Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea is an acute, self-limited skin disease. The etiology is not known, and it commonly occurs in young adults. Patients initially present with a single, ovoid "herald patch." This is followed by diffuse, pruritic, scaly, oval lesions over the trunk (often in a "Christmas tree" distribution on the back) and extremities. Pityriasis Rosea is an acute, self-limited skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions disease. The etiology is not known, and it commonly occurs in young adults. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship initially present with a single, ovoid “ herald patch Herald Patch Pityriasis Rosea.” This is followed by diffuse, pruritic, scaly, oval lesions over the trunk (often in a “Christmas tree” distribution on the back) and extremities. The diagnosis is clinical. Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea is an acute, self-limited skin disease. The etiology is not known, and it commonly occurs in young adults. Patients initially present with a single, ovoid "herald patch." This is followed by diffuse, pruritic, scaly, oval lesions over the trunk (often in a "Christmas tree" distribution on the back) and extremities. Pityriasis Rosea is a self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children condition; therefore, usually no treatment is required. However, topical steroids Steroids A group of polycyclic compounds closely related biochemically to terpenes. They include cholesterol, numerous hormones, precursors of certain vitamins, bile acids, alcohols (sterols), and certain natural drugs and poisons. Steroids have a common nucleus, a fused, reduced 17-carbon atom ring system, cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene. Most steroids also have two methyl groups and an aliphatic side-chain attached to the nucleus. Benign Liver Tumors and antihistamines Antihistamines Antihistamines are drugs that target histamine receptors, particularly H1 and H2 receptors. H1 antagonists are competitive and reversible inhibitors of H1 receptors. First-generation antihistamines cross the blood-brain barrier and can cause sedation. Antihistamines may be used for pruritus Pruritus An intense itching sensation that produces the urge to rub or scratch the skin to obtain relief. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema), if needed.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Primary:
Secondary:
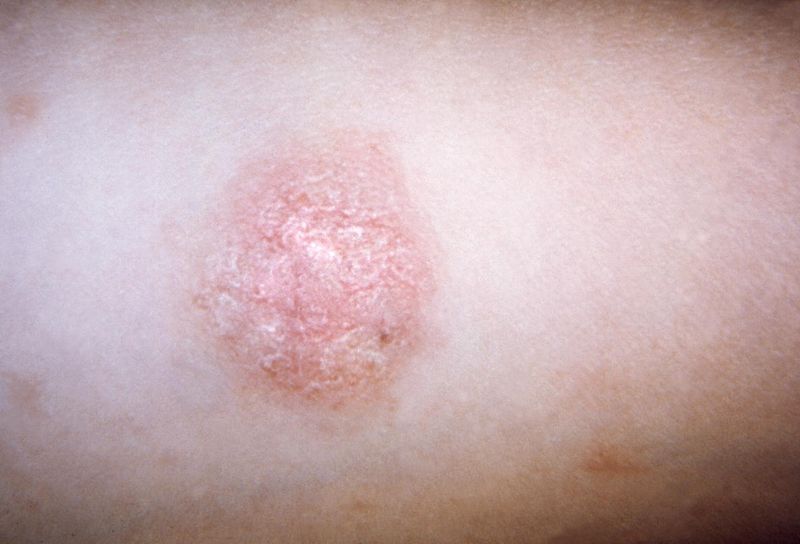
The primary “herald patch” in a patient with pityriasis rosea
Image: “Pityriasis rosea” by CDC Public Health Image Library. License: Public Domain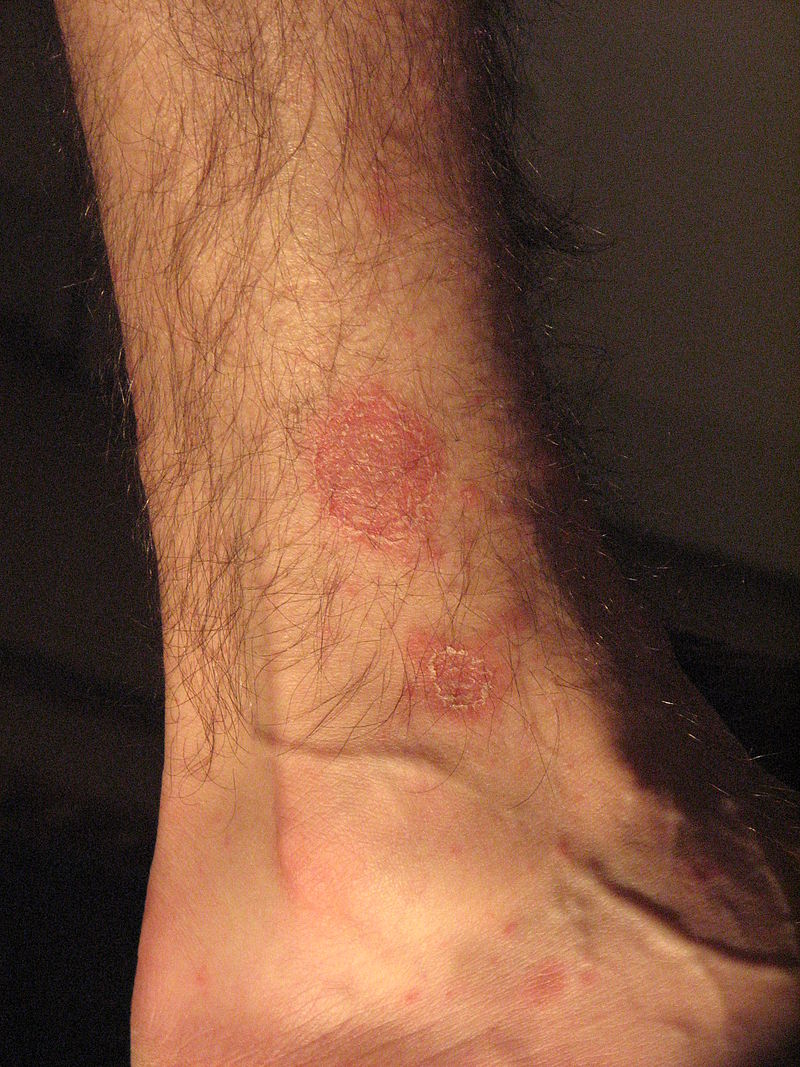
Demonstration of collarette scaling in pityriasis rosea:
Notice how the scale appears to lift near the center of the lesion, but remains attached closer to the border. The center appears wrinkled. These features give the lesion a cigarette paper appearance.
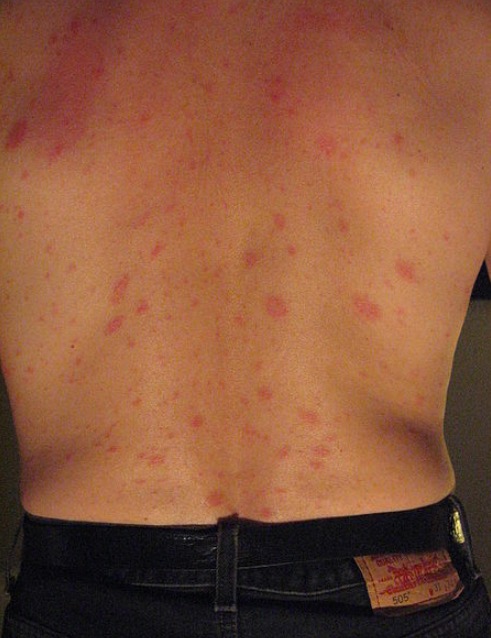
The secondary, generalized eruption of pityriasis rosea:
Multiple small, pink lesions are seen. Their oblique positioning is due to their orientation along Langer’s lines. In some patients, this can give a “Christmas tree” appearance.
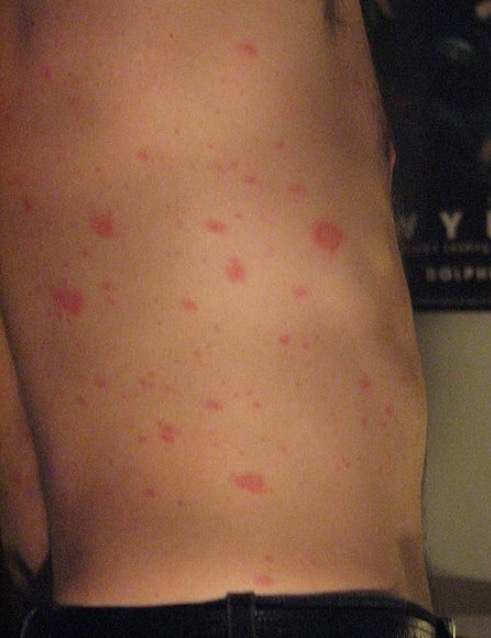
Generalized eruption of pityriasis rosea on the lateral torso of a patient
Image: “Pityriasis rosea” by Aceofhearts1968. License: Public DomainAtypical presentations[1,5,6]
There are several potential variations to the classic presentation. Some of these may include:
Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea is an acute, self-limited skin disease. The etiology is not known, and it commonly occurs in young adults. Patients initially present with a single, ovoid “herald patch.” This is followed by diffuse, pruritic, scaly, oval lesions over the trunk (often in a “Christmas tree” distribution on the back) and extremities. Pityriasis Rosea is a clinical diagnosis. The following tests may be used if the diagnosis is not clear.
Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea is an acute, self-limited skin disease. The etiology is not known, and it commonly occurs in young adults. Patients initially present with a single, ovoid “herald patch.” This is followed by diffuse, pruritic, scaly, oval lesions over the trunk (often in a “Christmas tree” distribution on the back) and extremities. Pityriasis Rosea is a self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children condition; therefore, usually no treatment is required. Consider referring for a dermatology consultation if lesions last > 3 months. The following measures may also be considered, though evidence is limited.
General:[5‒8]
Medical management:[5‒8]
Relapse Relapse Relapsing Fever:[5,6]
Diagnosis Codes:
This code is used to diagnose Pityriasis Rosea, a common, self-limited skin rash that begins with a single “herald patch” followed by a generalized eruption in a “Christmas tree” pattern on the back.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | L42 | Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea is an acute, self-limited skin disease. The etiology is not known, and it commonly occurs in young adults. Patients initially present with a single, ovoid “herald patch.” This is followed by diffuse, pruritic, scaly, oval lesions over the trunk (often in a “Christmas tree” distribution on the back) and extremities. Pityriasis Rosea |
| SNOMED CT | 13686004 | Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea Pityriasis rosea is an acute, self-limited skin disease. The etiology is not known, and it commonly occurs in young adults. Patients initially present with a single, ovoid “herald patch.” This is followed by diffuse, pruritic, scaly, oval lesions over the trunk (often in a “Christmas tree” distribution on the back) and extremities. Pityriasis Rosea (disorder) |