Pierre Robin sequence, also known as Pierre Robin syndrome or simply Robin sequence, is a condition in infants that is characterized by a smaller-than-normal mandible Mandible The largest and strongest bone of the face constituting the lower jaw. It supports the lower teeth. Jaw and Temporomandibular Joint: Anatomy, a tongue Tongue The tongue, on the other hand, is a complex muscular structure that permits tasting and facilitates the process of mastication and communication. The blood supply of the tongue originates from the external carotid artery, and the innervation is through cranial nerves. Lips and Tongue: Anatomy that retracts back into the throat Throat The pharynx is a component of the digestive system that lies posterior to the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and larynx. The pharynx can be divided into the oropharynx, nasopharynx, and laryngopharynx. Pharyngeal muscles play an integral role in vital processes such as breathing, swallowing, and speaking. Pharynx: Anatomy, and difficulty breathing. The exact etiology of the Pierre Robin sequence is unknown, although some contributing factors have been identified. The abnormal development of the lower jaw Jaw The jaw is made up of the mandible, which comprises the lower jaw, and the maxilla, which comprises the upper jaw. The mandible articulates with the temporal bone via the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). The 4 muscles of mastication produce the movements of the TMJ to ensure the efficient chewing of food. Jaw and Temporomandibular Joint: Anatomy during gestation, along with certain genetic mutations Genetic Mutations Carcinogenesis, can be the first of a series of steps leading to breathing and feeding problems in the neonate Neonate An infant during the first 28 days after birth. Physical Examination of the Newborn.
Last updated: Dec 20, 2024
The Pierre Robin sequence (PRS) is a triad of congenital micrognathia (small lower jaw Jaw The jaw is made up of the mandible, which comprises the lower jaw, and the maxilla, which comprises the upper jaw. The mandible articulates with the temporal bone via the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). The 4 muscles of mastication produce the movements of the TMJ to ensure the efficient chewing of food. Jaw and Temporomandibular Joint: Anatomy), glossoptosis (retraction of the tongue Tongue The tongue, on the other hand, is a complex muscular structure that permits tasting and facilitates the process of mastication and communication. The blood supply of the tongue originates from the external carotid artery, and the innervation is through cranial nerves. Lips and Tongue: Anatomy into the pharynx Pharynx The pharynx is a component of the digestive system that lies posterior to the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and larynx. The pharynx can be divided into the oropharynx, nasopharynx, and laryngopharynx. Pharyngeal muscles play an integral role in vital processes such as breathing, swallowing, and speaking. Pharynx: Anatomy), and airway Airway ABCDE Assessment obstruction.
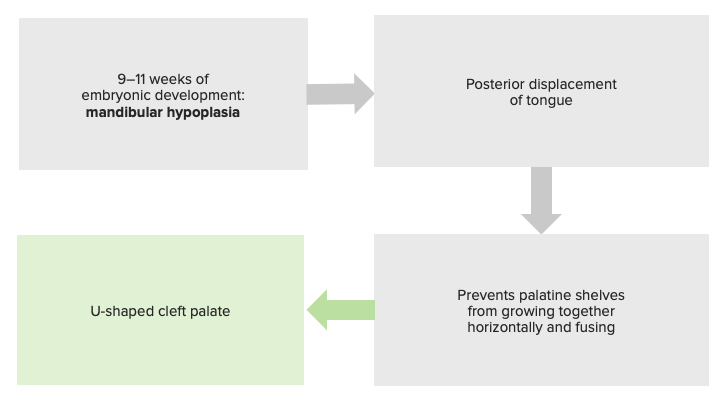
Pathophysiology of the Pierre Robin sequence, justifying its classification as a sequence and not a syndrome.
Image by Lecturio.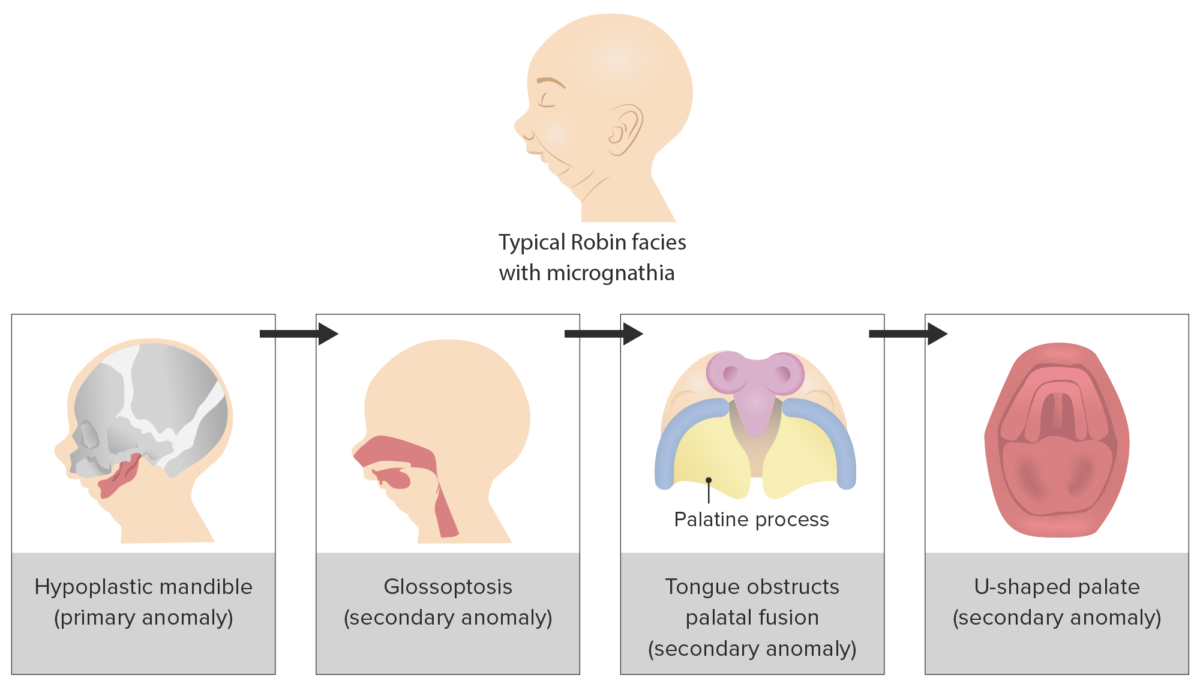
Progression of triad of events that underlies the Pierre Robin sequence clinical presentation
Image by Lecturio.Epidemiology: 5.15 per 10,000 live births in the United States
Etiology:
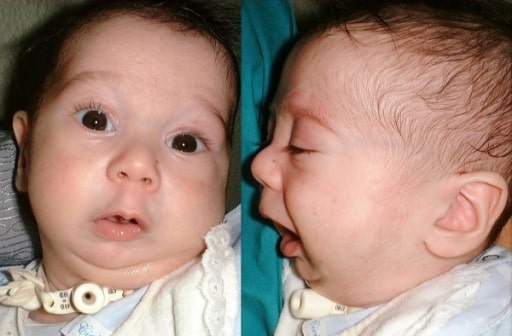
Frontal and lateral views of an infant with Pierre Robin sequence
Image: “Preoperative frontal and lateral views of an infant with Pierre Robin sequence” by Maxillo-Facial Surgery Division, Head and Neck Department, University and Hospital of Parma, Parma, Italy. License: CC BY 2.0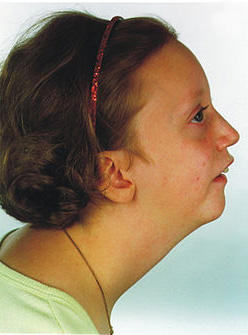
Micrognathia
Image: “Pitt-rogers-danks syndrome” by Marie Sogaard et al. License: CC BY 2.0, edited by Lecturio.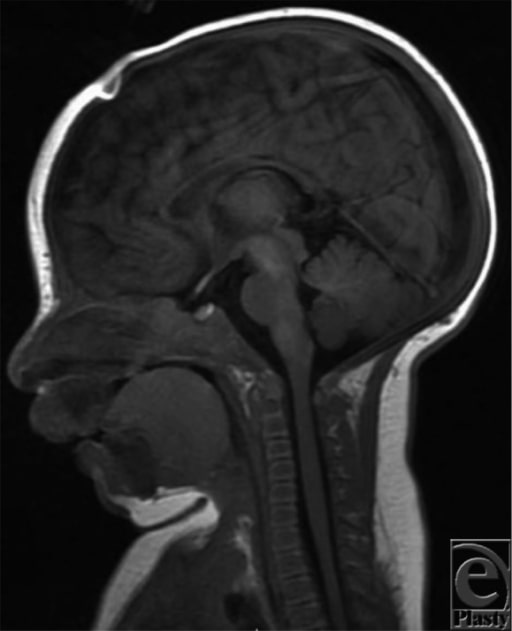
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 2 months of age indicating mandibular hypoplasia and posterior displacement of the tongue, causing significant pharyngeal airway obstruction
Image: “Magnetic resonance imaging” by Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, Grand Rapids, Mich. License: CC BY 2.0The following conditions are differential diagnoses for isolated or syndromic Pierre Robin sequence: