Pneumocystis jirovecii is a yeast-like fungus causing pneumocystis pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia (PCP) in immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship. Pneumocystis pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia is spread through airborne transmission and classically affects patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with AIDS, functioning as an AIDS-defining illness. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may present with insidious onset of fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, chills Chills The sudden sensation of being cold. It may be accompanied by shivering. Fever, dry cough Dry Cough Strongyloidiasis, chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and shortness of breath Shortness of breath Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea. The diagnosis is supported by an increased β-D-glucan level and diffuse, bilateral infiltrates on chest imaging in the immunocompromised patient Immunocompromised patient A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Herpes Zoster (Shingles). A definitive diagnosis can be given with microscopy of induced sputum or specimens from bronchoalveolar lavage Bronchoalveolar lavage Washing out of the lungs with saline or mucolytic agents for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. It is very useful in the diagnosis of diffuse pulmonary infiltrates in immunosuppressed patients. Pulmonary Fibrosis (BAL). Management involves antimicrobial therapy with a trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combination, and supportive care. Addressing the etiology of immunodeficiency Immunodeficiency Chédiak-Higashi Syndrome is paramount. Prophylaxis Prophylaxis Cephalosporins is often required to prevent infection or reinfection.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Pneumocystis is a yeast-like fungus.
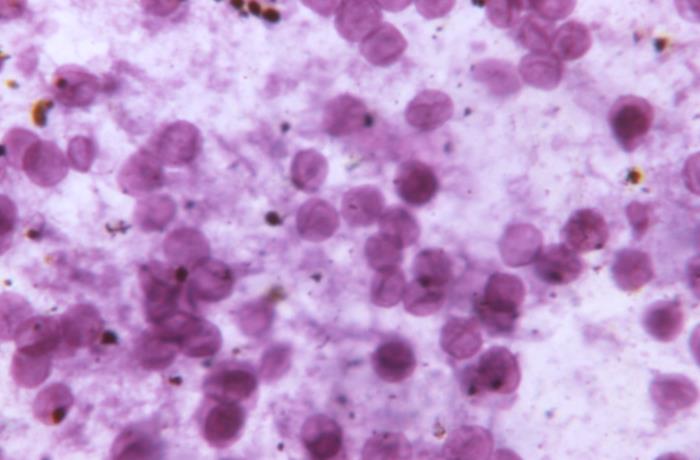
Photomicrograph of a toluidine blue-stained, lung-tissue impression showing numerous Pneumocystis jirovecii fungal cysts
Image: “This photomicrograph of a toluidine blue stained lung tissue impression smear, revealed the presence of numerous, Pneumocystis jirovecii, formerly known as Pneumocystis carinii, fungal cysts.” by CDC. License: Public DomainP. jirovecii (formerly known as P. carinii) causes pneumocystis pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia (PCP).
