Prader-Willi syndrome ( PWS PWS A vascular malformation of developmental origin characterized pathologically by ectasia of superficial dermal capillaries, and clinically by persistent macular erythema. In the past, port wine stains have frequently been termed capillary hemangiomas, which they are not; unfortunately this confusing practice persists: hemangioma, capillary is neoplastic, a port-wine stain is non-neoplastic. Port-wine stains vary in color from fairly pale pink to deep red or purple and in size from a few millimeters to many centimeters in diameter. The face is the most frequently affected site and they are most often unilateral. Sturge-Weber Syndrome (SWS)) and Angelman syndrome (AS) are both rare autosomal neurodevelopmental genetic disorders mapped to a specific region of chromosome 15 Chromosome 15 Marfan Syndrome attributed to genomic imprinting Imprinting The variable phenotypic expression of a gene depending on whether it is of paternal or maternal origin, which is a function of the DNA methylation pattern. Imprinted regions are observed to be more methylated and less transcriptionally active. Epigenetic Regulation. This means that the phenotype Phenotype The complete genetic complement contained in the DNA of a set of chromosomes in a human. The length of the human genome is about 3 billion base pairs. Basic Terms of Genetics depends on the gender Gender Gender Dysphoria of the parent donating the genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure. A paternally derived chromosome 15 Chromosome 15 Marfan Syndrome with this deletion results in 15q11-13 paternal deletion syndrome, or PWS PWS A vascular malformation of developmental origin characterized pathologically by ectasia of superficial dermal capillaries, and clinically by persistent macular erythema. In the past, port wine stains have frequently been termed capillary hemangiomas, which they are not; unfortunately this confusing practice persists: hemangioma, capillary is neoplastic, a port-wine stain is non-neoplastic. Port-wine stains vary in color from fairly pale pink to deep red or purple and in size from a few millimeters to many centimeters in diameter. The face is the most frequently affected site and they are most often unilateral. Sturge-Weber Syndrome (SWS), whereas a maternally derived chromosome 15 Chromosome 15 Marfan Syndrome with a similar deletion is associated with AS. Diagnosis is established with genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies. Management is mostly supportive and is focused on early intervention for developmental, neurologic, and physical abnormalities.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Prader-Willi syndrome ( PWS PWS A vascular malformation of developmental origin characterized pathologically by ectasia of superficial dermal capillaries, and clinically by persistent macular erythema. In the past, port wine stains have frequently been termed capillary hemangiomas, which they are not; unfortunately this confusing practice persists: hemangioma, capillary is neoplastic, a port-wine stain is non-neoplastic. Port-wine stains vary in color from fairly pale pink to deep red or purple and in size from a few millimeters to many centimeters in diameter. The face is the most frequently affected site and they are most often unilateral. Sturge-Weber Syndrome (SWS)) is a condition associated with loss of the paternal chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 15q11-13 region and is characterized by intellectual disability Disability Determination of the degree of a physical, mental, or emotional handicap. The diagnosis is applied to legal qualification for benefits and income under disability insurance and to eligibility for social security and workman’s compensation benefits. ABCDE Assessment, short stature, underdevelopment of the sexual organs, and obesity Obesity Obesity is a condition associated with excess body weight, specifically with the deposition of excessive adipose tissue. Obesity is considered a global epidemic. Major influences come from the western diet and sedentary lifestyles, but the exact mechanisms likely include a mixture of genetic and environmental factors. Obesity.
Angelman syndrome (AS) is a disorder associated with loss of the maternal chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 15q11-13 region and is characterized by severe neurodevelopmental delay.
Both PWS PWS A vascular malformation of developmental origin characterized pathologically by ectasia of superficial dermal capillaries, and clinically by persistent macular erythema. In the past, port wine stains have frequently been termed capillary hemangiomas, which they are not; unfortunately this confusing practice persists: hemangioma, capillary is neoplastic, a port-wine stain is non-neoplastic. Port-wine stains vary in color from fairly pale pink to deep red or purple and in size from a few millimeters to many centimeters in diameter. The face is the most frequently affected site and they are most often unilateral. Sturge-Weber Syndrome (SWS) and AS are associated with genomic imprinting Imprinting The variable phenotypic expression of a gene depending on whether it is of paternal or maternal origin, which is a function of the DNA methylation pattern. Imprinted regions are observed to be more methylated and less transcriptionally active. Epigenetic Regulation, which is the differential expression of certain genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure based on inheritance from a specific parent.
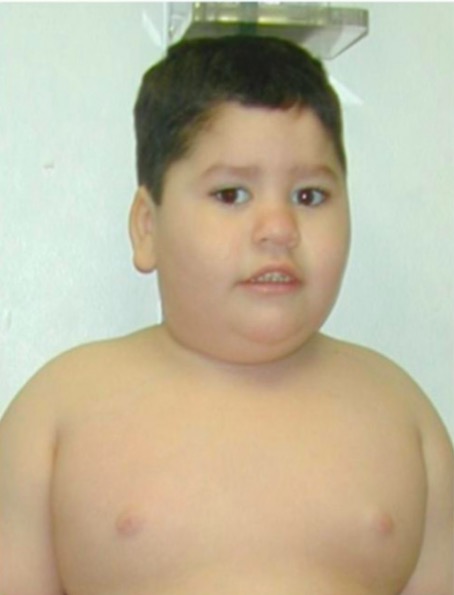
Prader-Willi syndrome:
typical facial features and truncal obesity
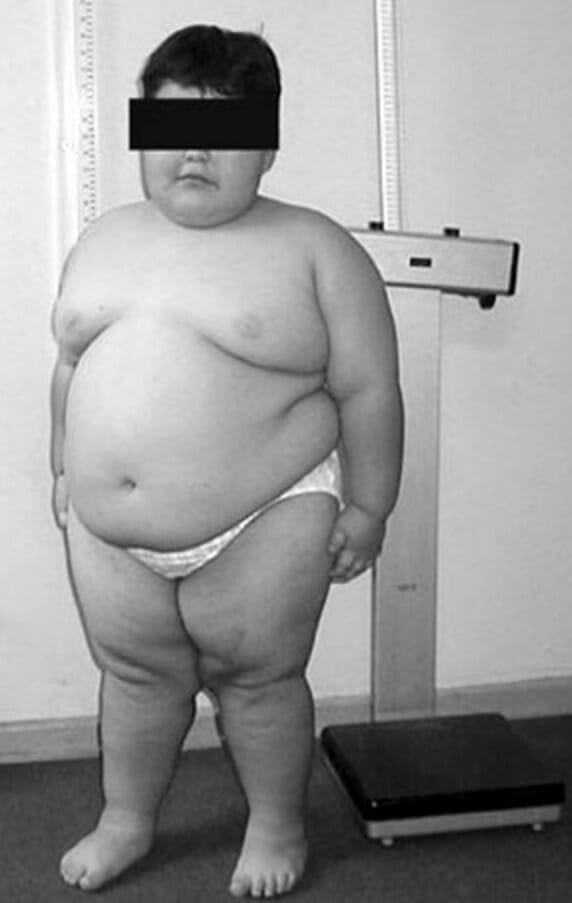
An 8-year-old child with Prader-Willi syndrome exhibiting characteristic truncal obesity
Image: “PWS8” by Fanny Cortés M1 et al. License: CC BY4.0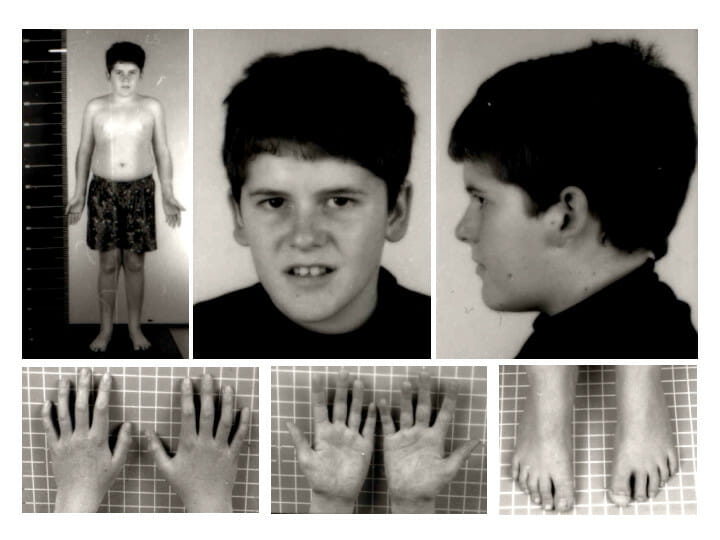
Prader-Willi syndrome phenotype at 15 years of age: Note the absence of typical Prader-Willi syndrome facial features and the presence of mild truncal obesity.
Image: “Pws” by Schüle B et al. License: CC BY 2.0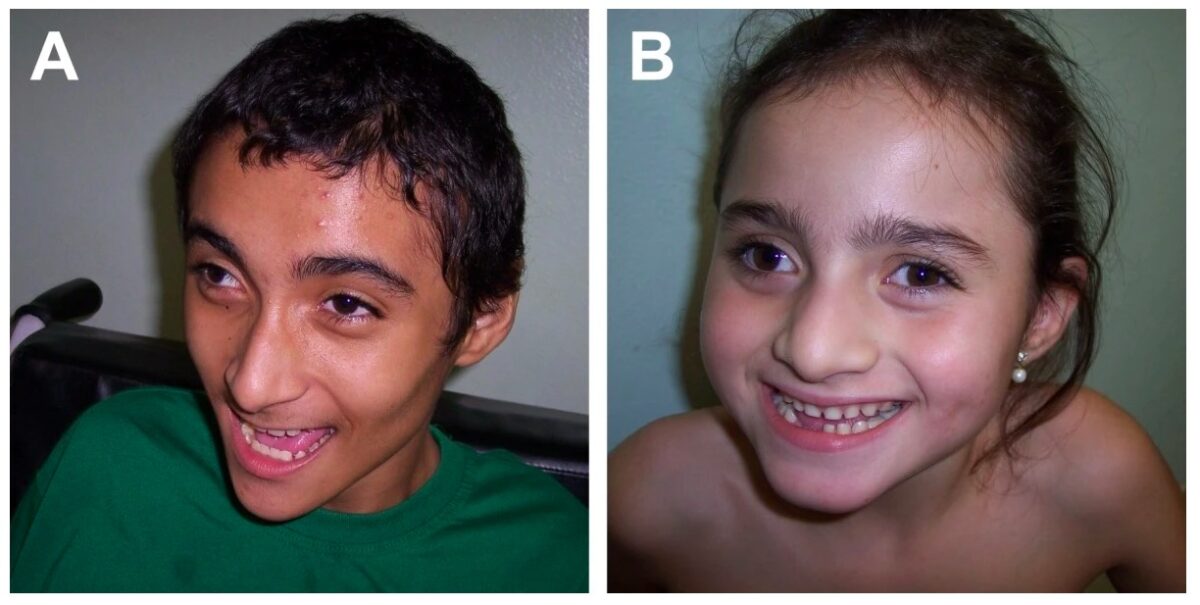
Angelman syndrome: typical craniofacial features, happy demeanor
Image: “Angelman syndrome” by Department of Genetics, Medical School of Ribeirao Preto, University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil. License: CC BY 2.0