Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM), previously known as premature Premature Childbirth before 37 weeks of pregnancy (259 days from the first day of the mother's last menstrual period, or 245 days after fertilization). Necrotizing Enterocolitis rupture of membranes, refers to the rupture of the amniotic sac before the onset of labor. Prelabor rupture of membranes may occur in term or preterm pregnancies. The presentation includes a painless discharge of clear or pale-yellow fluid from the vagina Vagina The vagina is the female genital canal, extending from the vulva externally to the cervix uteri internally. The structures have sexual, reproductive, and urinary functions and a rich blood supply, mainly arising from the internal iliac artery. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy in the form of a large gush or as small, intermittent trickles. Management depends on gestational age Gestational age The age of the conceptus, beginning from the time of fertilization. In clinical obstetrics, the gestational age is often estimated as the time from the last day of the last menstruation which is about 2 weeks before ovulation and fertilization. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. Beyond 34 weeks, the recommendation is to induce labor and, if indicated, use antibiotics for group B streptococcus Group B Streptococcus Meningitis in Children ( GBS GBS An acute inflammatory autoimmune neuritis caused by t cell- mediated cellular immune response directed towards peripheral myelin. Demyelination occurs in peripheral nerves and nerve roots. The process is often preceded by a viral or bacterial infection, surgery, immunization, lymphoma, or exposure to toxins. Common clinical manifestations include progressive weakness, loss of sensation, and loss of deep tendon reflexes. Weakness of respiratory muscles and autonomic dysfunction may occur. Polyneuropathy) prophylaxis Prophylaxis Cephalosporins. Prior to 34 weeks, management involves prolonging the pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care as long as possible while avoiding intra-amniotic infection (IAI), also known as chorioamnionitis Chorioamnionitis Chorioamnionitis, commonly referred to as intraamniotic infection (IAI), is a common obstetric complication involving infection and inflammation of the fetal membranes, amniotic fluid, placenta, or the fetus itself. Chorioamnionitis is typically caused by a polymicrobial infection that ascends from the lower genitourinary tract. Chorioamnionitis, and minimizing risk to the fetus. The primary complications associated with PROM are related to infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease and preterm birth Preterm birth Preterm labor refers to regular uterine contractions leading to cervical change prior to 37 weeks of gestation; preterm birth refers to birth prior to 37 weeks of gestation. Preterm birth may be spontaneous due to preterm labor, preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM), or cervical insufficiency. Preterm Labor and Birth.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Prelabor rupture of membranes (PROM) is defined as the rupture of fetal membranes (the fused chorion Chorion The outermost extraembryonic membrane surrounding the developing embryo. In reptiles and birds, it adheres to the shell and allows exchange of gases between the egg and its environment. In mammals, the chorion evolves into the fetal contribution of the placenta. Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity and amnion Amnion The innermost membranous sac that surrounds and protects the developing embryo which is bathed in the amniotic fluid. Amnion cells are secretory epithelial cells and contribute to the amniotic fluid. Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity) before the onset of labor ( regular Regular Insulin uterine contractions causing cervical change).
Prelabor rupture of membranes complicates approximately 2%–3% of pregnancies.
Risk factors:
| Pre-viable PROM | Preterm PROM (PPROM) | Term PROM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational age Gestational age The age of the conceptus, beginning from the time of fertilization. In clinical obstetrics, the gestational age is often estimated as the time from the last day of the last menstruation which is about 2 weeks before ovulation and fertilization. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care | < 24 weeks | 24–36 weeks | > 37 weeks |
| Frequency | < 1% of pregnancies |
|
~ 8% of pregnancies |
The fetal membranes create the amniotic sac to surround the fetus and protect it from infection.
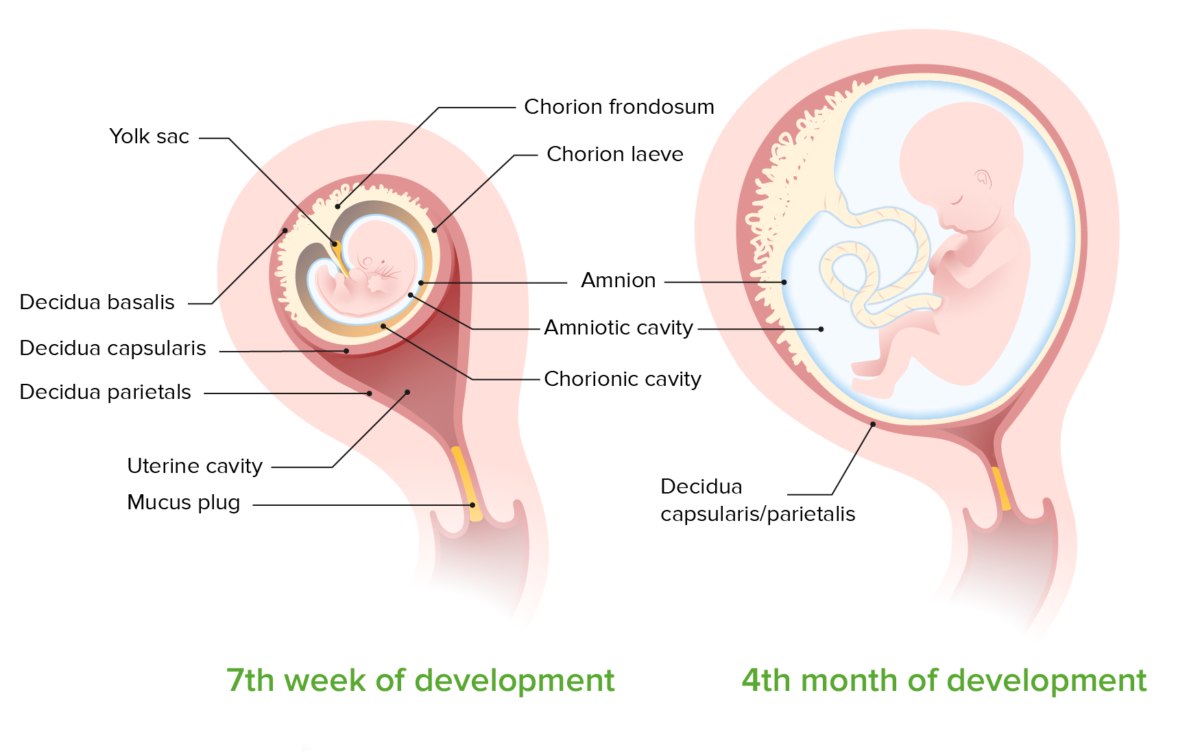
Fetal membranes at 7 weeks and 4 months of development:
The membranes arise from trophoblastic and mesodermal tissue. Early in pregnancy, the chorion and amnion are 2 distinct layers with a cavity between. As the pregnancy progresses, the 2 layers fuse to form a single amniochorion in direct contact with the maternal decidua.
Once labor is excluded, a sterile Sterile Basic Procedures speculum exam and ultrasound should be performed to diagnose PROM.
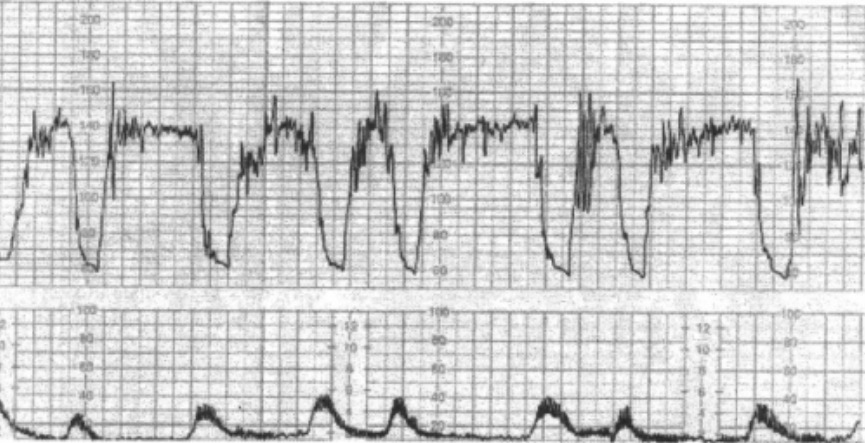
Intrapartum fetal monitoring with tocometry:
The bottom panel shows tocometry (records uterine contractions). The upper panel shows the fetal heart rate (baseline of around 140/min) with moderate variability and late heart rate decelerations (descent time > 60 sec with nadir after the peak of the contraction, and slow return up to baseline of 140). The tracing is from a case of fetal cord prolapse through the cervix (a potential complication of PROM), which compromises fetal blood flow. The fetal heart rate pattern is nonreassuring.
Management is based on gestational age Gestational age The age of the conceptus, beginning from the time of fertilization. In clinical obstetrics, the gestational age is often estimated as the time from the last day of the last menstruation which is about 2 weeks before ovulation and fertilization. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care, group B streptococcus Group B Streptococcus Meningitis in Children ( GBS GBS An acute inflammatory autoimmune neuritis caused by t cell- mediated cellular immune response directed towards peripheral myelin. Demyelination occurs in peripheral nerves and nerve roots. The process is often preceded by a viral or bacterial infection, surgery, immunization, lymphoma, or exposure to toxins. Common clinical manifestations include progressive weakness, loss of sensation, and loss of deep tendon reflexes. Weakness of respiratory muscles and autonomic dysfunction may occur. Polyneuropathy) status, signs of labor or contractions, and signs of IAI.
Fetal age ≥ 37 weeks:
Fetal age 34 0/7–36 6/7 weeks:
Fetal age 24–33 6/7 weeks:
Fetal age < 24 weeks:
Complications can be related to: