Polycystic ovarian syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome ( PCOS PCOS Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%‒10% of women in the age group. Characterized by hyperandrogenism Hyperandrogenism A condition caused by the excessive secretion of androgens from the adrenal cortex; the ovaries; or the testes. The clinical significance in males is negligible. In women, the common manifestations are hirsutism and virilism as seen in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome and adrenocortical hyperfunction. Potassium-sparing Diuretics, chronic anovulation Anovulation Suspension or cessation of ovulation in animals or humans with follicle-containing ovaries (ovarian follicle). Depending on the etiology, ovulation may be induced with appropriate therapy. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome leading to oligomenorrhea Oligomenorrhea Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (or amenorrhea Amenorrhea Absence of menstruation. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System), and metabolic dysfunction, PCOS PCOS Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome increases a woman’s risk for infertility Infertility Infertility is the inability to conceive in the context of regular intercourse. The most common causes of infertility in women are related to ovulatory dysfunction or tubal obstruction, whereas, in men, abnormal sperm is a common cause. Infertility, endometrial hyperplasia Hyperplasia An increase in the number of cells in a tissue or organ without tumor formation. It differs from hypertrophy, which is an increase in bulk without an increase in the number of cells. Cellular Adaptation or carcinoma, and cardiovascular disease. The pathophysiology is incompletely understood but thought to have a multifactorial genetic basis causing altered pulsatile release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone Gonadotropin-releasing hormone A decapeptide that stimulates the synthesis and secretion of both pituitary gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone. Gnrh is produced by neurons in the septum preoptic area of the hypothalamus and released into the pituitary portal blood, leading to stimulation of gonadotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland. Puberty (GnRH), as well as increases in luteinizing hormone ( LH LH A major gonadotropin secreted by the adenohypophysis. Luteinizing hormone regulates steroid production by the interstitial cells of the testis and the ovary. The preovulatory luteinizing hormone surge in females induces ovulation, and subsequent luteinization of the follicle. Luteinizing hormone consists of two noncovalently linked subunits, alpha and beta. Within a species, the alpha subunit is common in the three pituitary glycoprotein hormones (TSH, LH, and FSH), but the beta subunit is unique and confers its biological specificity. Menstrual Cycle), androgens Androgens Androgens are naturally occurring steroid hormones responsible for development and maintenance of the male sex characteristics, including penile, scrotal, and clitoral growth, development of sexual hair, deepening of the voice, and musculoskeletal growth. Androgens and Antiandrogens, estrogen Estrogen Compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of estradiol. Estrogens stimulate the female reproductive organs, and the development of secondary female sex characteristics. Estrogenic chemicals include natural, synthetic, steroidal, or non-steroidal compounds. Ovaries: Anatomy, and insulin Insulin Insulin is a peptide hormone that is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas. Insulin plays a role in metabolic functions such as glucose uptake, glycolysis, glycogenesis, lipogenesis, and protein synthesis. Exogenous insulin may be needed for individuals with diabetes mellitus, in whom there is a deficiency in endogenous insulin or increased insulin resistance. Insulin: The result is chronic anovulation Anovulation Suspension or cessation of ovulation in animals or humans with follicle-containing ovaries (ovarian follicle). Depending on the etiology, ovulation may be induced with appropriate therapy. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and hirsutism Hirsutism A condition observed in women and children when there is excess coarse body hair of an adult male distribution pattern, such as facial and chest areas. It is the result of elevated androgens from the ovaries, the adrenal glands, or exogenous sources. The concept does not include hypertrichosis, which is an androgen-independent excessive hair growth. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, which define the condition. Diagnosis is one of exclusion; therefore, other causes of abnormal uterine bleeding Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Abnormal uterine bleeding is the medical term for abnormalities in the frequency, volume, duration, and regularity of the menstrual cycle. Abnormal uterine bleeding is classified using the acronym PALM-COEIN, with PALM representing the structural causes and COEIN indicating the non-structural causes. Abnormal Uterine Bleeding and hirsutism Hirsutism A condition observed in women and children when there is excess coarse body hair of an adult male distribution pattern, such as facial and chest areas. It is the result of elevated androgens from the ovaries, the adrenal glands, or exogenous sources. The concept does not include hypertrichosis, which is an androgen-independent excessive hair growth. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome must be ruled out. Management includes attempting to restore normal ovulation Ovulation The discharge of an ovum from a rupturing follicle in the ovary. Menstrual Cycle through weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery, oral contraceptive Oral contraceptive Compounds, usually hormonal, taken orally in order to block ovulation and prevent the occurrence of pregnancy. The hormones are generally estrogen or progesterone or both. Benign Liver Tumors pills (OCPs), and fertility assistance.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The exact mechanisms are unknown, but thought to be complex and include both genetic and environmental factors. Metabolic syndrome Metabolic syndrome Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that significantly increases the risk for several secondary diseases, notably cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and nonalcoholic fatty liver. In general, it is agreed that hypertension, insulin resistance/hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia, along with central obesity, are components of the metabolic syndrome. Metabolic Syndrome and obesity Obesity Obesity is a condition associated with excess body weight, specifically with the deposition of excessive adipose tissue. Obesity is considered a global epidemic. Major influences come from the western diet and sedentary lifestyles, but the exact mechanisms likely include a mixture of genetic and environmental factors. Obesity are often, but not always, present and likely contribute to the pathophysiology in some individuals.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome ( PCOS PCOS Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome) should be suspected in any reproductive-age female with irregular menses Menses The periodic shedding of the endometrium and associated menstrual bleeding in the menstrual cycle of humans and primates. Menstruation is due to the decline in circulating progesterone, and occurs at the late luteal phase when luteolysis of the corpus luteum takes place. Menstrual Cycle and/or symptoms of hyperandrogenism Hyperandrogenism A condition caused by the excessive secretion of androgens from the adrenal cortex; the ovaries; or the testes. The clinical significance in males is negligible. In women, the common manifestations are hirsutism and virilism as seen in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome and adrenocortical hyperfunction. Potassium-sparing Diuretics, especially if obese or presenting with infertility Infertility Infertility is the inability to conceive in the context of regular intercourse. The most common causes of infertility in women are related to ovulatory dysfunction or tubal obstruction, whereas, in men, abnormal sperm is a common cause. Infertility.
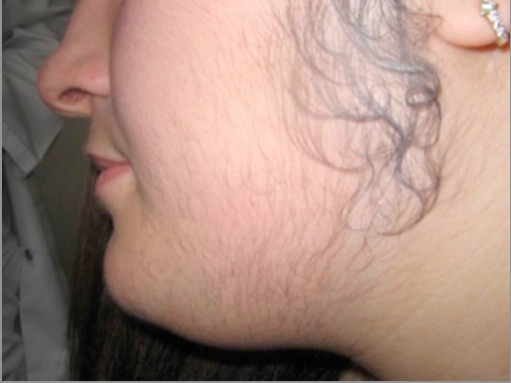
Hirsutism in PCOS:
Hair is noted along the side burns, chin, and upper lip; signs of hyperandrogenism.
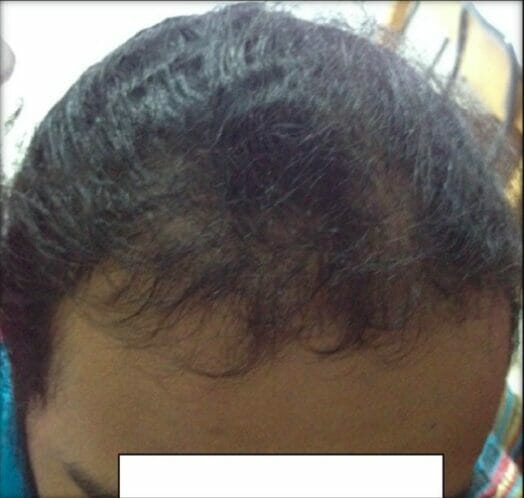
Male-pattern alopecia in PCOS:
The patient has frontal hair thinning, which is a sign of hyperandrogenism.
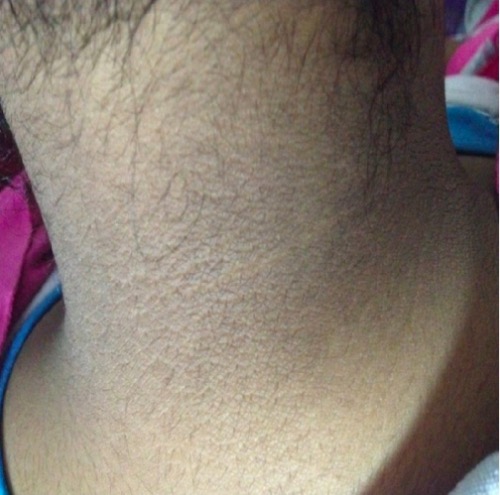
Acanthosis nigricans in PCOS:
Thickened, darkened skin can appear on the nape of the neck, axillae, or skinfolds as a sign of high insulin levels from insulin resistance.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome ( PCOS PCOS Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome) is a diagnosis of exclusion, so other causes of oligo- or amenorrhea Amenorrhea Absence of menstruation. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System and hyperandrogenism Hyperandrogenism A condition caused by the excessive secretion of androgens from the adrenal cortex; the ovaries; or the testes. The clinical significance in males is negligible. In women, the common manifestations are hirsutism and virilism as seen in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome and adrenocortical hyperfunction. Potassium-sparing Diuretics must be ruled out. The Rotterdam criteria Rotterdam Criteria Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome are commonly used to make the diagnosis once other causes are excluded.
Diagnosis requires 2 of the 3 following criteria:[2,13,14,16]
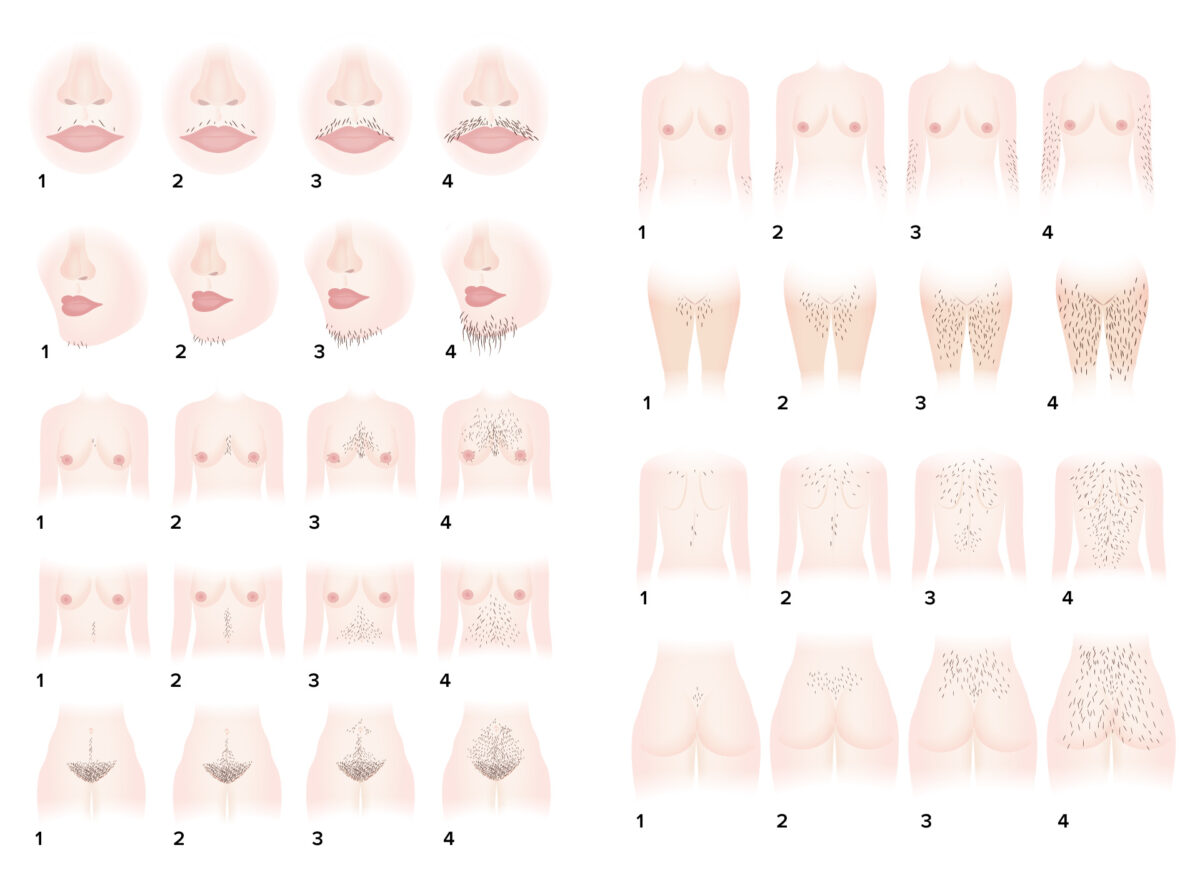
Ferriman-Gallwey hirsutism scoring system: a system for objective assessment of the degree of hirsutism
Image by Lecturio.| Hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types ↑ in PCOS PCOS Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome | Hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types ↓ in PCOS PCOS Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome |
|---|---|
|
|
FSH: follicle-stimulating hormone
HDL: high-density lipoproteins
LDL: low-density lipoproteins
LH: luteinizing hormone
PCOS: polycystic ovarian syndrome
SHBG: sex hormone-binding globulin
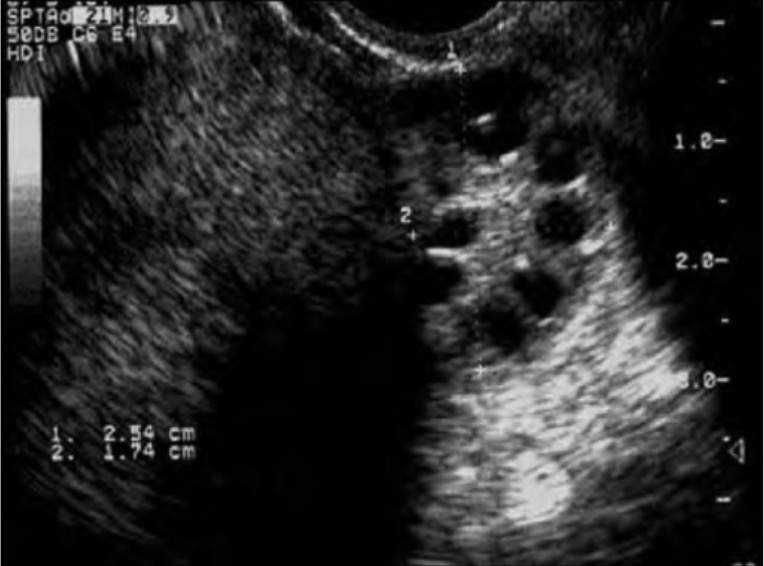
Ultrasound of a polycystic-appearing ovary:
Note the classic “pearls on a string” around the periphery of the ovary identifying the abnormally developing follicles seen in PCOS. Polycystic appearing ovaries are seen in approximately ⅔ of patients with PCOS and is 1 of the 3 diagnostic Rotterdam criteria.
The most commonly agreed-on criteria come from the National Cholesterol Cholesterol The principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils. Cholesterol Metabolism Education Program (NCEP) Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) in 2001; 3 of the 5 criteria must be present for diagnosis:[1]
Suspect PCOS PCOS Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome in individuals presenting with irregular menstrual bleeding, hirsutism Hirsutism A condition observed in women and children when there is excess coarse body hair of an adult male distribution pattern, such as facial and chest areas. It is the result of elevated androgens from the ovaries, the adrenal glands, or exogenous sources. The concept does not include hypertrichosis, which is an androgen-independent excessive hair growth. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, and/or infertility Infertility Infertility is the inability to conceive in the context of regular intercourse. The most common causes of infertility in women are related to ovulatory dysfunction or tubal obstruction, whereas, in men, abnormal sperm is a common cause. Infertility.
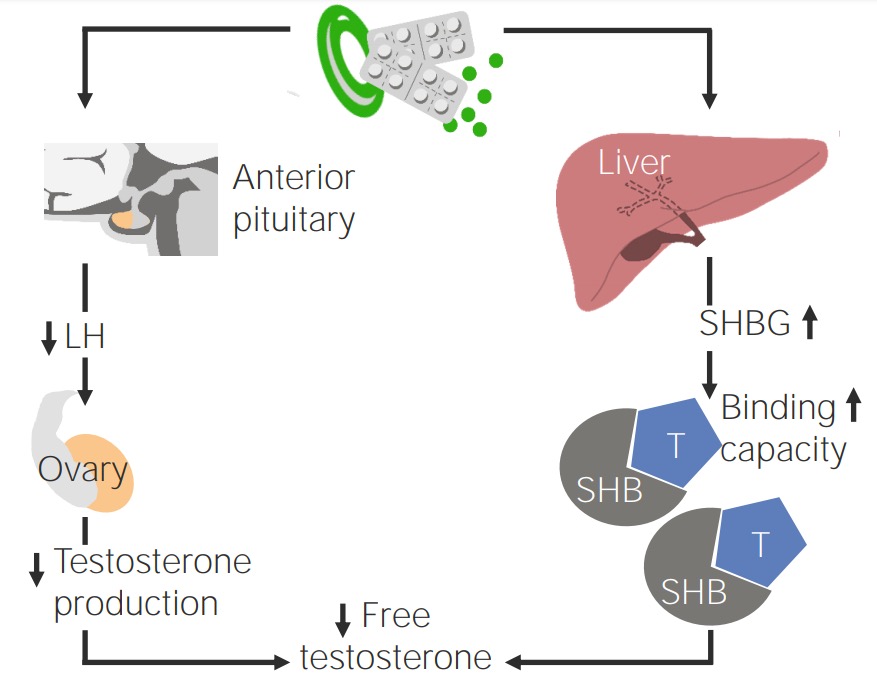
Effect of oral contraception on patients with PCOS
Image by Lecturio.Diagnosis Codes:
This code is used to diagnose
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (
PCOS
PCOS
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome), a common endocrine disorder among women of reproductive age, characterized by irregular periods, excess androgen levels, and polycystic
ovaries
Ovaries
Ovaries are the paired gonads of the female reproductive system that contain haploid gametes known as oocytes. The ovaries are located intraperitoneally in the pelvis, just posterior to the broad ligament, and are connected to the pelvic sidewall and to the uterus by ligaments. These organs function to secrete hormones (estrogen and progesterone) and to produce the female germ cells (oocytes).
Ovaries: Anatomy.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | E28.2 | Polycystic ovarian syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome |
| SNOMED CT | 237067003 | Polycystic ovary syndrome (disorder) |
Evaluation & Workup:
These codes are for tests used to support the diagnosis of
PCOS
PCOS
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome according to the
Rotterdam criteria
Rotterdam Criteria
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome, including a serum
testosterone
Testosterone
A potent androgenic steroid and major product secreted by the leydig cells of the testis. Its production is stimulated by luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland. In turn, testosterone exerts feedback control of the pituitary LH and FSH secretion. Depending on the tissues, testosterone can be further converted to dihydrotestosterone or estradiol.
Androgens and Antiandrogens level to check for
hyperandrogenism
Hyperandrogenism
A condition caused by the excessive secretion of androgens from the adrenal cortex; the ovaries; or the testes. The clinical significance in males is negligible. In women, the common manifestations are hirsutism and virilism as seen in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome and adrenocortical hyperfunction.
Potassium-sparing Diuretics and a pelvic ultrasound to look for polycystic morphology.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 84403 | Testosterone Testosterone A potent androgenic steroid and major product secreted by the leydig cells of the testis. Its production is stimulated by luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland. In turn, testosterone exerts feedback control of the pituitary LH and FSH secretion. Depending on the tissues, testosterone can be further converted to dihydrotestosterone or estradiol. Androgens and Antiandrogens; total |
| CPT | 76856 | Ultrasound, pelvic (nonobstetric), real time with image documentation Documentation Systematic organization, storage, retrieval, and dissemination of specialized information, especially of a scientific or technical nature. It often involves authenticating or validating information. Advance Directives; complete |
Medications:
These codes are for medications used to manage the symptoms of
PCOS
PCOS
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder of reproductive-age women, affecting nearly 5%-10% of women in the age group. It is characterized by hyperandrogenism, chronic anovulation leading to oligomenorrhea (or amenorrhea), and metabolic dysfunction.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Combined oral contraceptives are used to regulate menstrual cycles, while
metformin
Metformin
A biguanide hypoglycemic agent used in the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus not responding to dietary modification. Metformin improves glycemic control by improving insulin sensitivity and decreasing intestinal absorption of glucose.
Non-insulinotropic Diabetes Drugs is used to manage
insulin resistance
Insulin resistance
Diminished effectiveness of insulin in lowering blood sugar levels: requiring the use of 200 units or more of insulin per day to prevent hyperglycemia or ketosis.
Diabetes Mellitus.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 314466 | Drospirenone Drospirenone Hormonal Contraceptives / Ethinyl Estradiol Ethinyl estradiol A semisynthetic alkylated estradiol with a 17-alpha-ethinyl substitution. It has high estrogenic potency when administered orally, and is often used as the estrogenic component in oral contraceptives. Hormonal Contraceptives |
| RxNorm | 6809 | Metformin Metformin A biguanide hypoglycemic agent used in the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus not responding to dietary modification. Metformin improves glycemic control by improving insulin sensitivity and decreasing intestinal absorption of glucose. Non-insulinotropic Diabetes Drugs (ingredient) |