The reservoir Reservoir Animate or inanimate sources which normally harbor disease-causing organisms and thus serve as potential sources of disease outbreaks. Reservoirs are distinguished from vectors (disease vectors) and carriers, which are agents of disease transmission rather than continuing sources of potential disease outbreaks. Humans may serve both as disease reservoirs and carriers. Escherichia coli for P. jirovecii is unknown, but immunocompetent humans may play a role.
P. jirovecii spreads through airborne transmission.
Pneumocystis pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia occurs in immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis individuals:
Pneumocystis pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia can present in a nonspecific manner compared to other types of pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia.
Presentation may be subacute and evolve over the course of weeks:
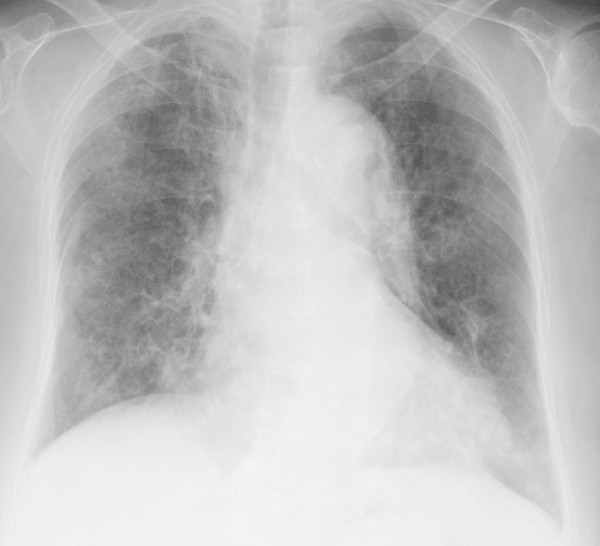
Chest X-ray image demonstrating diffuse, bilateral opacities consistent with pneumocystis pneumonia
Image: “Chest X-ray obtained after the diagnosis of pneumocystis pneumonia showed areas of ground-glass opacity bilaterally in almost all lung fields.” by Kato M et al. License: CC BY 2.0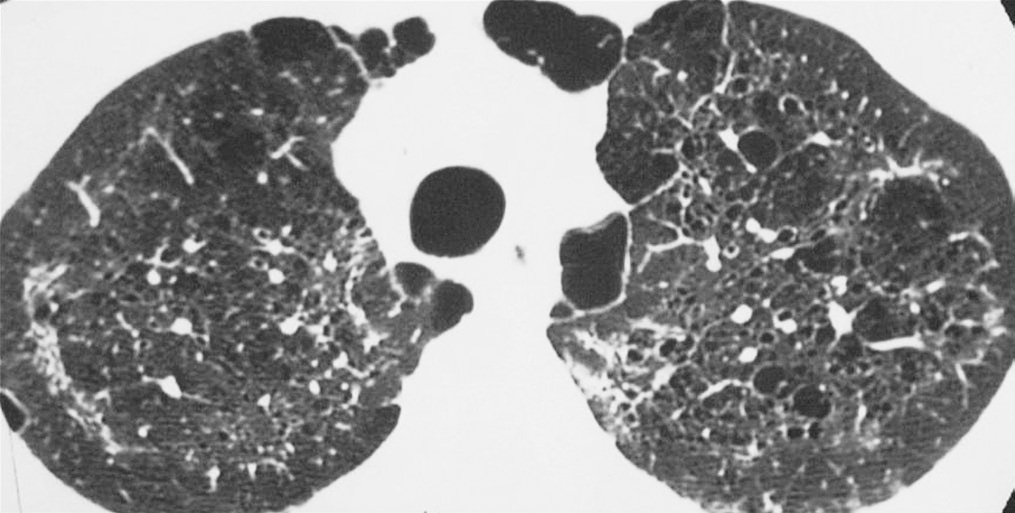
High-resolution CT of multiple lung cysts due to pneumocystis pneumonia
Image: “Lung cysts are usually multiple and bilateral, but range in size, shape and distribution. They are more commonly appreciated on computed tomography (CT)/high-resolution CT” by Carolyn M. License: CC BY 4.0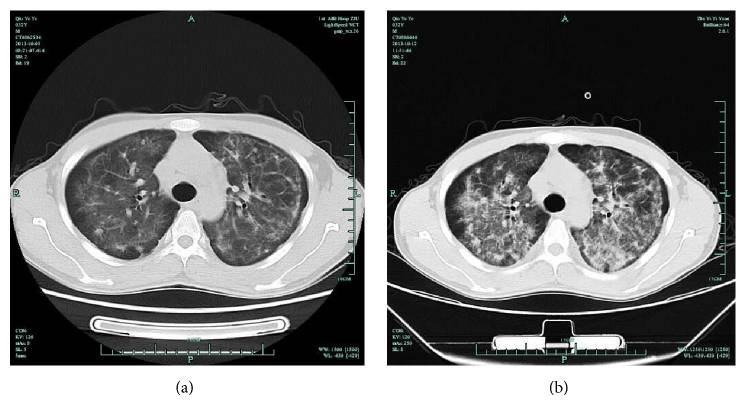
Chest CT in an AIDS patient with pneumocystis pneumonia:
(a) bilateral, symmetrical, interstitial opacities
(b) diffuse, perihilar opacities
Definitive diagnosis:
Supporting evaluation:
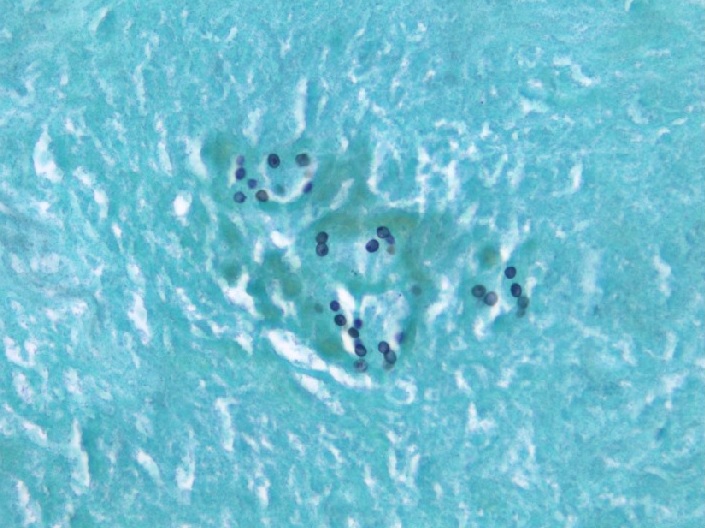

Methenamine silver stain demonstrating Pneumocystis jirovecii cysts within a necrosed granuloma
Image: “Microscopy 800x magnification: Gomori methenamine silver stain” by Patel K. License: CC BY 4.0Prophylaxis Prophylaxis Cephalosporins varies depending on the etiology of the immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis state:
Complications of PCP include:
Early recognition and initiation of therapy improves prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual’s condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas.
Factors negatively impacting outcomes: