Posterior cord syndrome (PCS) refers to a group of symptoms caused by an incomplete spinal cord injury that affects the dorsal columns, the corticospinal tracts Corticospinal Tracts Central Cord Syndrome ( CSTs CSTs Central Cord Syndrome), and descending autonomic tracts to the bladder Bladder A musculomembranous sac along the urinary tract. Urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters, and is held there until urination. Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess. Posterior cord syndrome is rare but has a diverse range of etiologies, including demyelinating disorders, degenerative spinal conditions, neoplasms Neoplasms New abnormal growth of tissue. Malignant neoplasms show a greater degree of anaplasia and have the properties of invasion and metastasis, compared to benign neoplasms. Benign Bone Tumors, vascular abnormalities, and hereditary neurodegenerative disorders. Clinical symptoms include gait ataxia Gait ataxia Impairment of the ability to coordinate the movements required for normal ambulation (walking) which may result from impairments of motor function or sensory feedback. This condition may be associated with brain diseases (including cerebellar diseases and basal ganglia diseases); spinal cord diseases; or peripheral nervous system diseases. Friedreich Ataxia, paresthesias with loss of position and vibration Vibration A continuing periodic change in displacement with respect to a fixed reference. Neurological Examination sense, and urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence (UI) is involuntary loss of bladder control or unintentional voiding, which represents a hygienic or social problem to the patient. Urinary incontinence is a symptom, a sign, and a disorder. The 5 types of UI include stress, urge, mixed, overflow, and functional. Urinary Incontinence. The diagnosis is made clinically and with neuroimaging Neuroimaging Non-invasive methods of visualizing the central nervous system, especially the brain, by various imaging modalities. Febrile Infant. Management addresses treatment of the underlying cause.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Posterior cord syndrome refers to a group of symptoms caused by an incomplete spinal cord Spinal cord The spinal cord is the major conduction pathway connecting the brain to the body; it is part of the CNS. In cross section, the spinal cord is divided into an H-shaped area of gray matter (consisting of synapsing neuronal cell bodies) and a surrounding area of white matter (consisting of ascending and descending tracts of myelinated axons). Spinal Cord: Anatomy injury that affects the dorsal columns, the corticospinal tracts Corticospinal Tracts Central Cord Syndrome ( CSTs CSTs Central Cord Syndrome), and descending autonomic tracts to the bladder Bladder A musculomembranous sac along the urinary tract. Urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters, and is held there until urination. Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess.
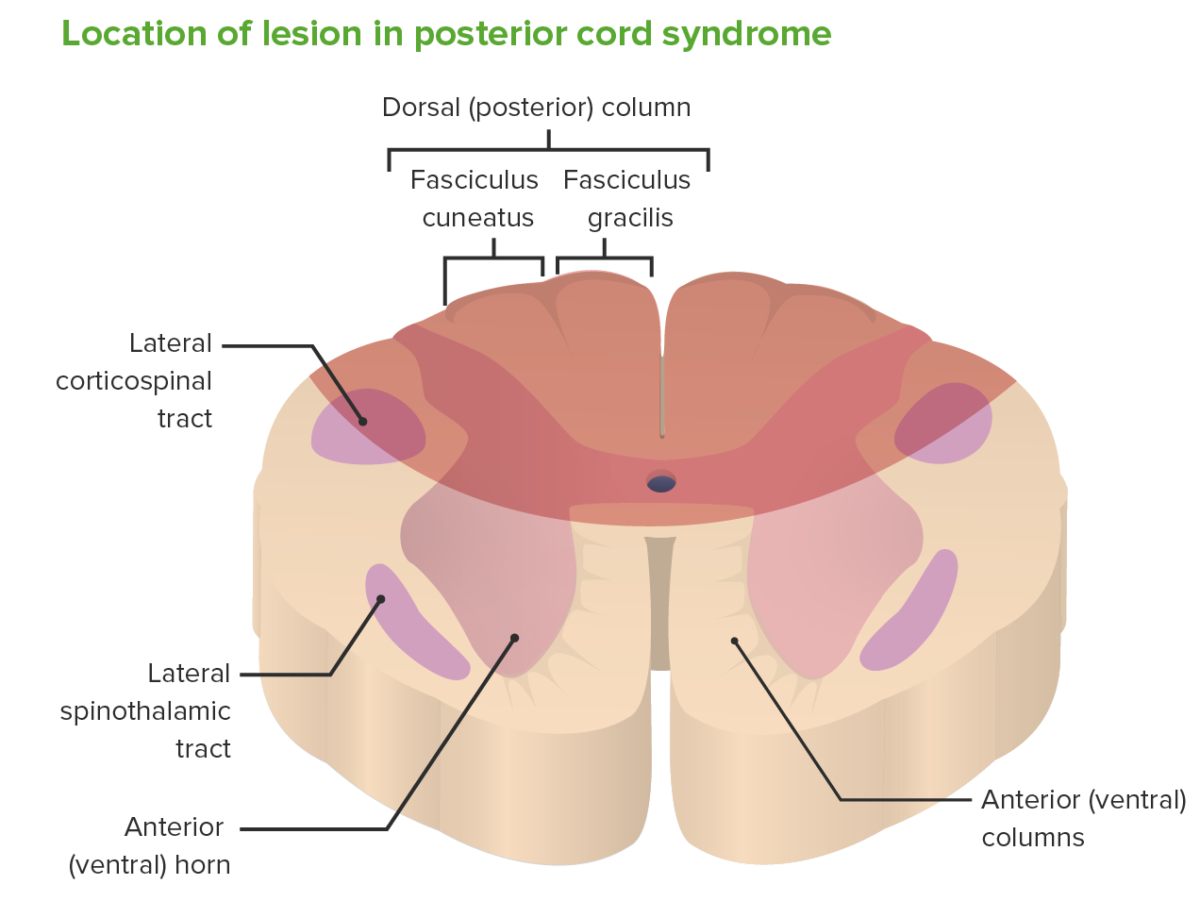
Area affected by posterior cord syndrome
Image by Lecturio.Understanding the structures affected by a posterior cord lesion is essential to their correlation Correlation Determination of whether or not two variables are correlated. This means to study whether an increase or decrease in one variable corresponds to an increase or decrease in the other variable. Causality, Validity, and Reliability with clinical signs and symptoms. Diagnosis of PCS is by clinical exam and diagnostic imaging.
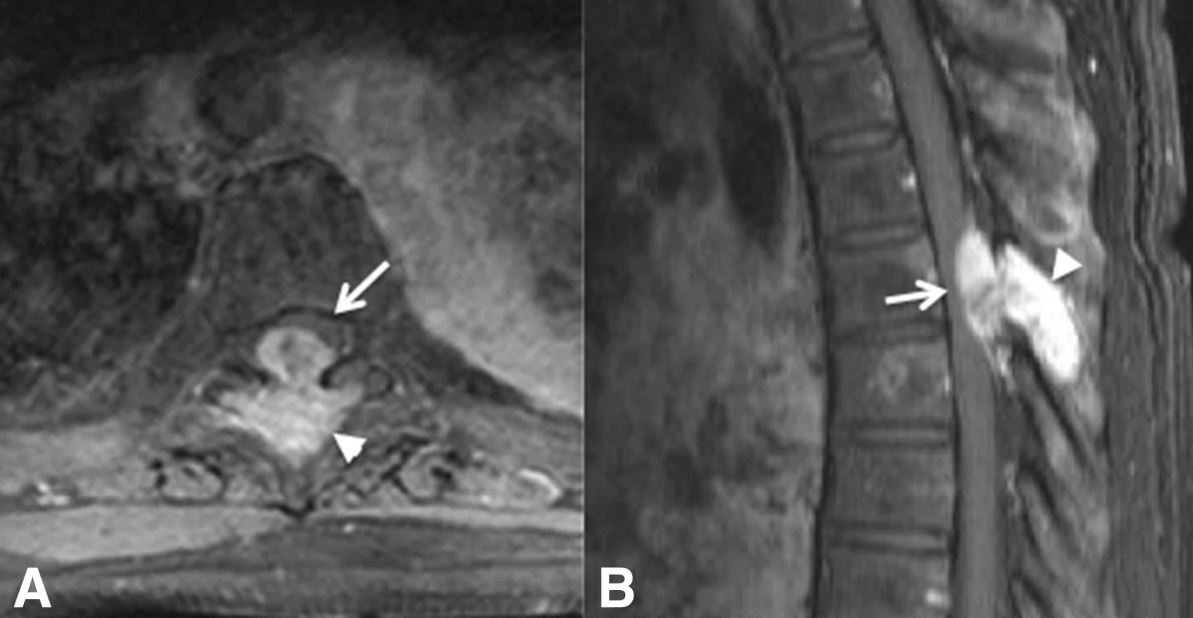
Axial (A) and sagittal (B) MRIs of a patient with posterior cord syndrome due to breast cancer metastasis to the spine:
The arrows and arrowheads show a bony lesion emerging from the spine and compressing the posterior aspect of the spinal cord.