During pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care, fetal development and growth are sustained completely by the mother until birth. The placenta consists of a fetal side and a maternal side, and it provides a vascular communication Communication The exchange or transmission of ideas, attitudes, or beliefs between individuals or groups. Decision-making Capacity and Legal Competence between the mother and the fetus. This communication Communication The exchange or transmission of ideas, attitudes, or beliefs between individuals or groups. Decision-making Capacity and Legal Competence allows the mother to provide nutrients to the fetus and allows for removal of waste products from fetal blood. The placenta is also called “the fetal lung” because it allows for gas exchange Gas exchange Human cells are primarily reliant on aerobic metabolism. The respiratory system is involved in pulmonary ventilation and external respiration, while the circulatory system is responsible for transport and internal respiration. Pulmonary ventilation (breathing) represents movement of air into and out of the lungs. External respiration, or gas exchange, is represented by the O2 and CO2 exchange between the lungs and the blood. Gas Exchange between the maternal and fetal circulation Fetal circulation Prenatal and Postnatal Physiology of the Neonate. Diseases or defects in the placenta often have severe, and even fatal, complications.
Last updated: Dec 29, 2025
The placenta has a pancake-like appearance, with 2 sides:
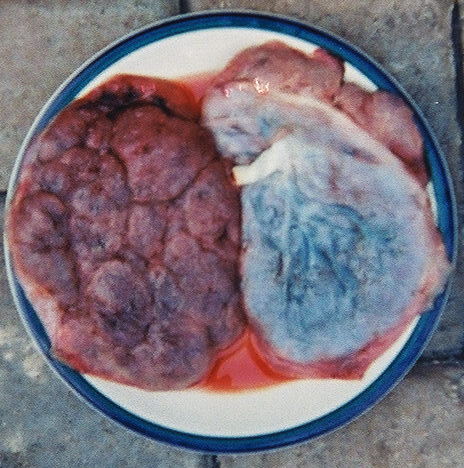
2 placentas:
Left: Maternal side
Right: Fetal side
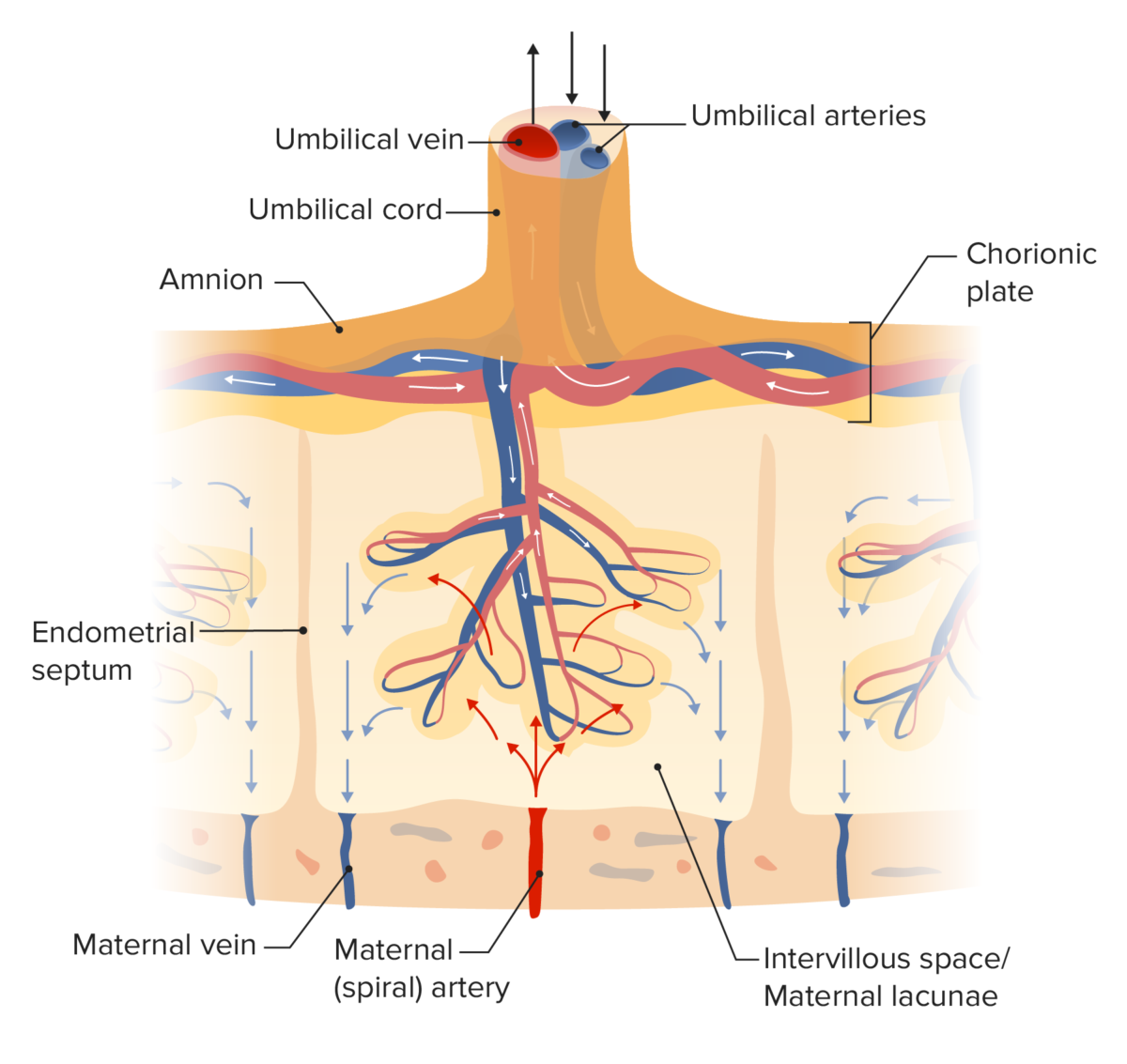
Diagram of placental circulation
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0The placental barrier is a selectively permeable membrane separating the maternal and fetal blood. The barrier is comprised of the following layers:
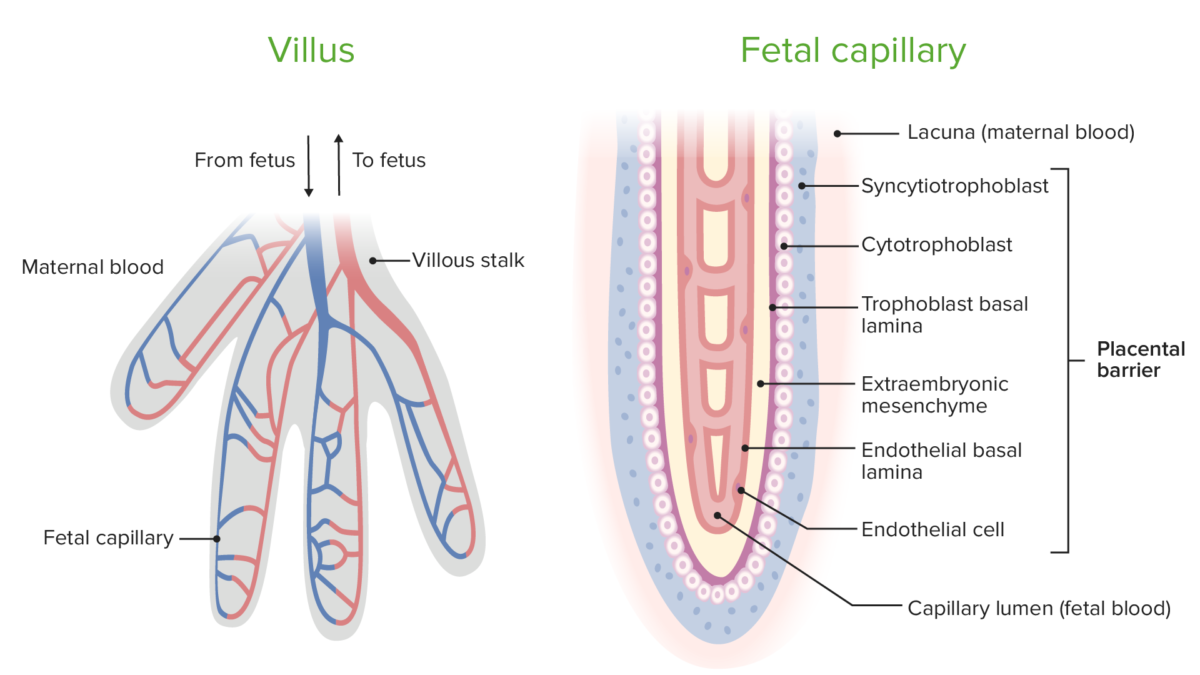
Circulation within chorionic villi and the components of the placental barrier
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0The table lists the many critical functions of the placenta for the fetus.
| Primary functions | Important details |
|---|---|
| Gas exchange Gas exchange Human cells are primarily reliant on aerobic metabolism. The respiratory system is involved in pulmonary ventilation and external respiration, while the circulatory system is responsible for transport and internal respiration. Pulmonary ventilation (breathing) represents movement of air into and out of the lungs. External respiration, or gas exchange, is represented by the O2 and CO2 exchange between the lungs and the blood. Gas Exchange |
|
| Nutrient exchange |
|
| Waste product removal |
|
| Hormonal secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies |
|
| Metabolic functions |
|
| Immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs rejection | Creation of an immunologically privileged site |
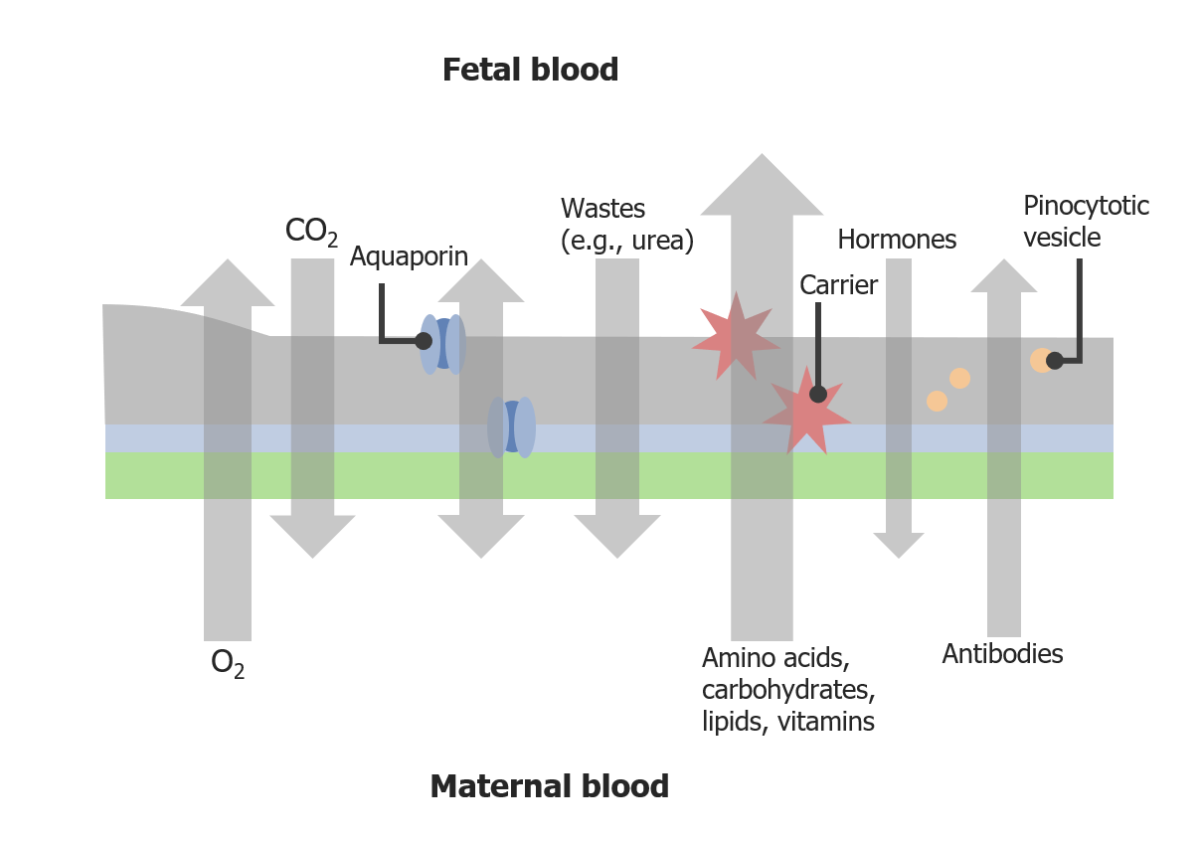
Transport across the placental barrier
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Steps in placental development:
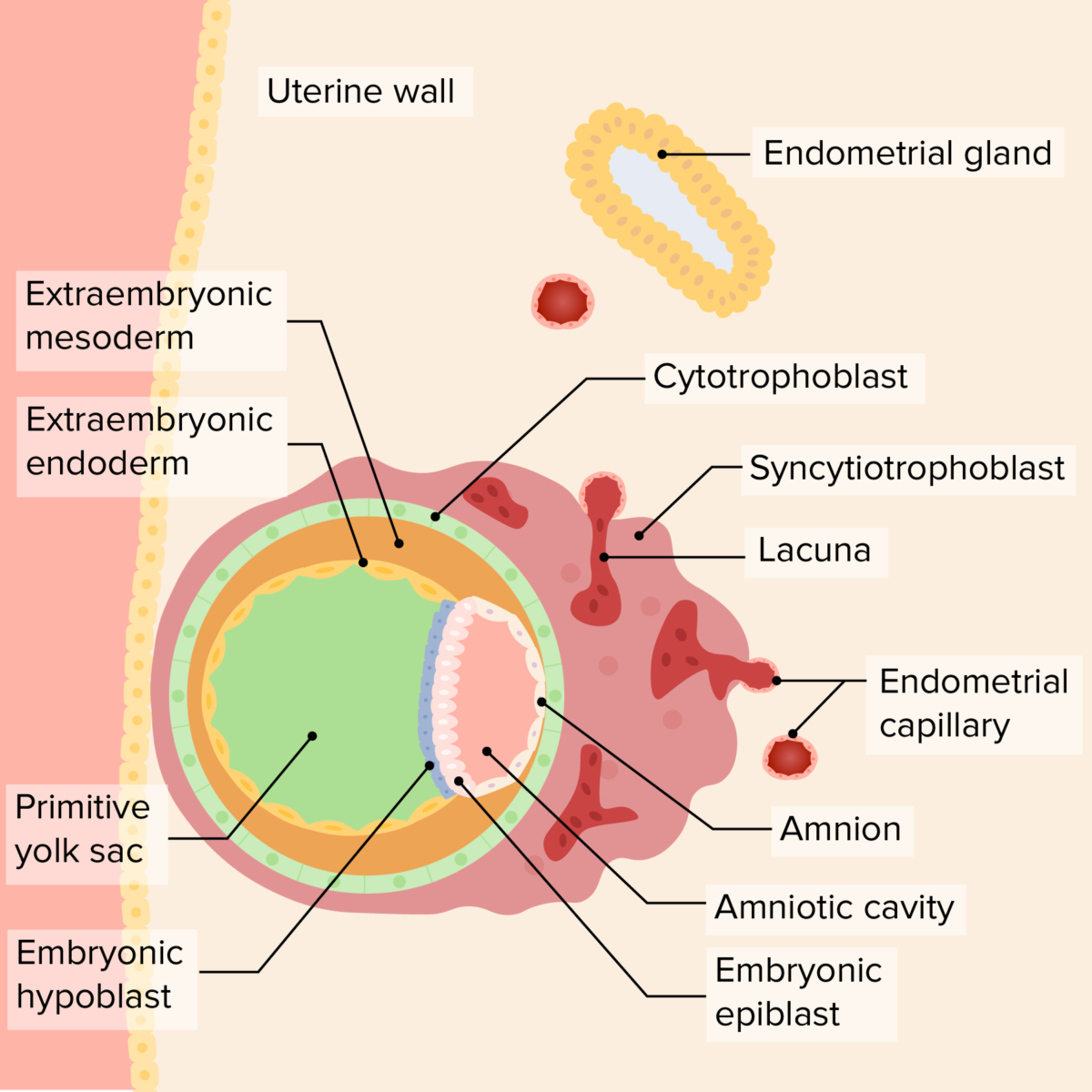
Implanted blastocyst
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0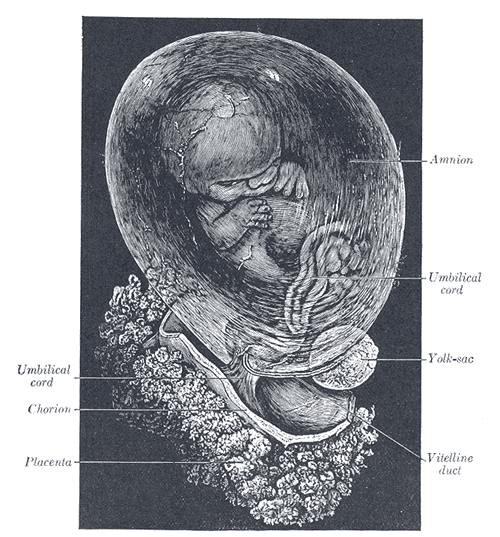
Fetus of about 8 weeks, enclosed in the amnion
Magnification: just over 2 diameters
The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta. The cord contains 2 arteries Arteries Arteries are tubular collections of cells that transport oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart to the tissues of the body. The blood passes through the arteries in order of decreasing luminal diameter, starting in the largest artery (the aorta) and ending in the small arterioles. Arteries are classified into 3 types: large elastic arteries, medium muscular arteries, and small arteries and arterioles. Arteries: Histology and 1 vein and extends from the fetal umbilicus to the fetal surface of the placenta.
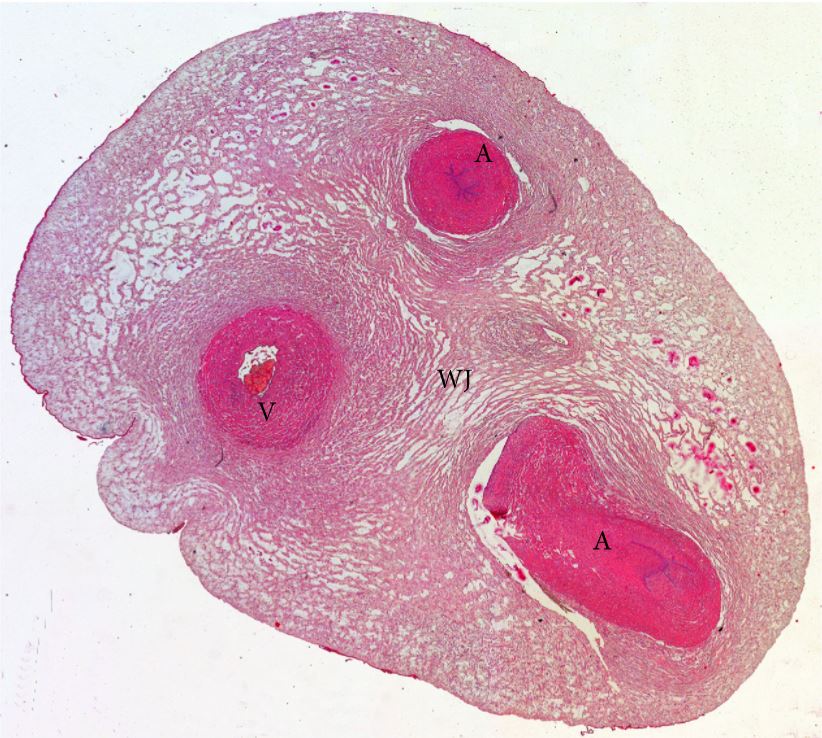
Cross section of the human umbilical cord
A: Artery
V: Vein
WJ: Wharton’s jelly
The amniotic cavity Amniotic cavity Embryoblast and Trophoblast Development is a fluid-filled cavity that encases the developing embryo Embryo The entity of a developing mammal, generally from the cleavage of a zygote to the end of embryonic differentiation of basic structures. For the human embryo, this represents the first two months of intrauterine development preceding the stages of the fetus. Fertilization and First Week/fetus; the fluid is called amniotic fluid.
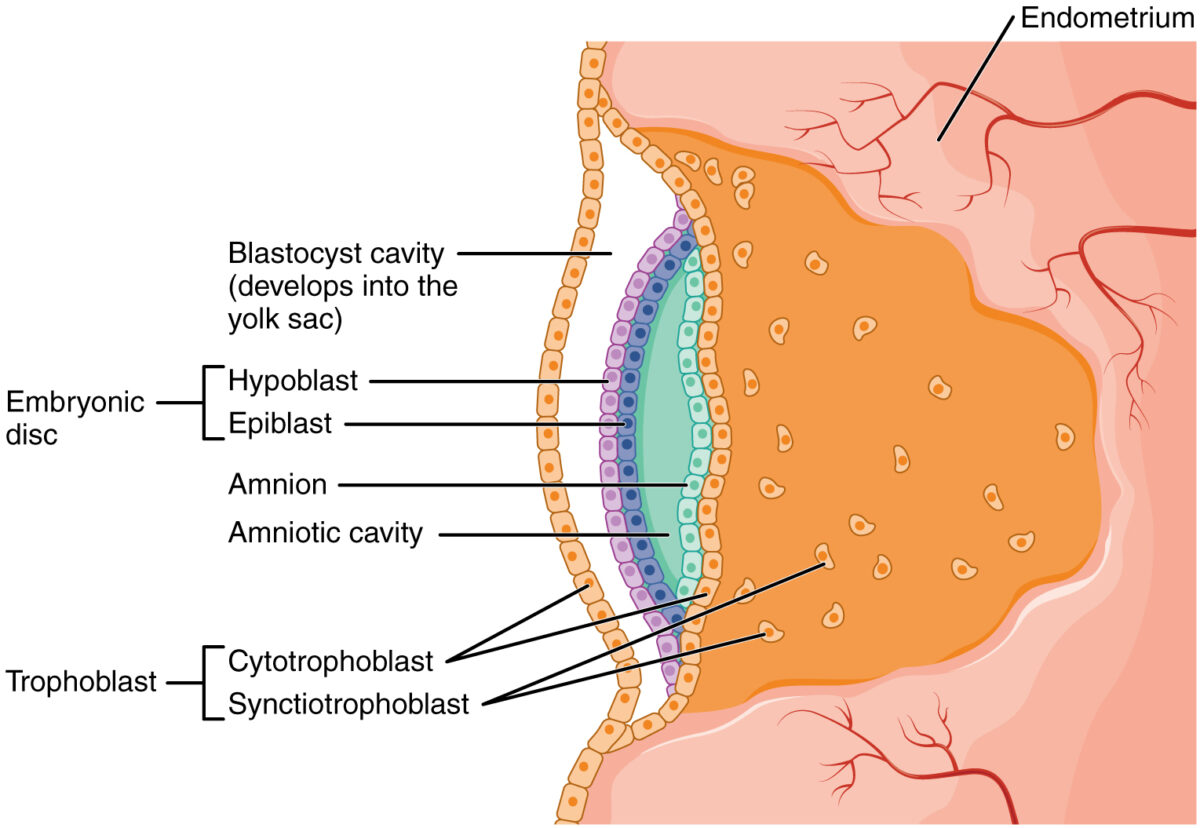
Initial development of the amniotic cavity during implantation
Image: “2907 Embroyonic Disc, Amniotic Cavity, Yolk Sac-02” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 3.0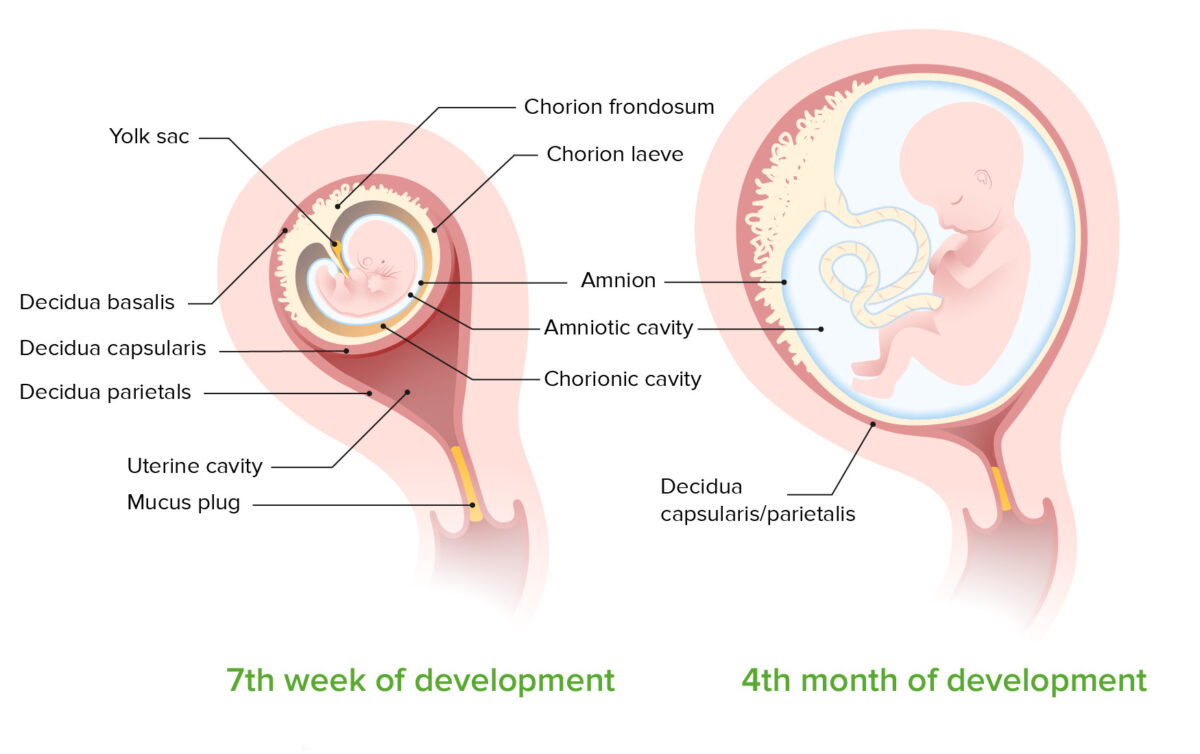
Development of the amniotic cavity between the 7th week and 4th month of development:
Note that by 7 months, the chorion and amnion have fused, obliterating the chorionic cavity.
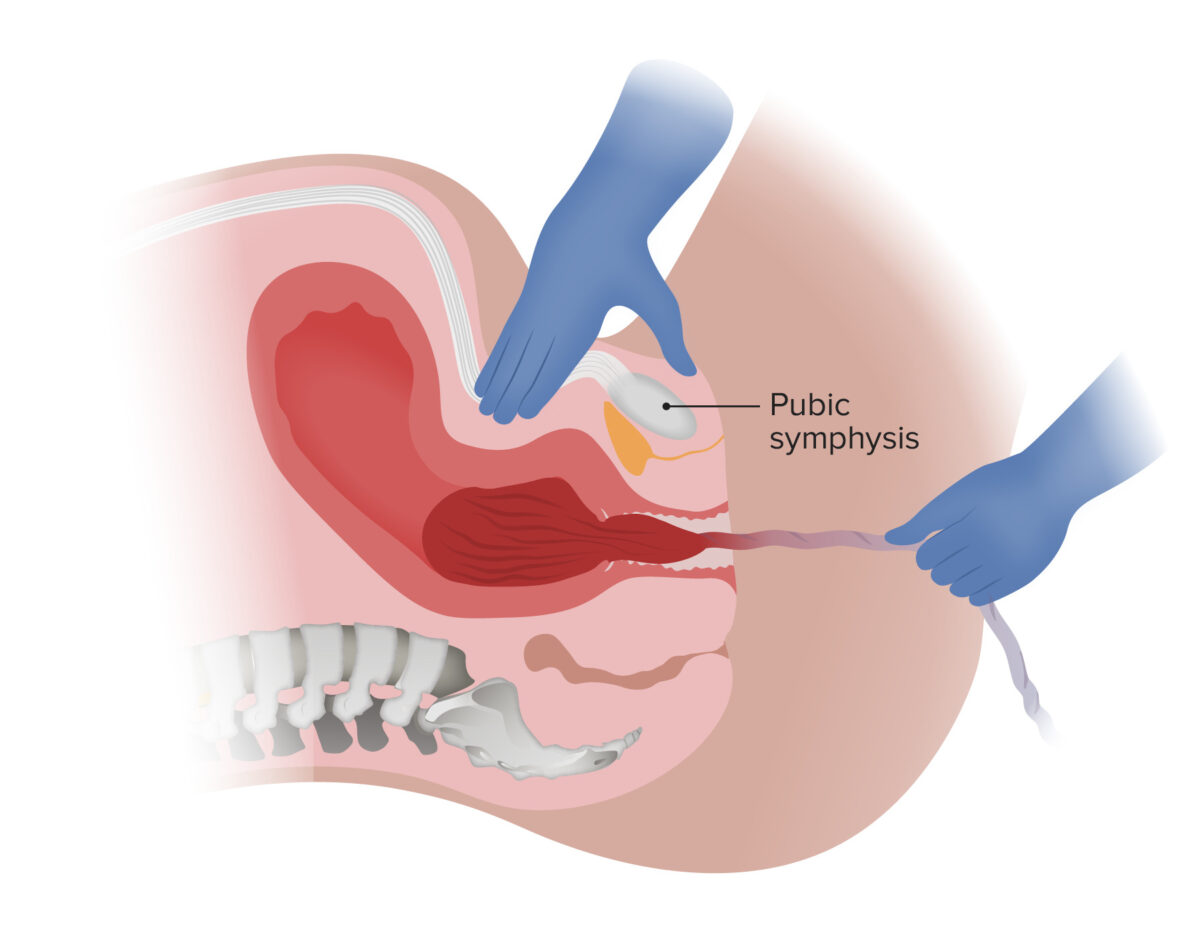
Delivery of the placenta via gentle downward traction on the umbilical cord and countertraction on the uterus:
Note that the umbilical cord is not clamped in this example.
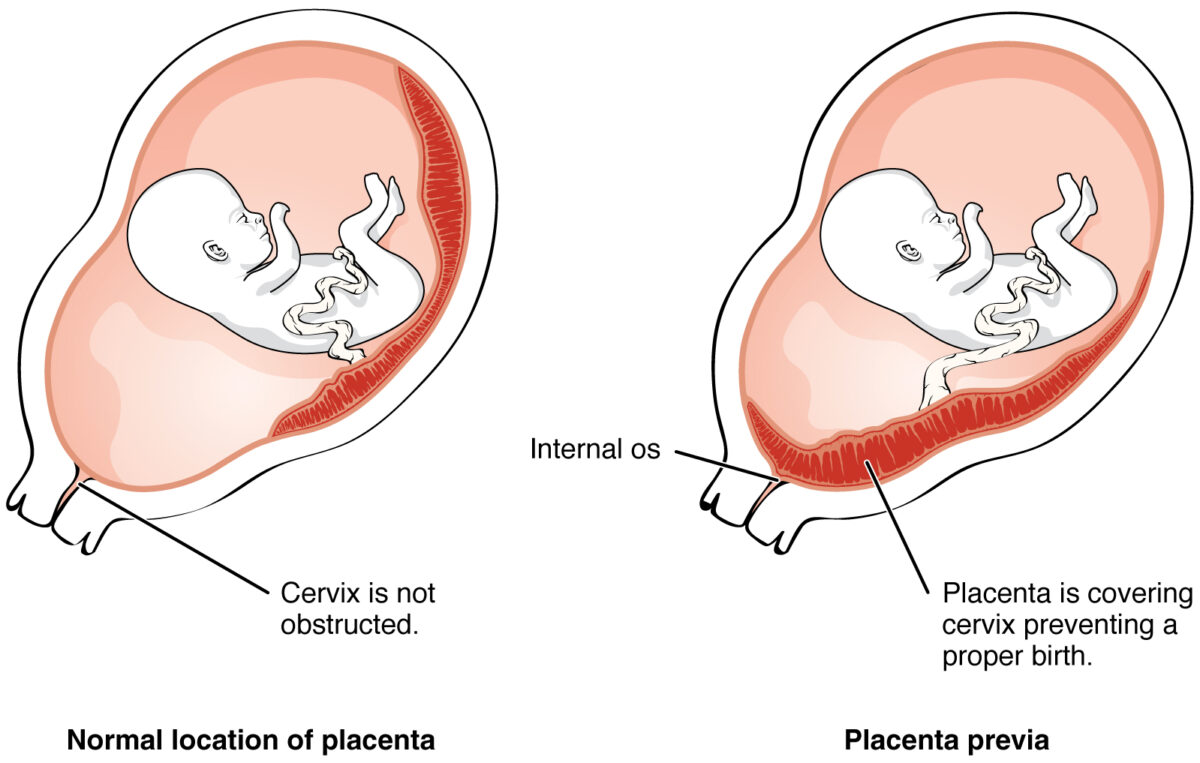
Placenta previa
Image: “2906 Placenta Previa-02” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 3.0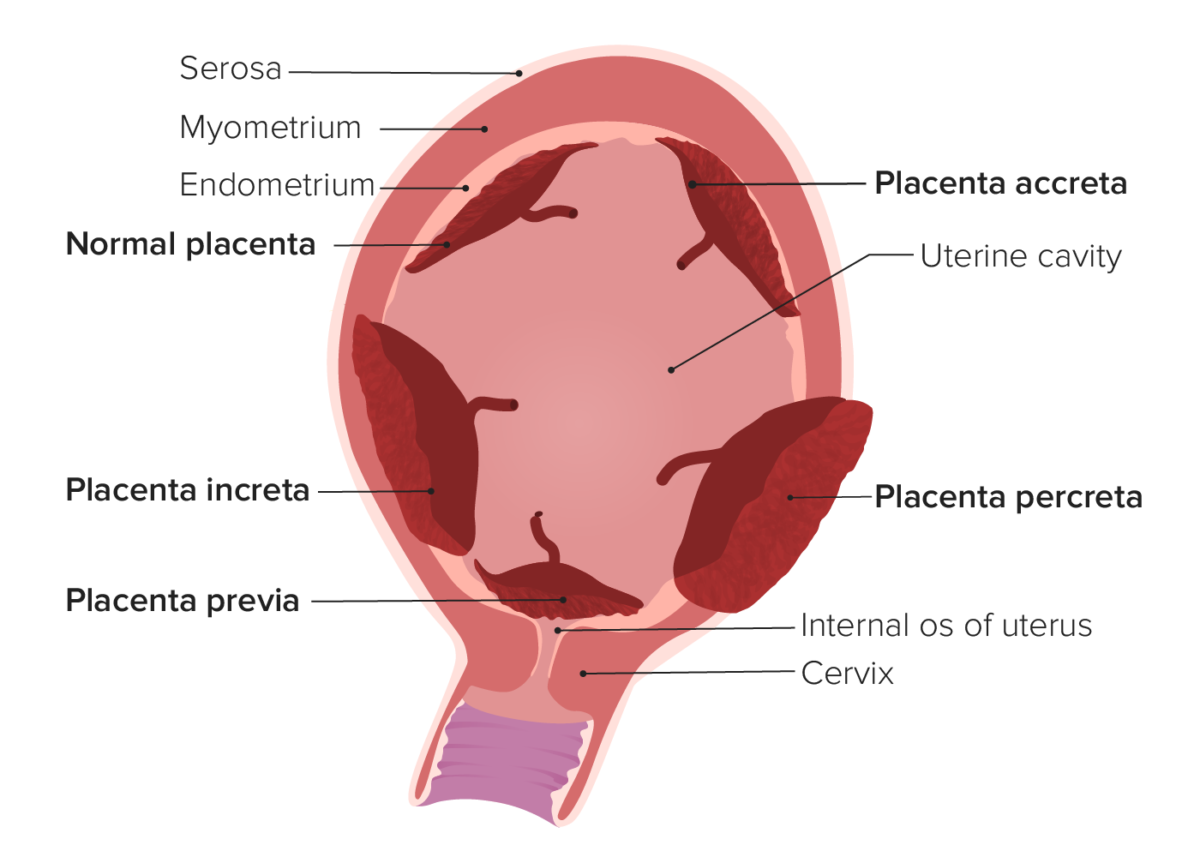
Types of abnormal placentation
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0