An intervention is any action taken to reduce the impact of a disease, including interventions to prevent disease, cure or reduce the mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status and morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status of a disease, or influence public behavior that increases the risk of disease. Interventions can be classified as preventive, therapeutic, or other public health interventions. In clinical studies, interventions are tested on subject groups to assess their effects on a disease or condition. The particular implementation of these interventions has considerable influence on the study design that will be ultimately chosen to assess them.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Preventive interventions are actions that prevent a disease and reduce the incidence Incidence The number of new cases of a given disease during a given period in a specified population. It also is used for the rate at which new events occur in a defined population. It is differentiated from prevalence, which refers to all cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency of new cases, including education, vaccines, nutritional interventions, maternal and neonatal interventions, behavioral interventions, and environmental interventions.
Vaccine vial along with components used to administer the vaccine
Image: “Smallpox vaccine” by James Gathany. License: Public Domain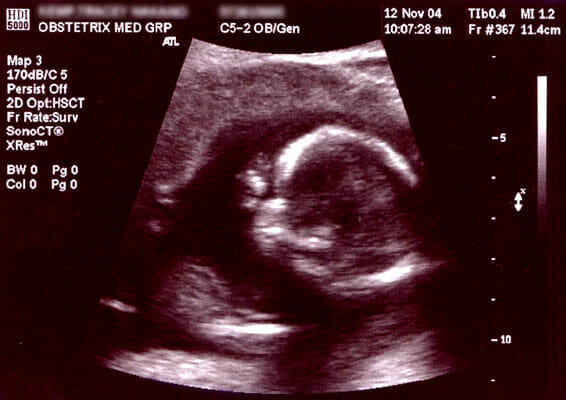
Prenatal ultrasonogram at 16 weeks of gestation:
The bright white area is the head of the fetus.
Therapeutic interventions alleviate or prevent mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status (reduce case fatality rate Case fatality rate Defined as the number of deaths of individuals with a certain disease or condition divided by the total number of people diagnosed with that same disease or condition over a specific time period. Measures of Health Status) and morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status of a disease once established, including the management of infectious Infectious Febrile Infant disease, surgical and radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma treatment, diagnostics to guide therapy, and control of chronic diseases.
Other interventions also affect Affect The feeling-tone accompaniment of an idea or mental representation. It is the most direct psychic derivative of instinct and the psychic representative of the various bodily changes by means of which instincts manifest themselves. Psychiatric Assessment disease burdens, including governmental and healthcare system Healthcare System The complexity of health systems and the delivery of healthcare has resulted in the growing field of health systems science, which has now joined basic and clinical sciences as the 3rd pillar of medical education. Health systems science allows for an understanding of the framework in which care providers practice, and in comprehension of the interconnected components of care delivery. Healthcare System changes.