Polycythemia vera (PV) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by the overproduction of RBCs. In addition, the WBC and platelet counts are also increased, which differentiates PV from erythrocytosis seen with chronic hypoxia and other chronic conditions. Polycythemia vera is presumed to have a genetic basis due to mutations in the Janus kinase-2 gene. The clinical presentation may consist of symptoms related to increased blood volume and viscosity, such as headache, visual changes, and venous or arterial thrombosis; however, many cases are found incidentally with asymptomatic elevated hemoglobin levels on a CBC. Diagnosis is based on peripheral blood analysis and bone marrow biopsy findings. Management is with phlebotomy or drug therapy. The prognosis is generally good, and patient survival is anticipated to improve further with the wide use of new therapies.
Last updated: Jul 16, 2025
Polycythemia Polycythemia An increase in the total red cell mass of the blood. Renal Cell Carcinoma vera (PV) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by the overproduction of RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology (erythrocytosis), WBCs, and platelets Platelets Platelets are small cell fragments involved in hemostasis. Thrombopoiesis takes place primarily in the bone marrow through a series of cell differentiation and is influenced by several cytokines. Platelets are formed after fragmentation of the megakaryocyte cytoplasm. Platelets: Histology. This triad differentiates PV from erythrocytosis seen with chronic hypoxia Hypoxia Sub-optimal oxygen levels in the ambient air of living organisms. Ischemic Cell Damage and other conditions.
Polycythemia Polycythemia An increase in the total red cell mass of the blood. Renal Cell Carcinoma vera is often diagnosed incidentally when a CBC obtained for other reasons reveals increased hemoglobin and hematocrit Hematocrit The volume of packed red blood cells in a blood specimen. The volume is measured by centrifugation in a tube with graduated markings, or with automated blood cell counters. It is an indicator of erythrocyte status in disease. For example, anemia shows a low value; polycythemia, a high value. Neonatal Polycythemia. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship also present with disease-related symptoms or complications.
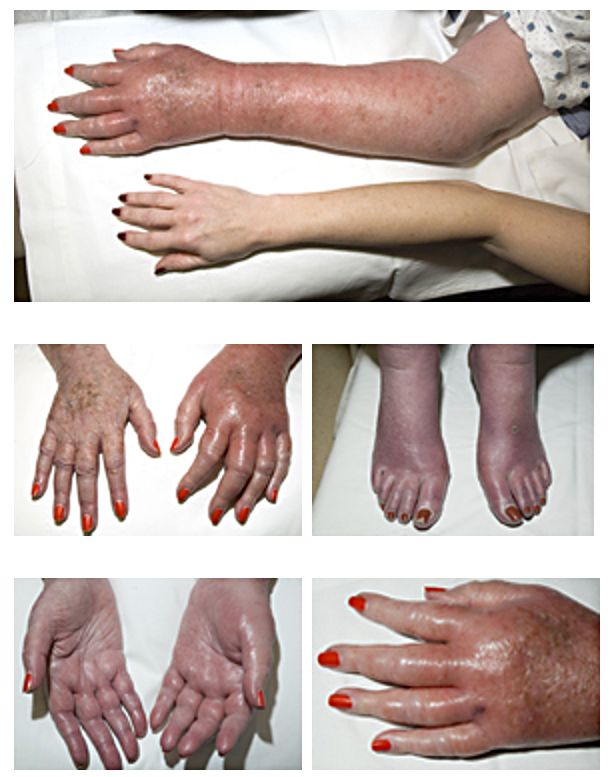
Erythromelalgia:
A sensation of burning pain in the feet or hands accompanied by erythema, pallor, or cyanosis, in the presence of palpable pulses
Polycythemia Polycythemia An increase in the total red cell mass of the blood. Renal Cell Carcinoma vera is suspected in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with characteristic physical findings and/or increased levels of hemoglobin and hematocrit Hematocrit The volume of packed red blood cells in a blood specimen. The volume is measured by centrifugation in a tube with graduated markings, or with automated blood cell counters. It is an indicator of erythrocyte status in disease. For example, anemia shows a low value; polycythemia, a high value. Neonatal Polycythemia on a CBC.
Rule out secondary causes of polycythemia Polycythemia An increase in the total red cell mass of the blood. Renal Cell Carcinoma (high EPO EPO Glycoprotein hormone, secreted chiefly by the kidney in the adult and the liver in the fetus, that acts on erythroid stem cells of the bone marrow to stimulate proliferation and differentiation. Erythrocytes: Histology levels):
Laboratory findings for primary PV:
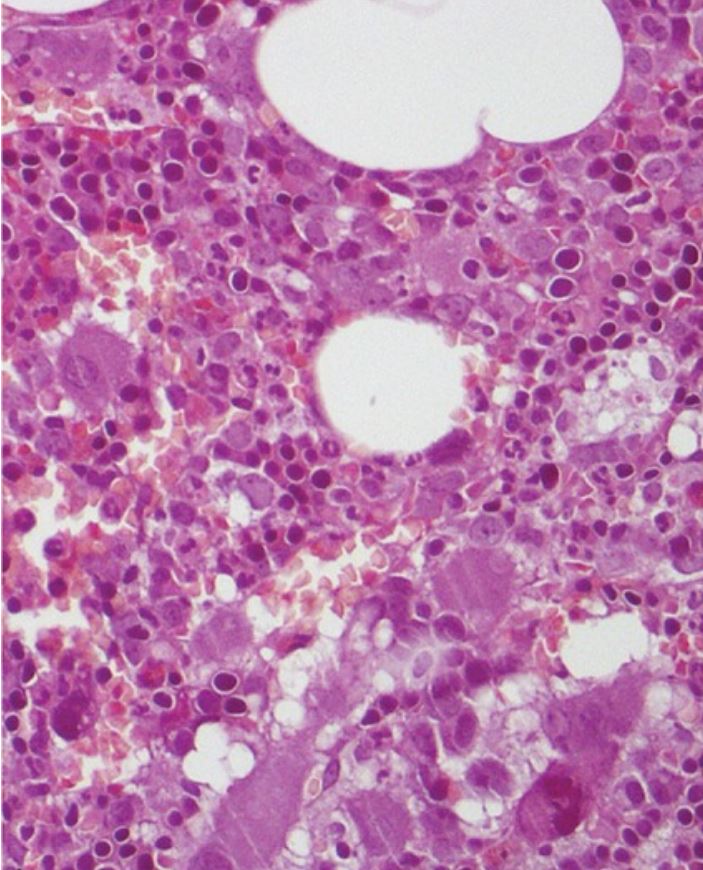
Morphological bone marrow analysis for an individual with polycythemia vera shows no evident change in bone marrow fibrosis or blast percentage, and no significant lymphoid infiltrate.
Image: “Erdheim-Chester Disease With Multiorgan Involvement, Following Polycythemia Vera: A Case Report” by Iurlo, A., et al. License: CC BY 4.0, cropped by Lecturio.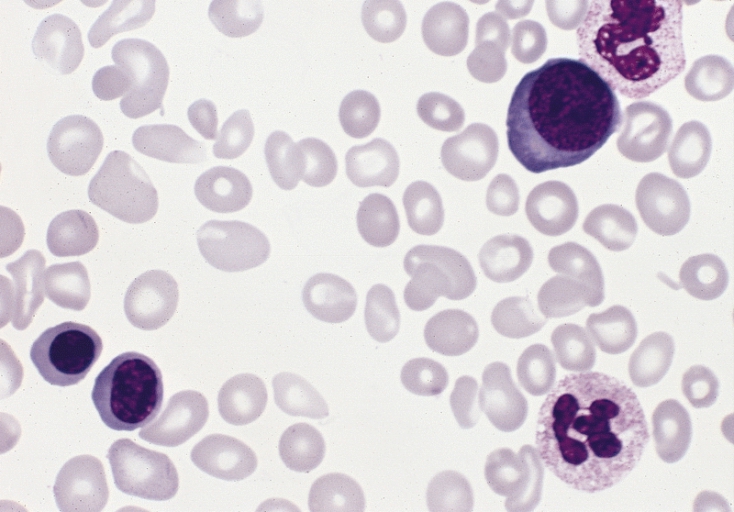
Blood smear of different RBC morphology in an individual with polycythemia vera:
3 red blood cell precursors are present and there is slight to moderate anisopoikilocytosis (Wright-Giemsa stain).