Primary ovarian insufficiency Primary ovarian insufficiency Cessation of ovarian function after menarche but before the age of 40, without or with ovarian follicle depletion. It is characterized by the presence of oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, elevated gonadotropins, and low estradiol levels. It is a state of female hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Etiologies include genetic defects, autoimmune processes, chemotherapy, radiation, and infections. The most commonly known genetic cause is the expansion of a cgg repeat to 55 to 199 copies in the 5' untranslated region in the X-linked fmr1 gene. Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI) is a condition resulting from the depletion or dysfunction of the ovarian follicles, leading to cessation of ovulation Ovulation The discharge of an ovum from a rupturing follicle in the ovary. Menstrual Cycle and menses Menses The periodic shedding of the endometrium and associated menstrual bleeding in the menstrual cycle of humans and primates. Menstruation is due to the decline in circulating progesterone, and occurs at the late luteal phase when luteolysis of the corpus luteum takes place. Menstrual Cycle before age 40. Primary ovarian insufficiency Primary ovarian insufficiency Cessation of ovarian function after menarche but before the age of 40, without or with ovarian follicle depletion. It is characterized by the presence of oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, elevated gonadotropins, and low estradiol levels. It is a state of female hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Etiologies include genetic defects, autoimmune processes, chemotherapy, radiation, and infections. The most commonly known genetic cause is the expansion of a cgg repeat to 55 to 199 copies in the 5' untranslated region in the X-linked fmr1 gene. Primary Ovarian Insufficiency is primarily idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis, but it can also be seen in association with chromosomal and genetic defects, including Turner syndrome Turner syndrome Turner syndrome is a genetic condition affecting women, in which 1 X chromosome is partly or completely missing. The classic result is the karyotype 45,XO with a female phenotype. Turner syndrome is associated with decreased sex hormone levels and is the most common cause of primary amenorrhea. Turner Syndrome (45,X karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System) and FMR1 premutation. Affected individuals present with signs and symptoms of menopause Menopause Menopause is a physiologic process in women characterized by the permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs after the loss of ovarian activity. Menopause can only be diagnosed retrospectively, after 12 months without menstrual bleeding. Menopause prior to age 40, including oligomenorrhea Oligomenorrhea Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome or amenorrhea Amenorrhea Absence of menstruation. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System, vaginal dryness (often leading to dyspareunia Dyspareunia Recurrent genital pain occurring during, before, or after sexual intercourse in either the male or the female. Primary Ovarian Insufficiency), and infertility Infertility Infertility is the inability to conceive in the context of regular intercourse. The most common causes of infertility in women are related to ovulatory dysfunction or tubal obstruction, whereas, in men, abnormal sperm is a common cause. Infertility. Key laboratory findings include elevated follicle-stimulating hormone ( FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle) and low estrogen Estrogen Compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of estradiol. Estrogens stimulate the female reproductive organs, and the development of secondary female sex characteristics. Estrogenic chemicals include natural, synthetic, steroidal, or non-steroidal compounds. Ovaries: Anatomy levels. Once the diagnosis of POI is made, screening Screening Preoperative Care for autoimmune adrenal antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions should be performed and a karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System, FMR1 premutation screen, and baseline DEXA DEXA Osteoporosis scan should be obtained. Management includes hormone replacement therapy Hormone Replacement Therapy Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause and in combination to suppress ovulation. Risks and side effects include uterine bleeding, predisposition to cancer, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine headaches, hypertension, bloating, and mood changes. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins ( HRT HRT Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause and in combination to suppress ovulation. Risks and side effects include uterine bleeding, predisposition to cancer, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine headaches, hypertension, bloating, and mood changes. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins), addressing fertility concerns as desired, and psychological support.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Primary ovarian insufficiency Primary ovarian insufficiency Cessation of ovarian function after menarche but before the age of 40, without or with ovarian follicle depletion. It is characterized by the presence of oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, elevated gonadotropins, and low estradiol levels. It is a state of female hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Etiologies include genetic defects, autoimmune processes, chemotherapy, radiation, and infections. The most commonly known genetic cause is the expansion of a cgg repeat to 55 to 199 copies in the 5′ untranslated region in the X-linked fmr1 gene. Primary Ovarian Insufficiency is the depletion or dysfunction of ovarian follicles resulting in cessation of ovulation Ovulation The discharge of an ovum from a rupturing follicle in the ovary. Menstrual Cycle and menses Menses The periodic shedding of the endometrium and associated menstrual bleeding in the menstrual cycle of humans and primates. Menstruation is due to the decline in circulating progesterone, and occurs at the late luteal phase when luteolysis of the corpus luteum takes place. Menstrual Cycle prior to age 40.
Hypothalamus Hypothalamus The hypothalamus is a collection of various nuclei within the diencephalon in the center of the brain. The hypothalamus plays a vital role in endocrine regulation as the primary regulator of the pituitary gland, and it is the major point of integration between the central nervous and endocrine systems. Hypothalamus:
Pituitary Pituitary A small, unpaired gland situated in the sella turcica. It is connected to the hypothalamus by a short stalk which is called the infundibulum. Hormones: Overview and Types:
Ovary:
Clinical importance of functioning HPO axis HPO axis Gonadal Hormones in younger women:
Primary ovarian insufficiency Primary ovarian insufficiency Cessation of ovarian function after menarche but before the age of 40, without or with ovarian follicle depletion. It is characterized by the presence of oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, elevated gonadotropins, and low estradiol levels. It is a state of female hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Etiologies include genetic defects, autoimmune processes, chemotherapy, radiation, and infections. The most commonly known genetic cause is the expansion of a cgg repeat to 55 to 199 copies in the 5′ untranslated region in the X-linked fmr1 gene. Primary Ovarian Insufficiency can be caused by chromosomal and genetic defects, an autoimmune process, or ovarian toxins; however, in the vast majority of cases, a clear cause is never identified.
The primary presenting complaints are usually oligomenorrhea Oligomenorrhea Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome or amenorrhea Amenorrhea Absence of menstruation. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System (either primary or secondary). Pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care always needs to be excluded first, even in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship who deny sexual intercourse.[1,4,6]
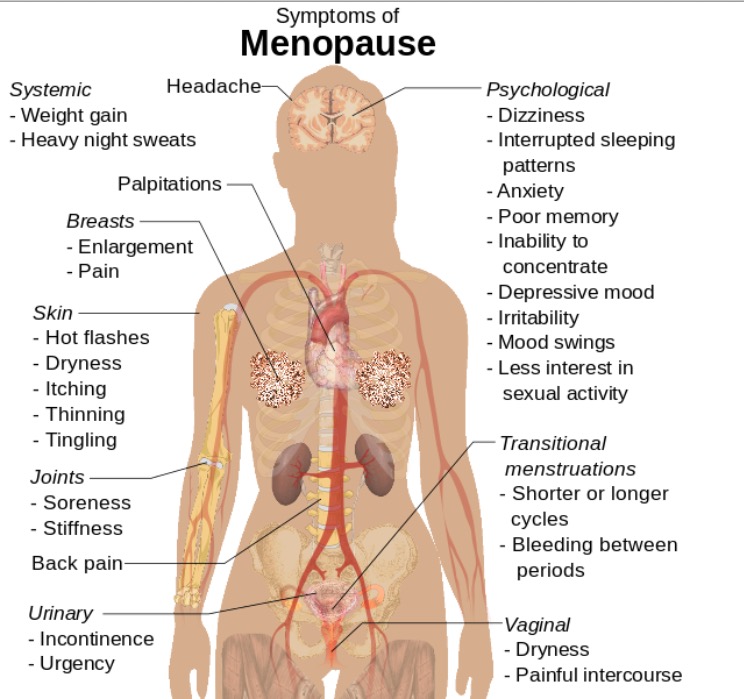
Symptoms of menopause that can also be seen in POI
Image: “Symptoms of menopause” by Mikael Häggström. License: CC0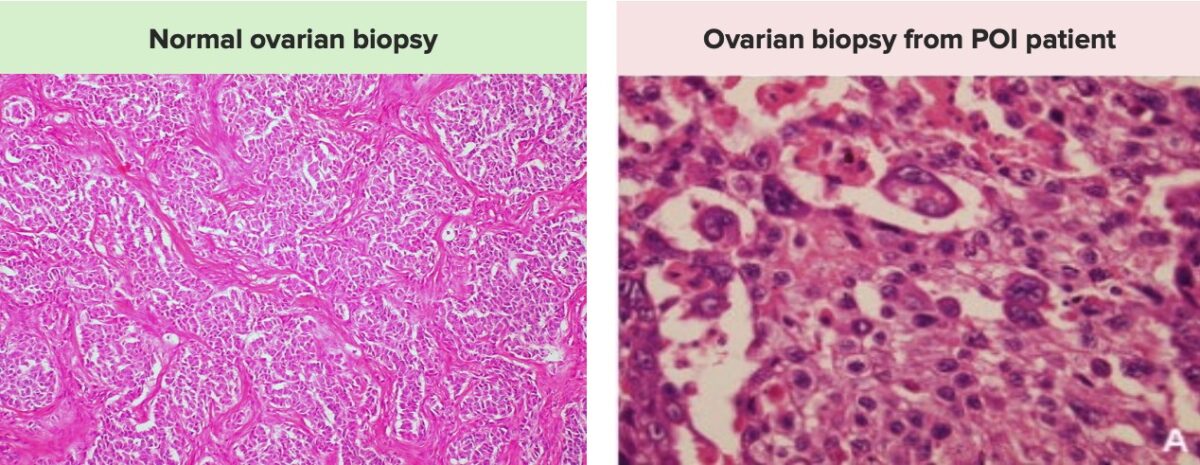
Images demonstrating the differences between a normal ovarian biopsy on the left, with a normal number of follicles, and an ovarian biopsy from a patient with POI on the right, showing a significantly decreased number of ovarian follicles and oocytes.
Note that ovarian biopsies are typically not obtained for diagnostic purposes.
Hormone replacement therapy Hormone Replacement Therapy Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause and in combination to suppress ovulation. Risks and side effects include uterine bleeding, predisposition to cancer, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine headaches, hypertension, bloating, and mood changes. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins ( HRT HRT Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause and in combination to suppress ovulation. Risks and side effects include uterine bleeding, predisposition to cancer, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine headaches, hypertension, bloating, and mood changes. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins) is required to prevent osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease. Regimens should include both estrogen Estrogen Compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of estradiol. Estrogens stimulate the female reproductive organs, and the development of secondary female sex characteristics. Estrogenic chemicals include natural, synthetic, steroidal, or non-steroidal compounds. Ovaries: Anatomy and progestins Progestins Compounds that interact with progesterone receptors in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of progesterone. Primary actions of progestins, including natural and synthetic steroids, are on the uterus and the mammary gland in preparation for and in maintenance of pregnancy. Hormonal Contraceptives.
Diagnosis Codes:
This code is used to diagnose
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency
Primary ovarian insufficiency
Cessation of ovarian function after menarche but before the age of 40, without or with ovarian follicle depletion. It is characterized by the presence of oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea, elevated gonadotropins, and low estradiol levels. It is a state of female hypergonadotropic hypogonadism. Etiologies include genetic defects, autoimmune processes, chemotherapy, radiation, and infections. The most commonly known genetic cause is the expansion of a cgg repeat to 55 to 199 copies in the 5′ untranslated region in the X-linked fmr1 gene.
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI), a condition where a woman’s
ovaries
Ovaries
Ovaries are the paired gonads of the female reproductive system that contain haploid gametes known as oocytes. The ovaries are located intraperitoneally in the pelvis, just posterior to the broad ligament, and are connected to the pelvic sidewall and to the uterus by ligaments. These organs function to secrete hormones (estrogen and progesterone) and to produce the female germ cells (oocytes).
Ovaries: Anatomy stop working normally before age 40, leading to
infertility
Infertility
Infertility is the inability to conceive in the context of regular intercourse. The most common causes of infertility in women are related to ovulatory dysfunction or tubal obstruction, whereas, in men, abnormal sperm is a common cause.
Infertility and symptoms of
menopause
Menopause
Menopause is a physiologic process in women characterized by the permanent cessation of menstruation that occurs after the loss of ovarian activity. Menopause can only be diagnosed retrospectively, after 12 months without menstrual bleeding.
Menopause.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | E28.310 | Primary ovarian failure |
| SNOMED CT | 65846001 | Premature ovarian failure Premature ovarian failure Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) is a condition resulting from the depletion or dysfunction of the ovarian follicles, leading to cessation of ovulation and menses before age 40. Primary ovarian insufficiency is primarily idiopathic. Patients present with signs and symptoms of menopause prior to age 40, including oligo- or amenorrhea, vaginal dryness (often leading to dyspareunia), and infertility. Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (disorder) |
Evaluation & Workup:
These codes are for the key hormonal tests to diagnose POI. The diagnosis is confirmed by finding elevated Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (
FSH
FSH
A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity.
Menstrual Cycle) levels on two separate occasions in a woman under 40 with irregular periods.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 83001 | Gonadotropin; follicle stimulating hormone ( FSH FSH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Follicle-stimulating hormone stimulates gametogenesis and the supporting cells such as the ovarian granulosa cells, the testicular sertoli cells, and leydig cells. Fsh consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle) |
| CPT | 82670 | Estradiol Estradiol The 17-beta-isomer of estradiol, an aromatized C18 steroid with hydroxyl group at 3-beta- and 17-beta-position. Estradiol-17-beta is the most potent form of mammalian estrogenic steroids. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins |
Medications:
This code is for
estradiol
Estradiol
The 17-beta-isomer of estradiol, an aromatized C18 steroid with hydroxyl group at 3-beta- and 17-beta-position. Estradiol-17-beta is the most potent form of mammalian estrogenic steroids.
Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins, the primary component of
hormone replacement therapy
Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause and in combination to suppress ovulation. Risks and side effects include uterine bleeding, predisposition to cancer, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine headaches, hypertension, bloating, and mood changes.
Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins (
HRT
HRT
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause and in combination to suppress ovulation. Risks and side effects include uterine bleeding, predisposition to cancer, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine headaches, hypertension, bloating, and mood changes.
Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins), which is the main treatment for POI to manage menopausal symptoms and reduce long-term health risks like
osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications.
Osteoporosis.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 4099 | Estradiol Estradiol The 17-beta-isomer of estradiol, an aromatized C18 steroid with hydroxyl group at 3-beta- and 17-beta-position. Estradiol-17-beta is the most potent form of mammalian estrogenic steroids. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins (ingredient) |