The popliteal fossa or the “knee pit” is a diamond-shaped, fat-filled, shallow depression on the posterior aspect of the knee joint Knee joint The knee joint is made up of the articulations between the femur, tibia, and patella bones, and is one of the largest and most complex joints of the human body. The knee is classified as a synovial hinge joint, which primarily allows for flexion and extension with a more limited degree of translation and rotation. Knee Joint: Anatomy. The popliteal fossa is located at the dorsal aspect of the knee and contains an increased number of lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 - 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy as well as structures of the neurovascular system that travel from the thigh Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb found between the hip and the knee joint. There is a single bone in the thigh called the femur, which is surrounded by large muscles grouped into 3 fascial compartments. Thigh: Anatomy to the lower leg Leg The lower leg, or just "leg" in anatomical terms, is the part of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle joint. The bony structure is composed of the tibia and fibula bones, and the muscles of the leg are grouped into the anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments by extensions of fascia. Leg: Anatomy. The boundaries are formed by various muscles of the thigh Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb found between the hip and the knee joint. There is a single bone in the thigh called the femur, which is surrounded by large muscles grouped into 3 fascial compartments. Thigh: Anatomy and leg Leg The lower leg, or just "leg" in anatomical terms, is the part of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle joint. The bony structure is composed of the tibia and fibula bones, and the muscles of the leg are grouped into the anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments by extensions of fascia. Leg: Anatomy.
Last updated: Nov 19, 2024
Multiple muscles of the dorsal thigh Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb found between the hip and the knee joint. There is a single bone in the thigh called the femur, which is surrounded by large muscles grouped into 3 fascial compartments. Thigh: Anatomy and lower leg Leg The lower leg, or just “leg” in anatomical terms, is the part of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle joint. The bony structure is composed of the tibia and fibula bones, and the muscles of the leg are grouped into the anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments by extensions of fascia. Leg: Anatomy form the majority of the boundaries of the popliteal fossa.
| Boundaries | Structures |
|---|---|
| Superolaterally |
|
| Superomedially |
|
| Inferolaterally |
|
| Inferomedially |
|
| Roof |
|
| Floor |
|
The boundaries of the popliteal fossa
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio.| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Innervation | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semimembranosus Semimembranosus Thigh: Anatomy |
|
Medial condyle of the tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy | Tibial nerve |
|
| Semitendinosus Semitendinosus Thigh: Anatomy | Superomedial surface of the tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy | |||
| Biceps femoris Biceps femoris Thigh: Anatomy |
|
Head of the fibula Fibula The bone of the lower leg lateral to and smaller than the tibia. In proportion to its length, it is the most slender of the long bones. Leg: Anatomy and the lateral tibial condyle |
|
|
| Gastrocnemius Gastrocnemius Leg: Anatomy |
|
Helps form the calcaneal or Achilles tendon, inserted into the posterior aspect of the calcaneus Calcaneus The largest of the tarsal bones which is situated at the lower and back part of the foot, forming the heel. Foot: Anatomy bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types |
|
|
| Popliteus |
|
Tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy, below the medial tibial condyle |
|
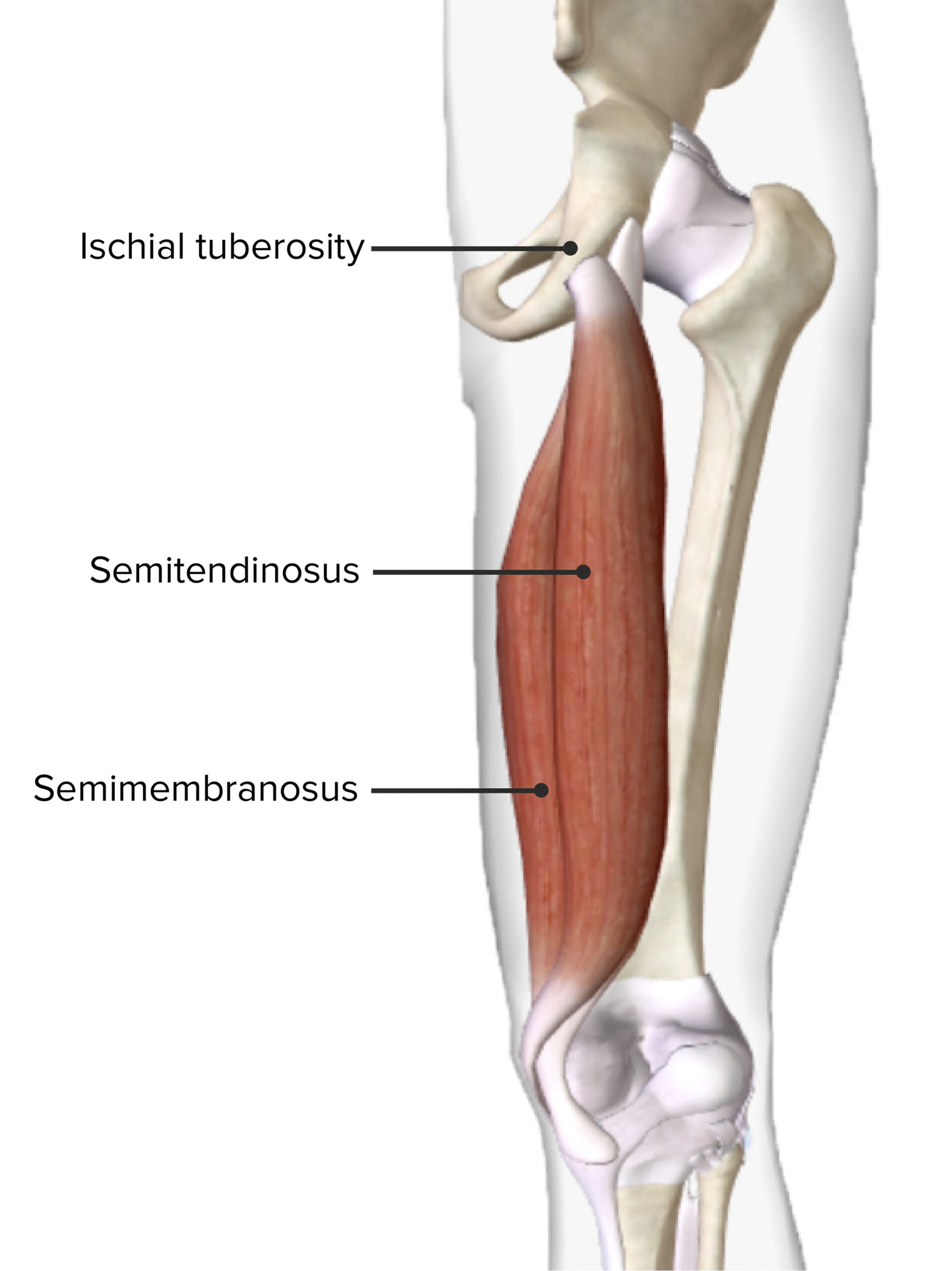
Posterior view of the right thigh featuring the origin and insertion of the semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles
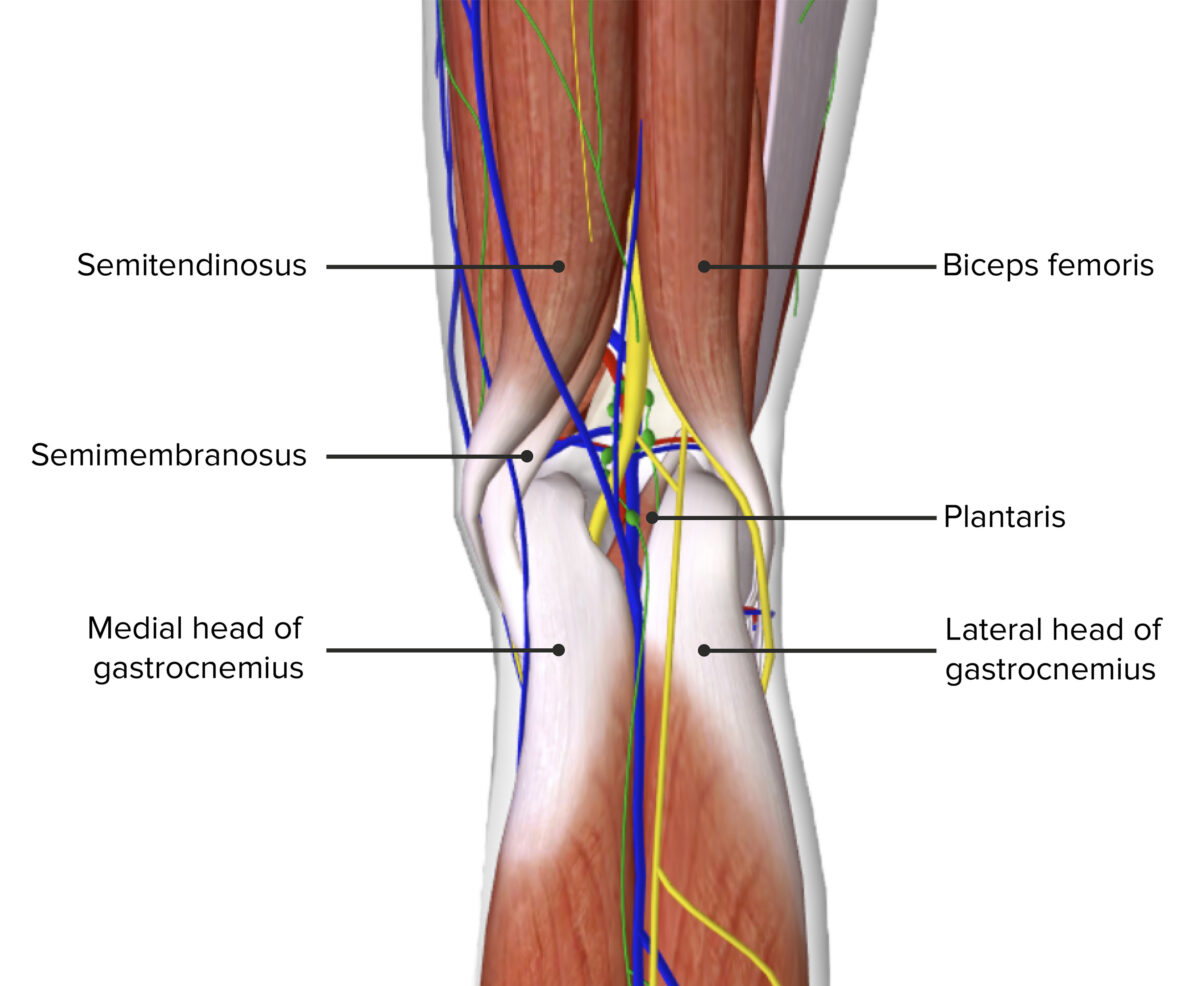
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio.The popliteal fossa is the location of many important nerves and vessels of the lower extremity and is the main channel for the neurovascular system between the thigh Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb found between the hip and the knee joint. There is a single bone in the thigh called the femur, which is surrounded by large muscles grouped into 3 fascial compartments. Thigh: Anatomy and the lower leg Leg The lower leg, or just “leg” in anatomical terms, is the part of the lower limb between the knee and the ankle joint. The bony structure is composed of the tibia and fibula bones, and the muscles of the leg are grouped into the anterior, lateral, and posterior compartments by extensions of fascia. Leg: Anatomy.
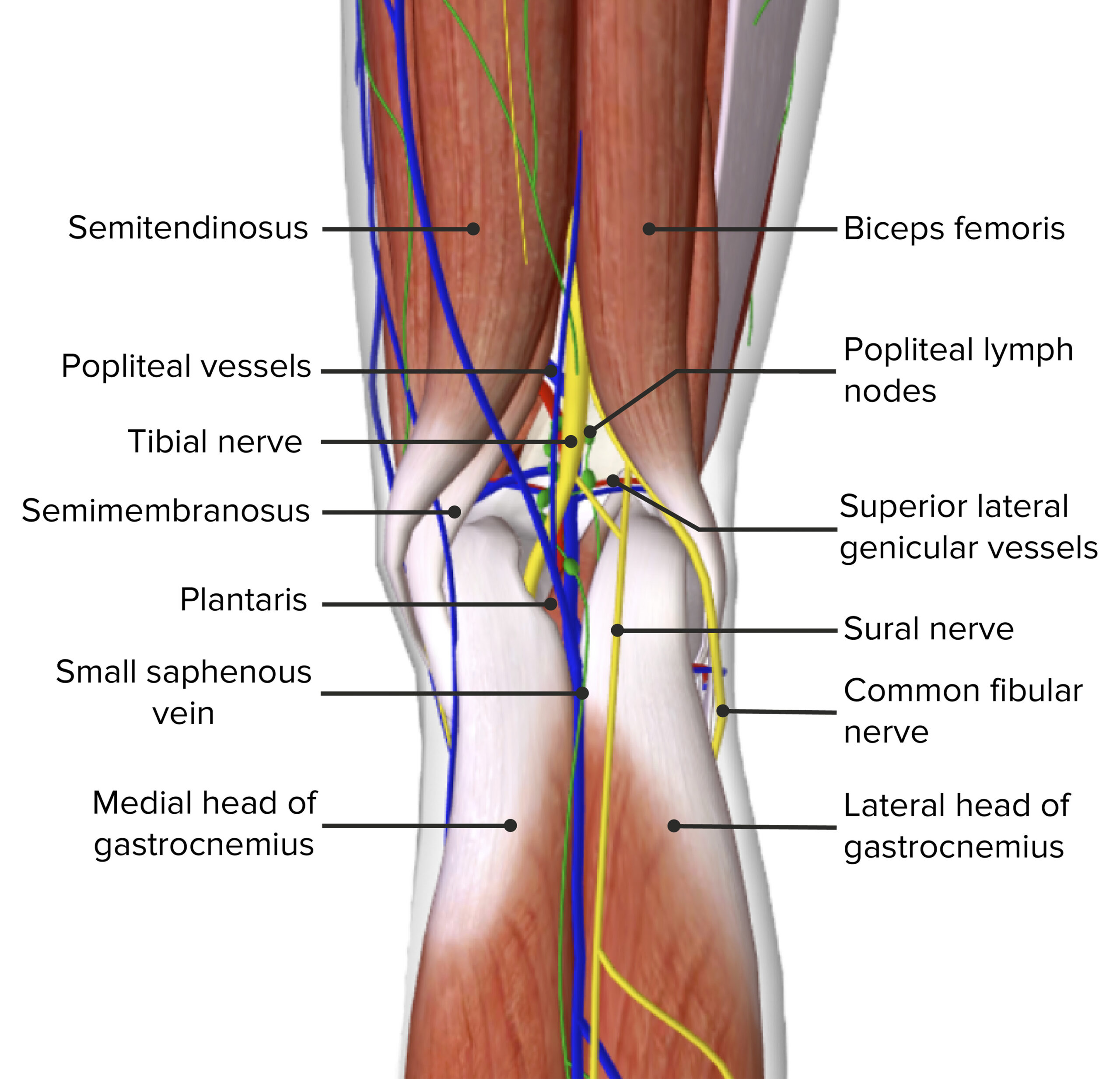
Contents of the popliteal fossa
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio.Mnemonic
To recall the contents of the popliteal fossa from medial to lateral, remember to Serve and Volley Next Ball:
Popliteal artery:
Popliteal vein:
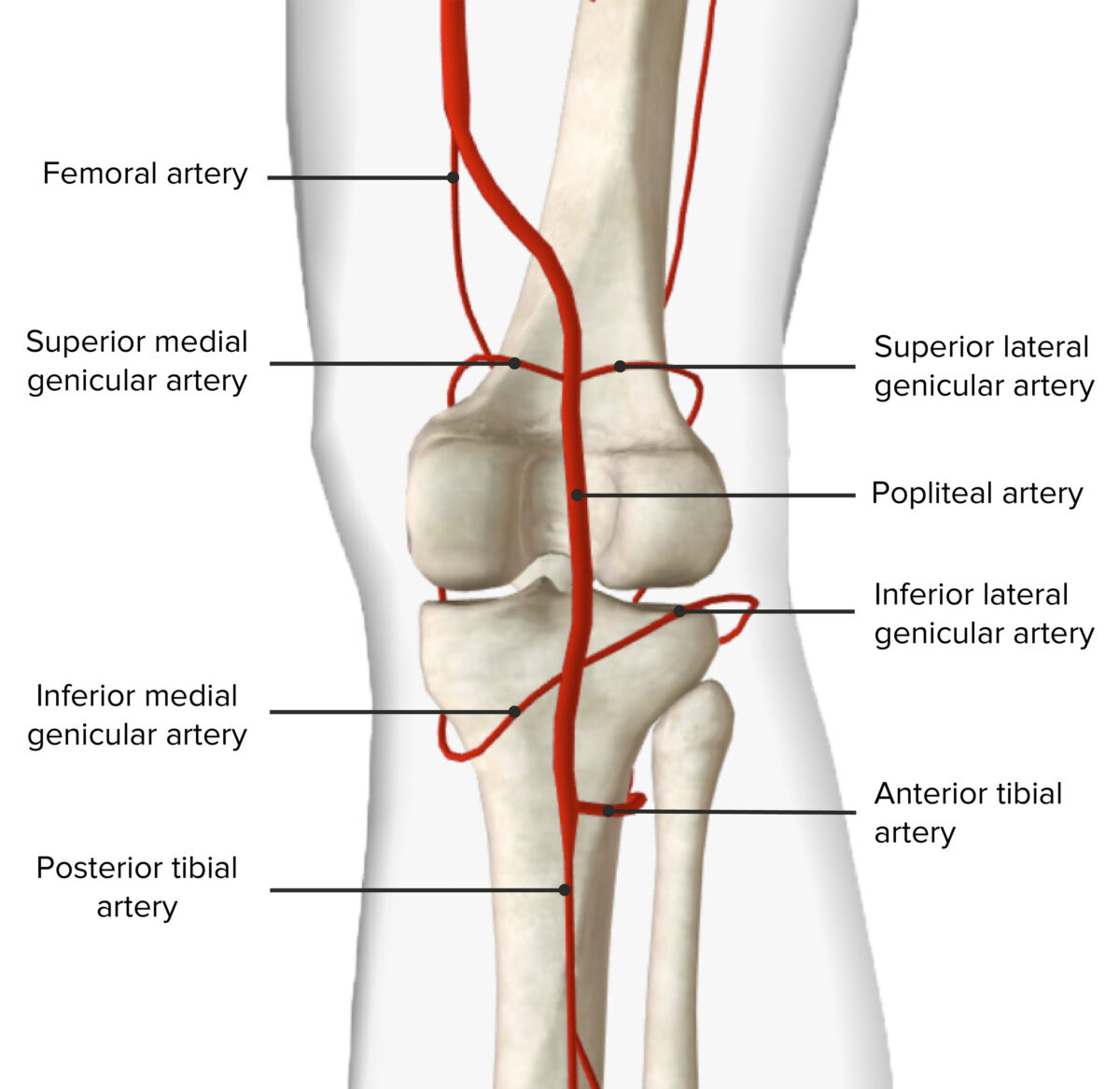
Arterial supply of the popliteal fossa
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio.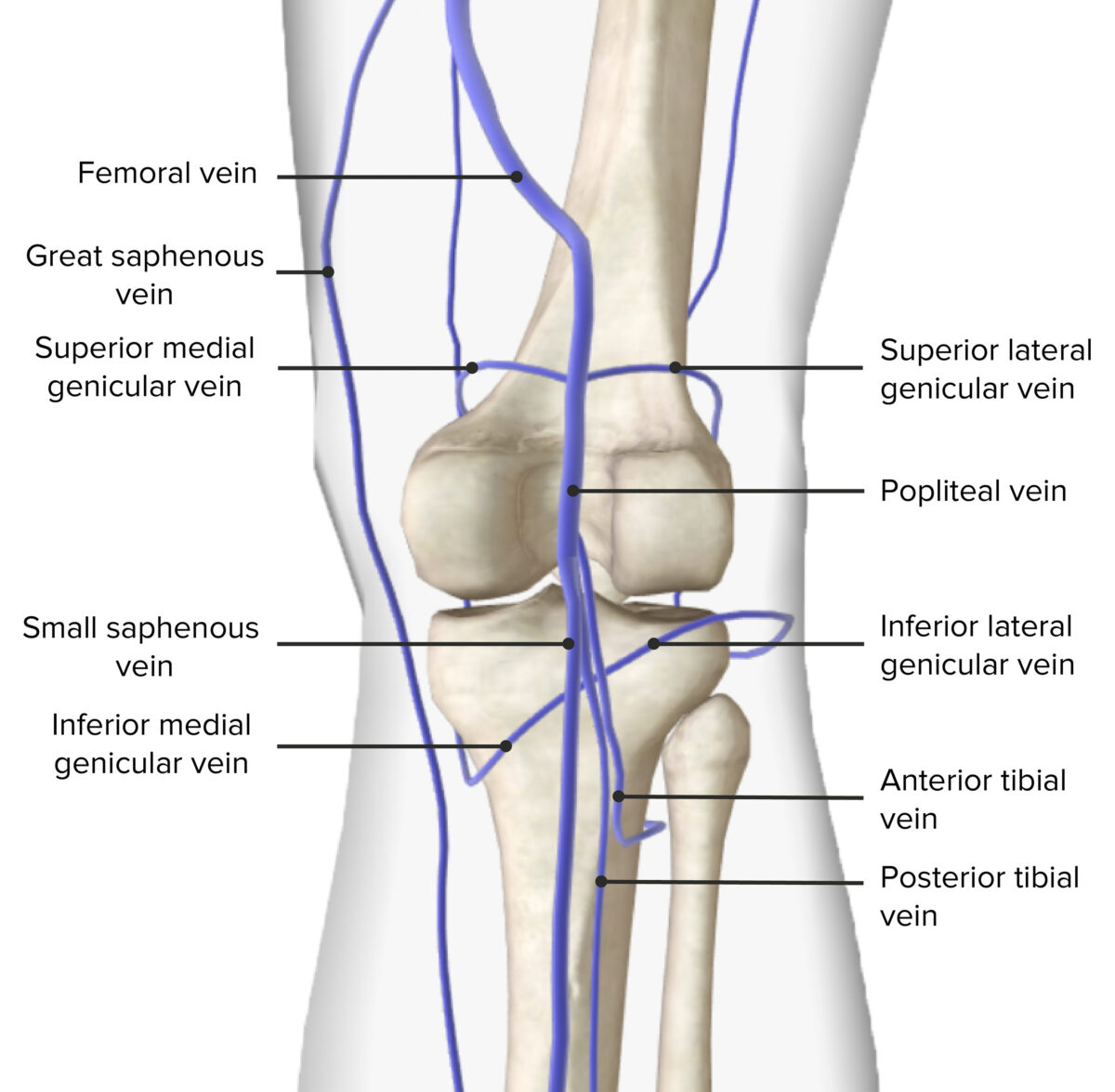
Venous drainage of the popliteal fossa
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio.The main nerves of the popliteal fossa are the 2 branches of the sciatic nerve Sciatic Nerve A nerve which originates in the lumbar and sacral spinal cord (l4 to s3) and supplies motor and sensory innervation to the lower extremity. The sciatic nerve, which is the main continuation of the sacral plexus, is the largest nerve in the body. It has two major branches, the tibial nerve and the peroneal nerve. Gluteal Region: Anatomy, which is the largest branch of the lumbosacral plexus and bifurcates at the superior angle of the popliteal fossa into the following:
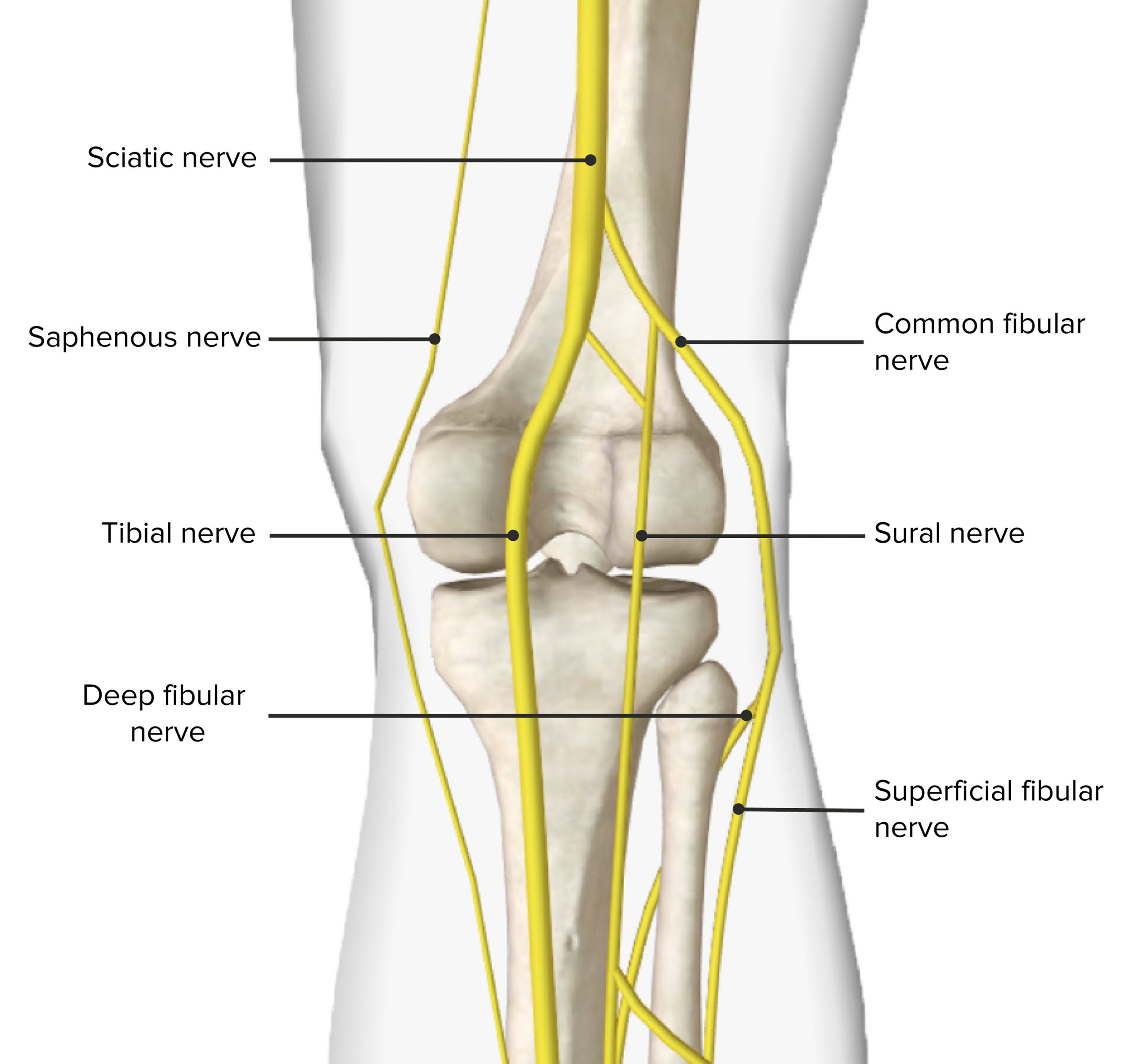
Innervation of the popliteal fossa
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio.The following is an important clinical concept related to the structures found within the popliteal fossa:
The following conditions are of clinical significance regarding the popliteal fossa: