Posttraumatic stress disorder is a psychiatric illness characterized by overwhelming stress and anxiety Anxiety Feelings or emotions of dread, apprehension, and impending disaster but not disabling as with anxiety disorders. Generalized Anxiety Disorder experienced after exposure to a life-threatening event. Symptoms last more than 1 month and involve re-experiencing the event as flashbacks or nightmares, avoiding reminders of the event, irritability, hyperarousal, and poor memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment and concentration. Treatment is mainly based on CBT and eye movement desensitization. Pharmacological regimens, such as antidepressants, might be indicated in some cases.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Posttraumatic stress disorder is a severe, chronic psychiatric disorder that develops after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. The response to the trauma lasts more than 1 month and often includes severe fear manifesting as intrusive thoughts, flashbacks, or nightmares, which in turn negatively impact the patient’s life.
Alterations in brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification physiology:
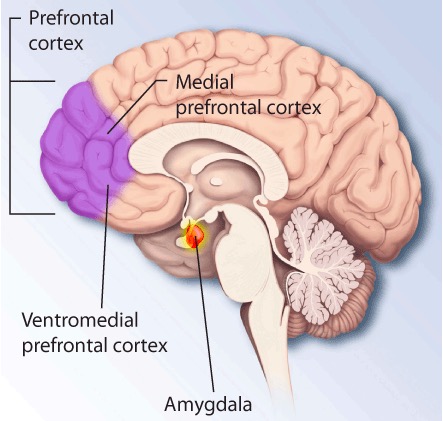
Brain regions that are affected by PTSD
Image: “PTSD brain” by The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH). License: Public DomainAlteration in functioning of neuro-hormonal and neuro-transmitter functioning:
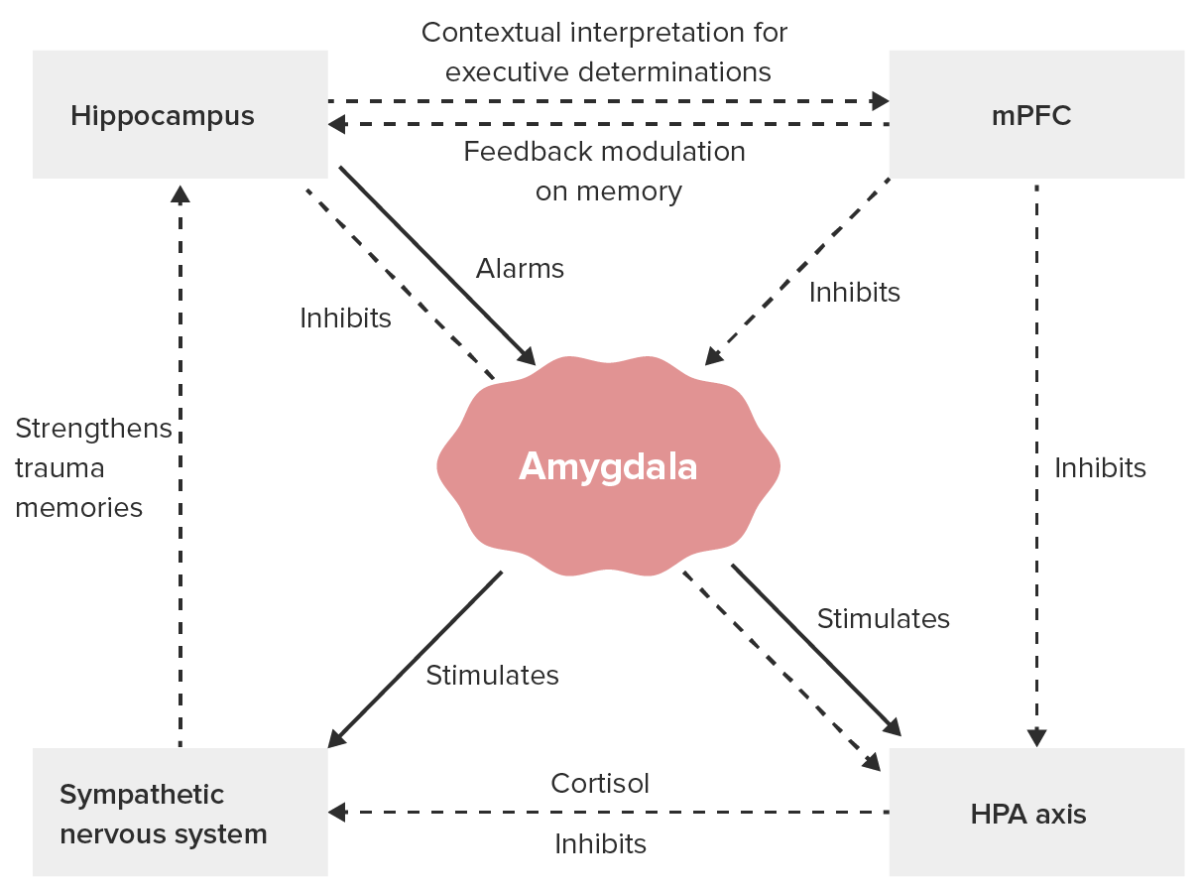
Major neurobiological processes in PTSD:
HPA: hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal
mPFC: medial prefrontal cortex
Diagnosis is clinical. Laboratory investigations or imaging studies are performed to exclude other medical conditions or for research Research Critical and exhaustive investigation or experimentation, having for its aim the discovery of new facts and their correct interpretation, the revision of accepted conclusions, theories, or laws in the light of newly discovered facts, or the practical application of such new or revised conclusions, theories, or laws. Conflict of Interest purposes.