Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic disease resulting in autoimmune destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts. The typical presentation is that of a middle-aged woman with pruritus, fatigue, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Elevated liver enzymes and antimitochondrial antibodies (AMAs) establish the diagnosis. Medical management includes ursodeoxycholic acid as the 1st-line treatment and for symptom management. Definitive treatment is liver transplantation Liver transplantation The transference of a part of or an entire liver from one human or animal to another. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases, which is performed in late stages ( cirrhosis Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a late stage of hepatic parenchymal necrosis and scarring (fibrosis) most commonly due to hepatitis C infection and alcoholic liver disease. Patients may present with jaundice, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cirrhosis can also cause complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, and hepatorenal syndrome. Cirrhosis).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
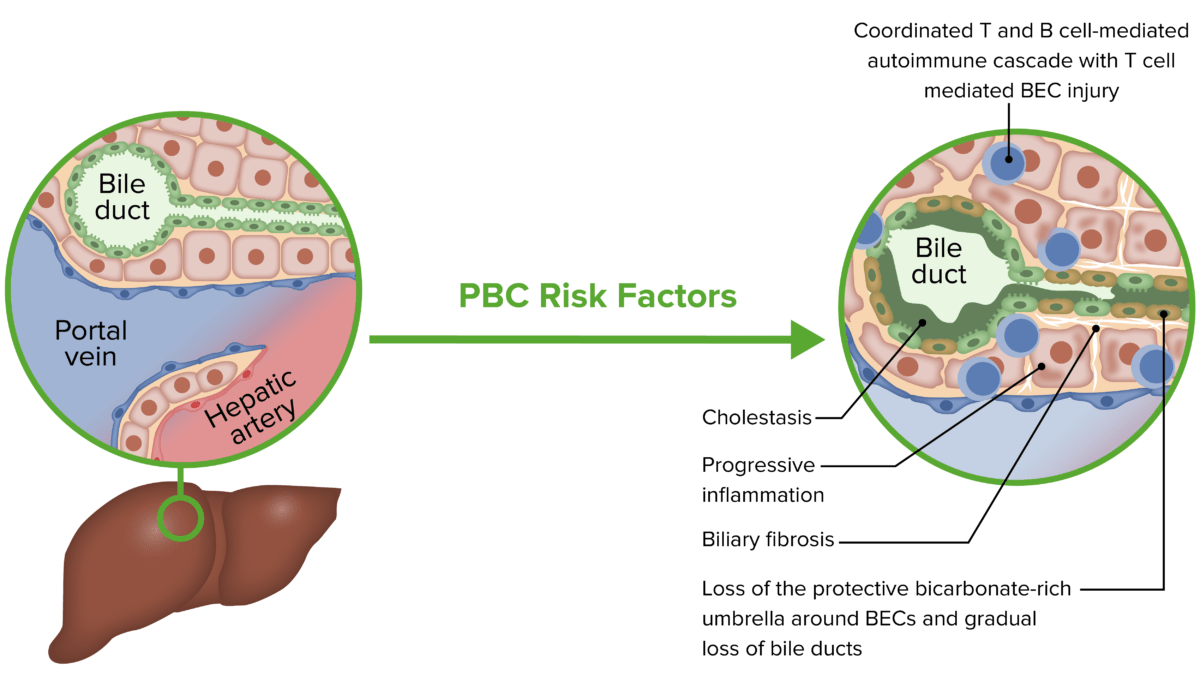
Pathophysiology of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC):
A risk factor or trigger may lead to a coordinated T and B cell-mediated response, resulting in biliary epithelial cell (BEC) injury, cholestasis, and fibrosis.
Primary biliary cholangitis has a wide range of symptoms. The condition is often asymptomatic in the early phase and features symptoms of decompensated cirrhosis Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a late stage of hepatic parenchymal necrosis and scarring (fibrosis) most commonly due to hepatitis C infection and alcoholic liver disease. Patients may present with jaundice, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cirrhosis can also cause complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, and hepatorenal syndrome. Cirrhosis in the late phase Late Phase Sepsis in Children.
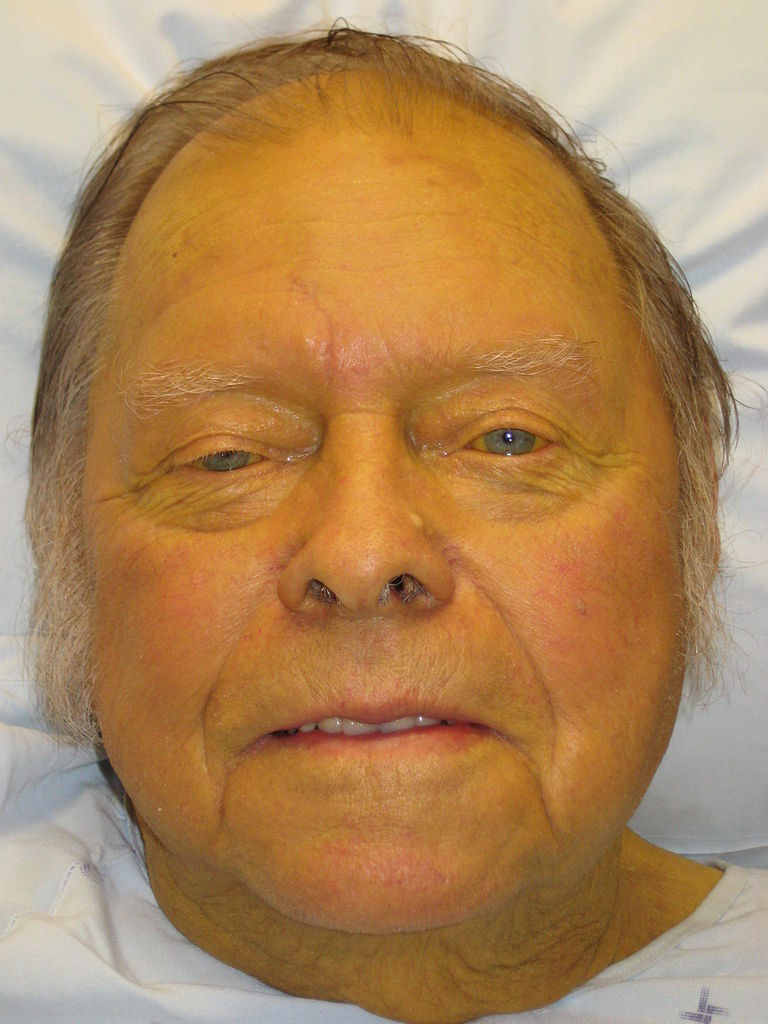
Jaundice: yellow discoloration of the skin due to bilirubin deposition
Image: “Jaundice08” by James Heilman, MD. License: CC BY 3.0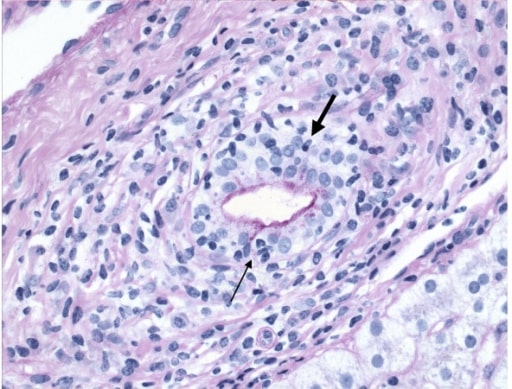
Primary biliary cirrhosis, demonstrating chronic nonsuppurative destructive cholangitis: Infiltration of lymphocyte (arrow) and plasma cell (bold arrow) into the bile duct is shown.
Image: “Primary biliary cirrhosis” by Department of Medicine, Toronto Western Hospital (University Health Network/University of Toronto), Toronto, Ontario, Canada. License: CC BY 2.0