After any procedure performed in the operating room, all patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship must undergo close observation at least in the recovery room. After larger procedures and for patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship who require hospitalization Hospitalization The confinement of a patient in a hospital. Delirium, observation must continue on the surgical ward. The primary intent of this practice is the early detection of postoperative complications. The entire medical team must be vigilant and aware of the patient’s history, the procedure performed, and risk factors for potential complications. Some of the most important things to attend to include monitoring vital signs (which may indicate severe complications such as bleeding), wound and drain care, postoperative pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways control, nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics and vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia, pulmonary hygiene to prevent atelectasis Atelectasis Atelectasis is the partial or complete collapse of a part of the lung. Atelectasis is almost always a secondary phenomenon from conditions causing bronchial obstruction, external compression, surfactant deficiency, or scarring. Atelectasis, deep vein thrombosis Thrombosis Formation and development of a thrombus or blood clot in the blood vessel. Epidemic Typhus prophylaxis Prophylaxis Cephalosporins, and fluid management.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The recovery room is reserved for patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship in the immediate postoperative period who have received general anesthesia General anesthesia Procedure in which patients are induced into an unconscious state through use of various medications so that they do not feel pain during surgery. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts. Observation usually lasts 6 hours (until they are conscious and their vital signs are stable).
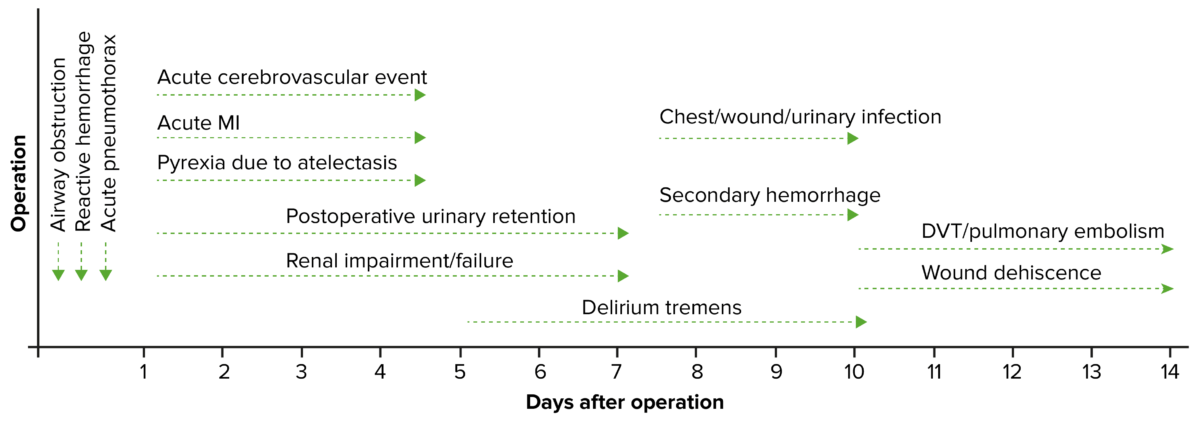
Timeline of postoperative complications
DVT: deep vein thrombosis
MI: myocardial infarction
The patient is moved to the surgical ward for continued observation.
All patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship should be physically evaluated by a member of the surgical team at least once daily (if not more often).
Wound infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease can affect either the superficial or the deep incisional spaces. Pressure sores may also develop in immobile patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship.
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are typically ready for discharge when they meet the following criteria:
Review all restrictions and instructions with patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship prior to discharge:
Ensure patient is set up with:
Most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship should have a postoperative appointment around 7–14 days after discharge:
The following conditions include common complications that can occur in any patient undergoing a surgical procedure that requires general anesthesia General anesthesia Procedure in which patients are induced into an unconscious state through use of various medications so that they do not feel pain during surgery. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts.