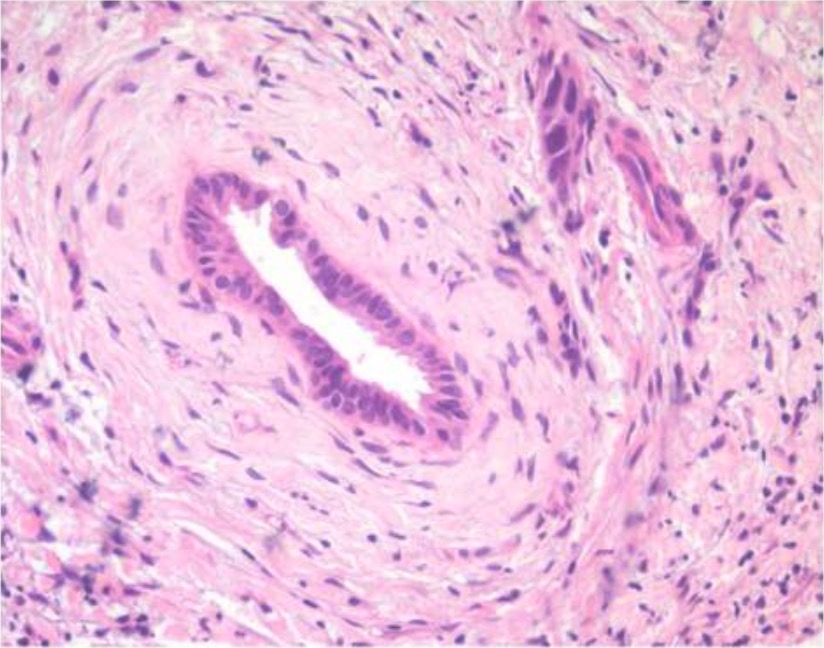
Histologic features of PSC, which may be seen on biopsy: Notice the concentric fibrosis around the bile duct, known as “onion skin” fibrosis.
Image: “Histological features of primary sclerosing cholangitis” by the Department of Gastroenterology, John Radcliffe Hospital, Headington, Oxford, OX3 9DU, UK. License: CC BY 2.0.Primary sclerosing cholangitis is a progressive and chronic disease that causes inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation in the bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy ducts, which can lead to several complications:
Primary sclerosing cholangitis should be differentiated from primary biliary cholangitis Primary Biliary Cholangitis Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic disease resulting in autoimmune destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts. The typical presentation is that of a middle-aged woman with pruritus, fatigue, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Elevated liver enzymes and antimitochondrial antibodies (AMAs) establish the diagnosis. Primary Biliary Cholangitis ( PBC PBC Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic disease resulting in autoimmune destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts. The typical presentation is that of a middle-aged woman with pruritus, fatigue, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Elevated liver enzymes and antimitochondrial antibodies (AMAs) establish the diagnosis. Primary Biliary Cholangitis), because the 2 conditions are similar in presentation:
| PBC PBC Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic disease resulting in autoimmune destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts. The typical presentation is that of a middle-aged woman with pruritus, fatigue, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Elevated liver enzymes and antimitochondrial antibodies (AMAs) establish the diagnosis. Primary Biliary Cholangitis | PSC |
|---|---|
| Predominantly women | Predominantly men |
| Associated with autoimmune diseases Autoimmune diseases Disorders that are characterized by the production of antibodies that react with host tissues or immune effector cells that are autoreactive to endogenous peptides. Selective IgA Deficiency | Associated with IBD |
| Intrahepatic involvement only | Intra- and extrahepatic involvement |
| Absence of bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy duct narrowing on MRCP | MRCP shows narrowing and dilation of bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy ducts. |
| AMA AMA Primary Biliary Cholangitis positive in 95% of cases. |
|