Postinfectious glomerulonephritis (GN) is a type of nephritis classically caused by a prior infection with group A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus , which is referred to as poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN). The clinical presentation of PSGN can range from asymptomatic, microscopic hematuria to full-blown acute nephritic syndrome, which is characterized by red-to-brown urine, proteinuria, edema, and acute kidney injury. The diagnosis is made based on clinical findings in the setting of recent group A Streptococcus (GAS) infection. Management is supportive and involves treating the clinical manifestations. The prognosis is generally favorable (especially in children), typically with spontaneous resolution.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
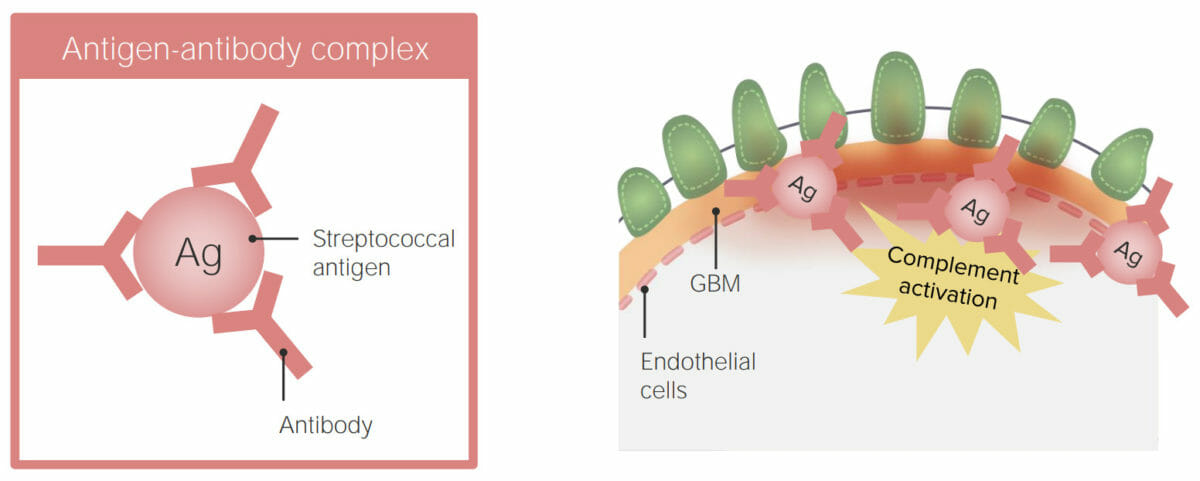
Suspected pathophysiology of postinfectious glomerulonephritis: immune complex deposition in the glomerular basement membrane (GBM)
Image by Lecturio.Individual’s history:
Physical exam findings:
Lab findings:
Renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis:
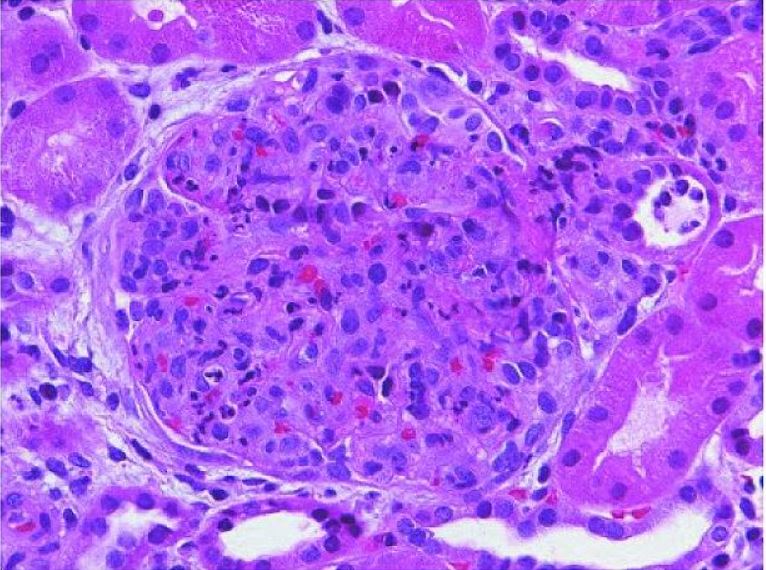
Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis:
The glomerulus shows hypercellularity with infiltrating monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (H&E stain).
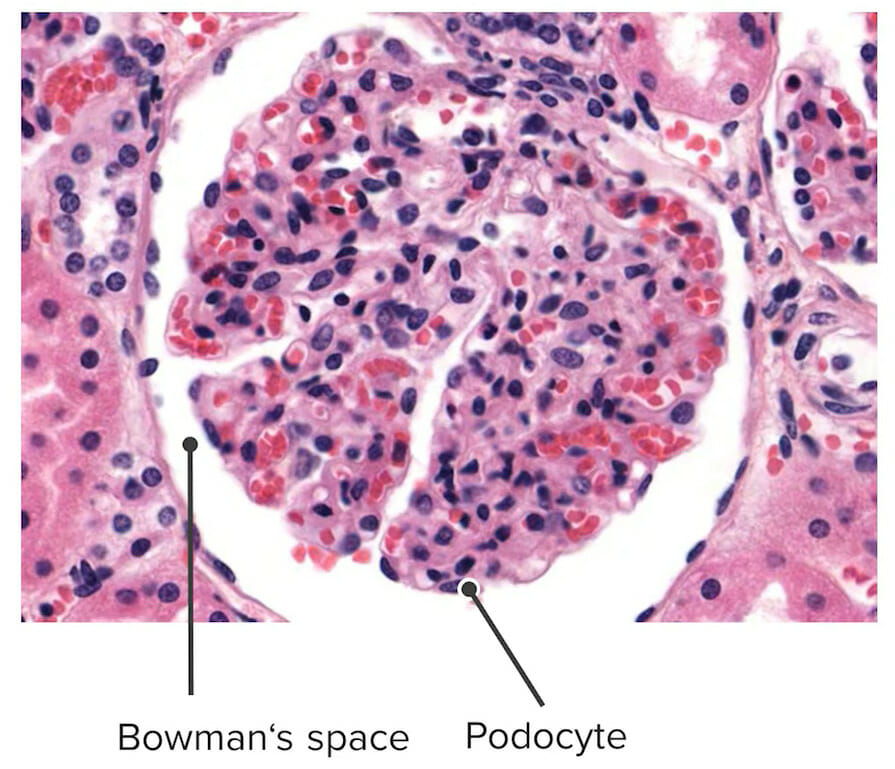
Normal glomerulus
Image by Lecturio.