A neonate, or newborn, is defined as a child less than 28 days old. A thorough physical examination should be performed within the first 24 hours of life to identify abnormalities and improve outcomes by offering timely treatment. Physical examination of the newborn is typically performed sequentially from head to toe, keeping in mind common neonatal pathologies based on family and prenatal history, risk factors, and geographic region.
Last updated: Jun 8, 2023
Before examining the infant, a thorough chart review should be performed.
| Sign | 0 points | 1 point | 2 points | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Appearance | Cyanotic or mottled | Cyanotic extremities, pink body | Pink extremities and body |
| P | Pulse | Absent | < 100/min | > 100/min |
| G | Grimace | No response to stimulation | Grimace with suction or aggressive stimulation | Cry on stimulation |
| A | Activity | None | Some flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs of arms and legs | Active flexion Flexion Examination of the Upper Limbs against resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing |
| R | Respirations | Absent | Weak, irregular, and slow | Strong cry |
The normal range for neonatal vital signs is unique.
During the perinatal period, growth parameters Growth Parameters Child and Adolescent Care should be plotted daily on a growth chart.
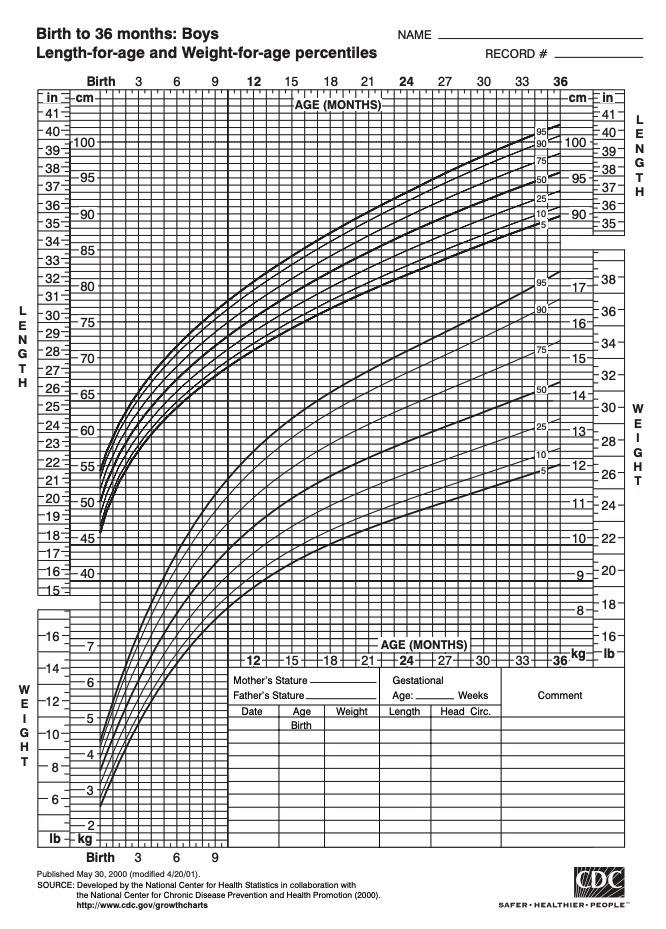
Example of a height and weight growth chart for boys from 0–36 months of age
Physical exam findings can help confirm the gestational date (Ballard score):
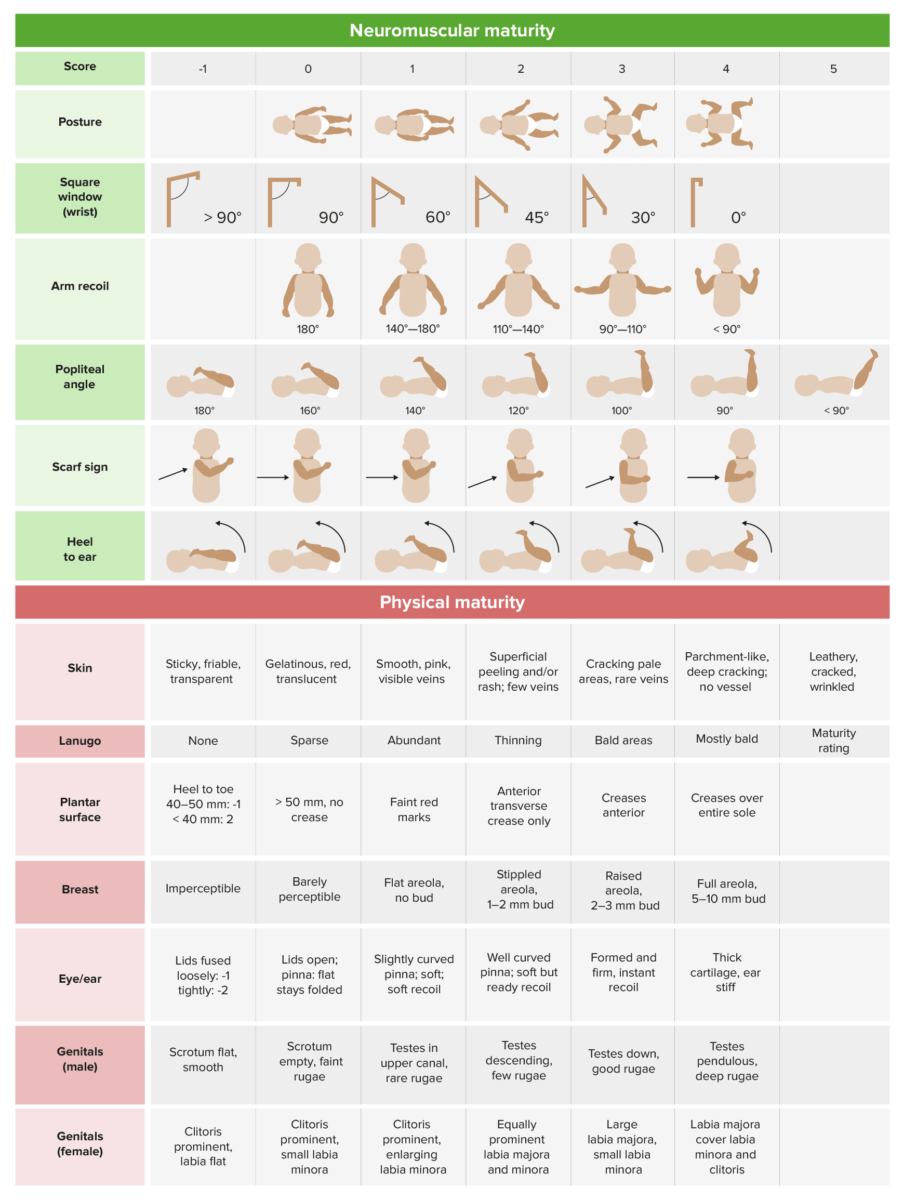
Ballard scoring: scoring system that uses physical exam findings to determine likely neonatal maturity and gestational age
Score: gestational age
-10: 20 weeks
-5: 22 weeks
0: 24 weeks
5: 26 weeks
10: 28 weeks
15: 30 weeks
20: 32 weeks
25: 34 weeks
30: 36 weeks
35: 38 weeks
40: 40 weeks
45: 42 weeks
50: 44 weeks
The infant’s reaction to the examination is useful in assessing:
Tachypnea Tachypnea Increased respiratory rate. Pulmonary Examination may indicate:
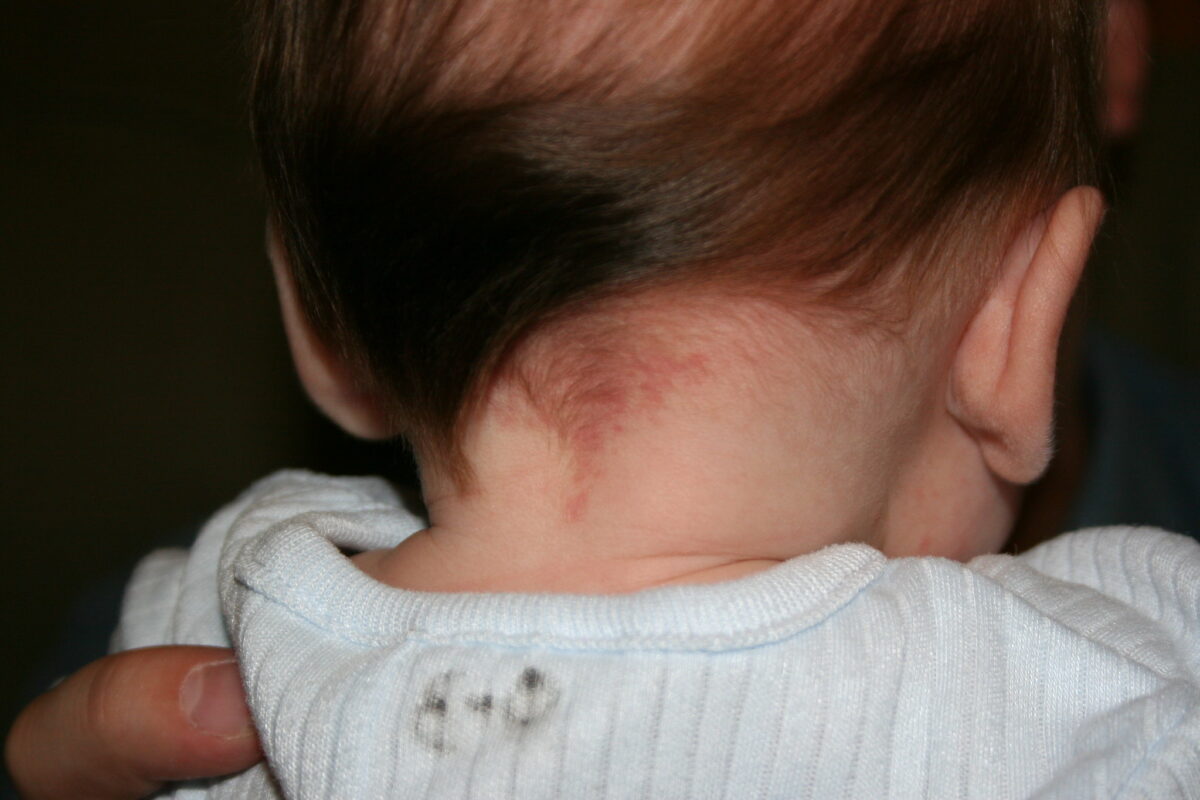
Nevus simplex (“stork bite” or “angel’s kiss”): common salmon-colored patch, seen here on the nape of the patient’s neck
Image: “IMG_9564” by Abigail Batchelder. License: CC BY 2.0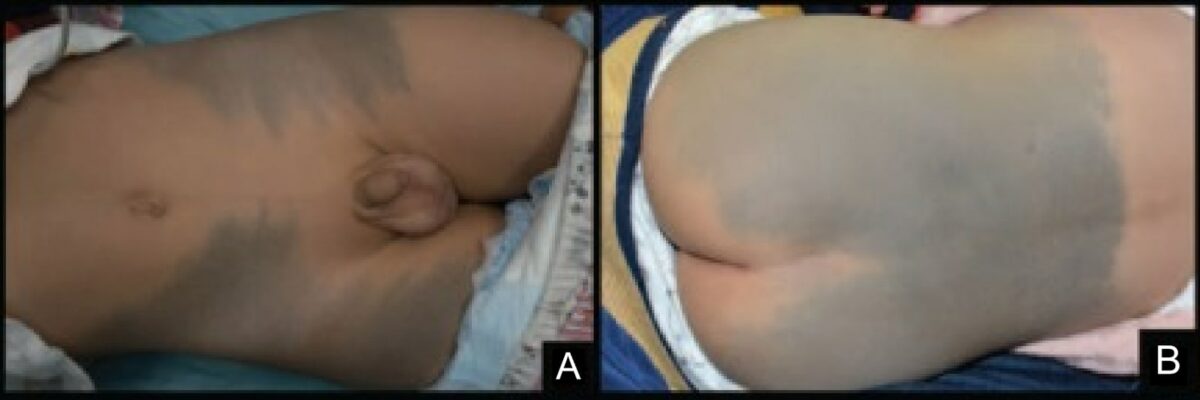
Congenital dermal melanocytosis (formerly known as “Mongolian spot”):
(A) Gray-blue patches spread over thigh
(B) Gray-blue patches spread over waist and breech
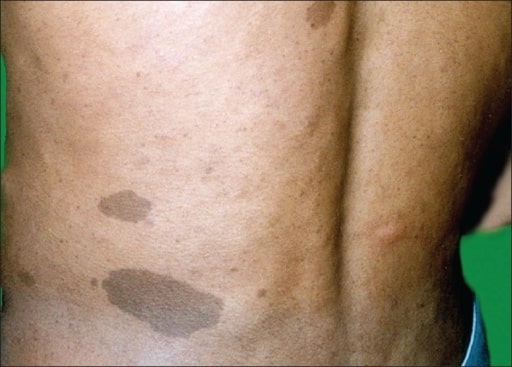
Clinical photograph of neurofibromatosis showing 3 cafe-au-lait spots on the left side of the lower back along with freckling
Image: “Cafe au lait spots” by Department of Pathology, Mahatma Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences, Sevagram, Wardha, India. License: CC BY 2.0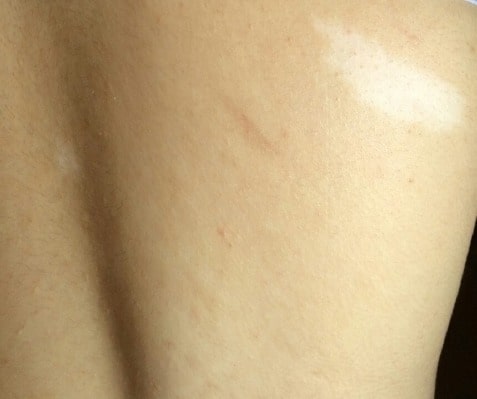
Hypomelanotic lesions (ash-leaf spots) on skin in a patient with tuberous sclerosis
Image: “Hypomelanotic lesions” by Department of Medical Genetics, School of Medicine, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. License: CC BY 3.0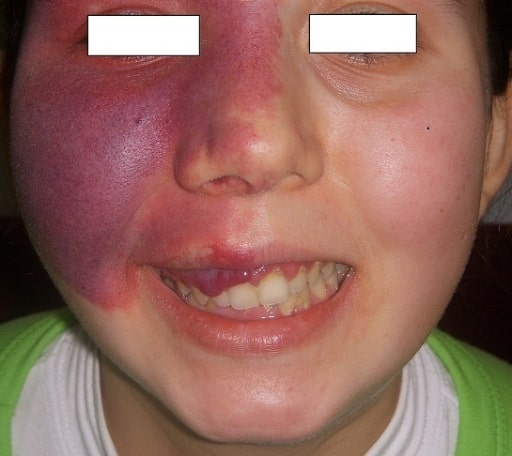
Sturge-Weber syndrome showing nevus flammeus (“port-wine stain”) on right nasal, periorbital, frontal, and maxillary areas, corresponding to trigeminal nerve distribution
Image: “Congestive skin lesion” by Istanbul Medeniyet University Goztepe Education and Research Hospital, Neurology Department, Istanbul, Turkey. License: CC BY 2.0Palpate the anterior (3–6 cm in diameter) and posterior (1–1.5 cm) fontanelles:
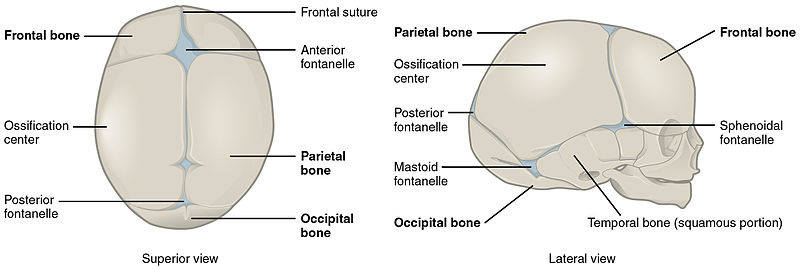
Cranium of a newborn, showing the fontanelles
Image: “Newborn Skull-01” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 3.0Palpate for symmetry:
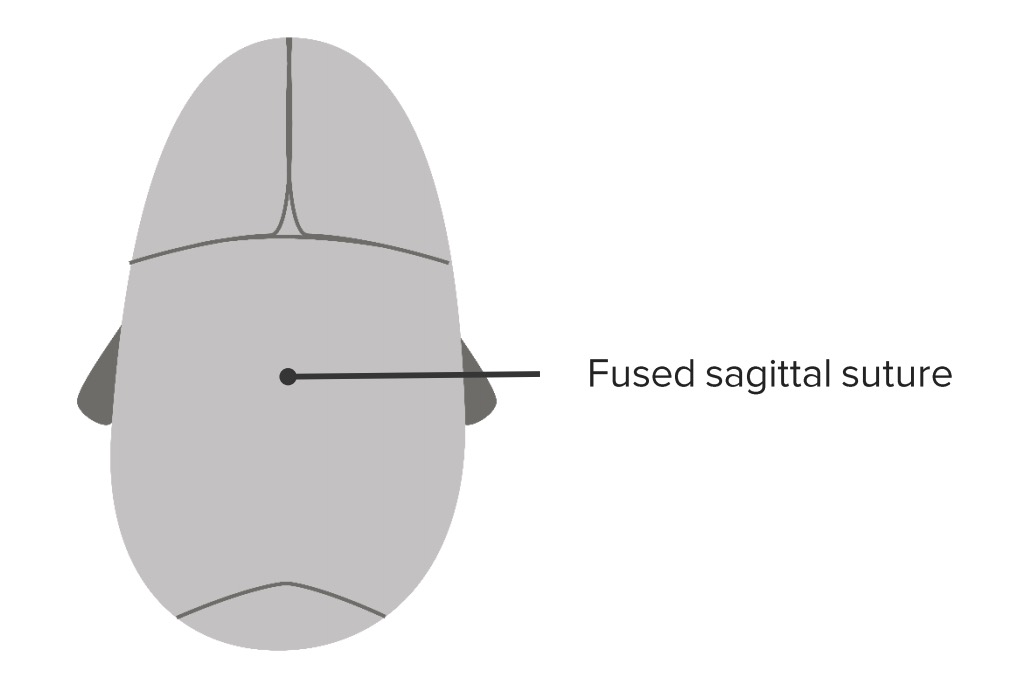
Diagram of a head with sagittal craniosynostosis. Note the fusion of the sagittal suture.
Image by Lecturio.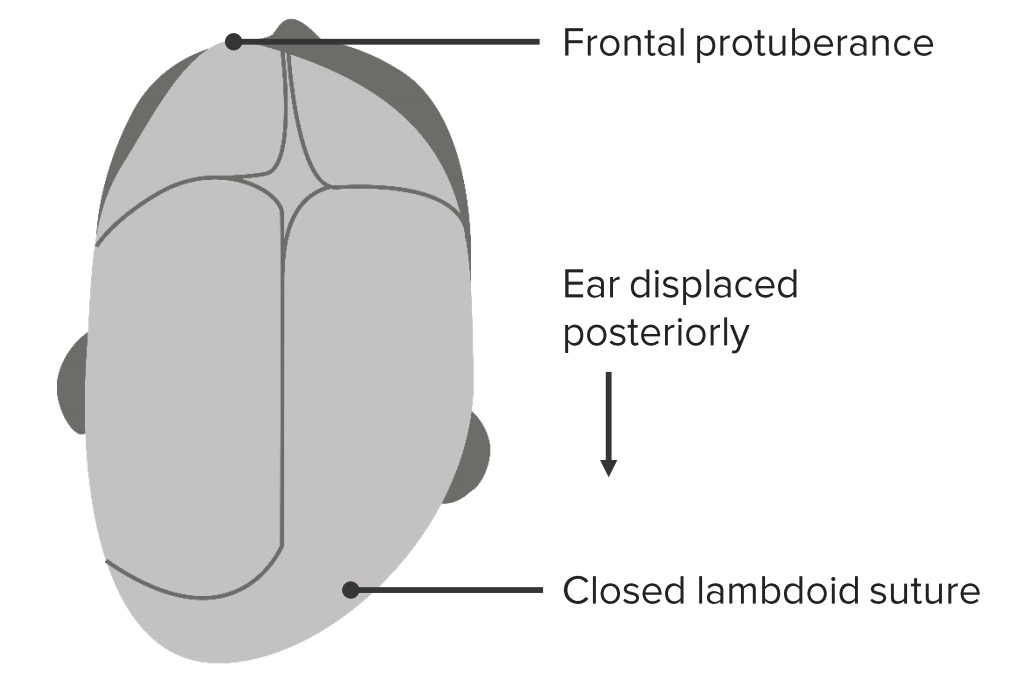
Diagram of a head with lambdoidal craniosynostosis. Note the fusion of the lambdoid suture, the anterior and posterior protuberances, and the posterior displacement of the ear.
Image by Lecturio.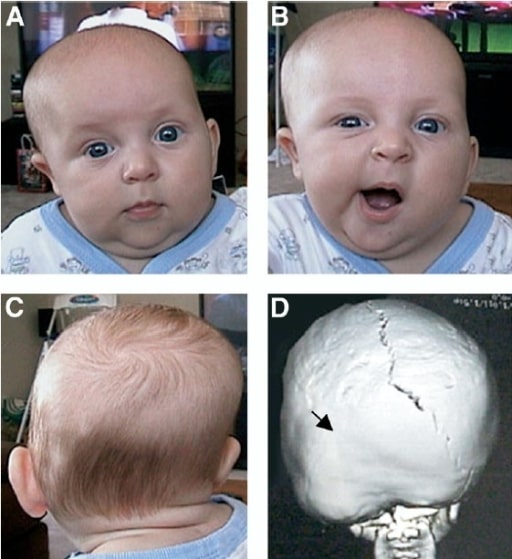
Posterior plagiocephaly caused by lambdoid synostosis.
(A, B) frontal and (C) posterior views of an infant with left lambdoid synostosis; the 3-dimensional computed tomography (CT) reconstruction (D, posterior view) shows premature fusion of the left lambdoidal suture (arrow). Note the facial asymmetry of the patient secondary to the lambdoid synostosis (B) that does not occur in positional plagiocephaly.
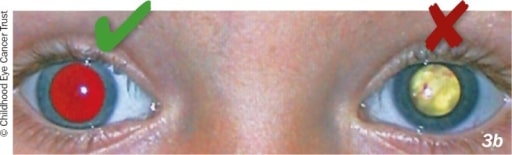
Abnormal red reflex
Image: “Retinoblastoma” by Community eye health / International Centre for Eye Health. License: CC BY 2.0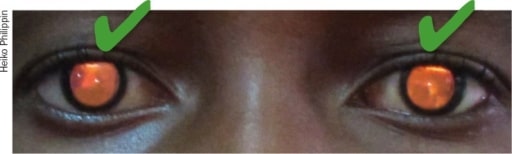
Normal red reflex
Image: “The normal red reflex” by US National Library of Medicine. License: CC BY 2.0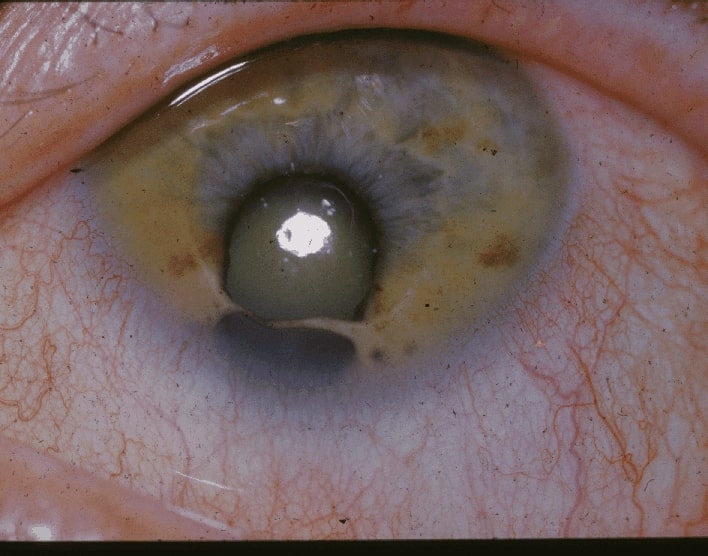
Example of coloboma
Image: “Coloboma” by National Eye Institute. License: Public Domain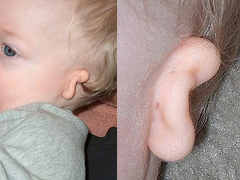
Detail of microtia (outer ear deformity). Right ear is normal.
Image: “Microtia” by Mulgamutt. License: Public Domain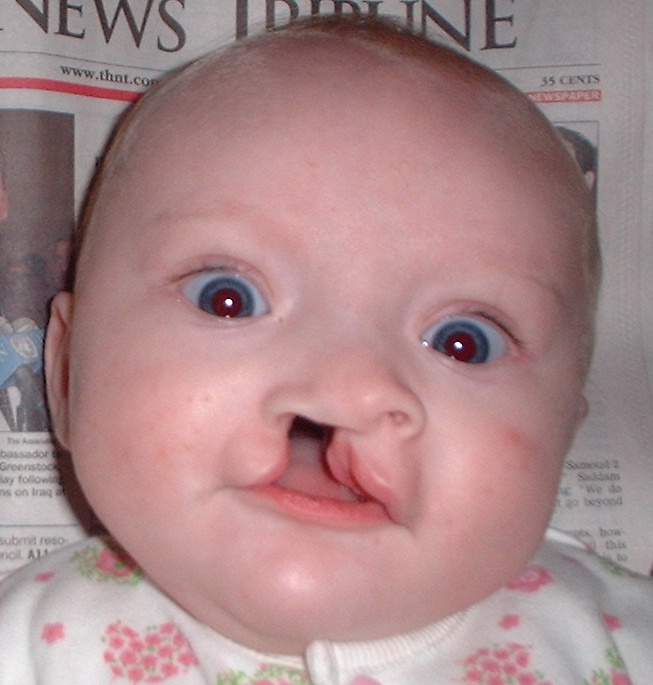
Six-month-old girl before going into surgery to have her unilateral complete cleft lip repaired
Image: “Child born with cleft palate at 5 months of age” by King97tut. License: Public Domain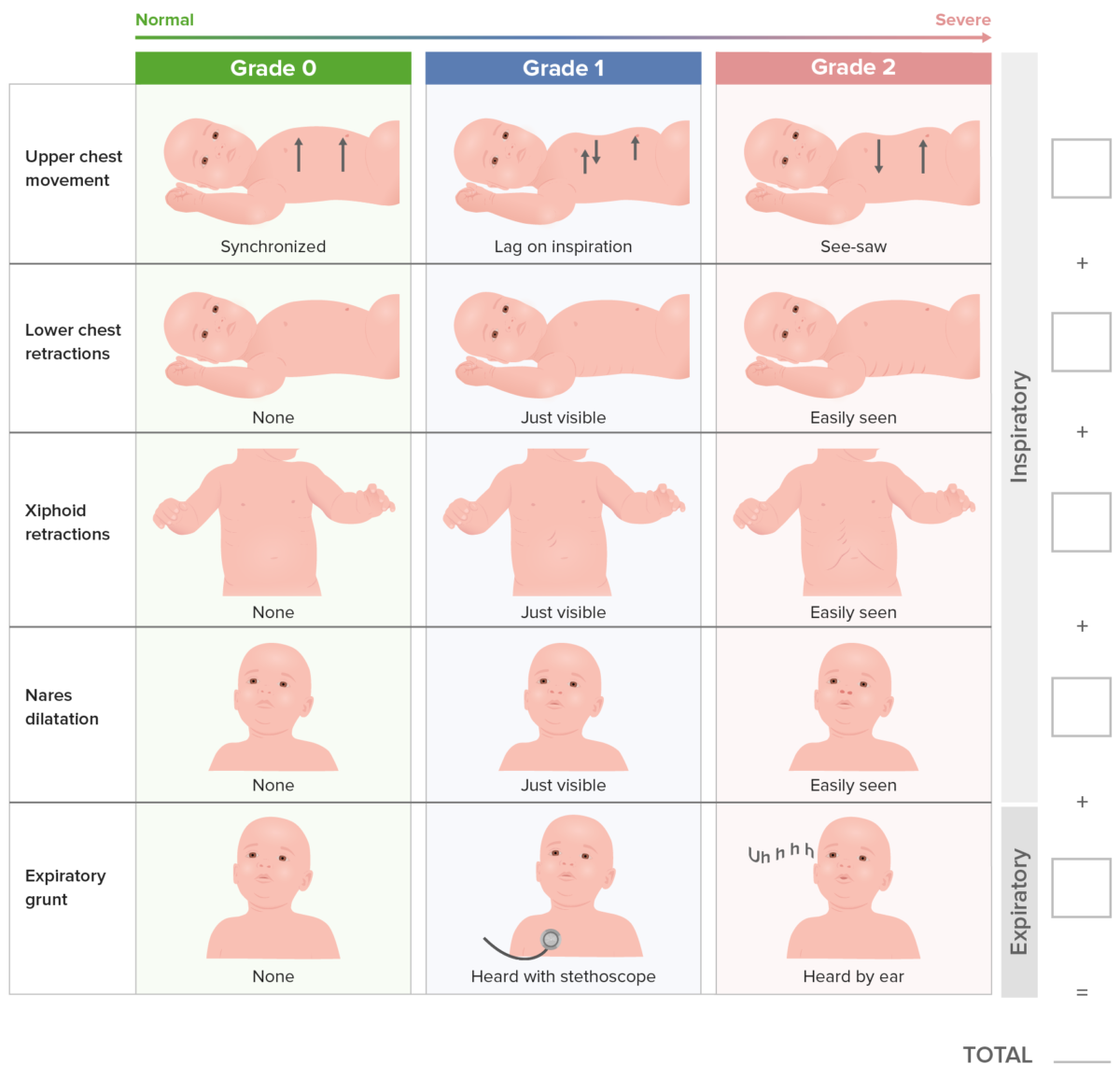
Silverman scoring system for respiratory difficulty
Image by Lecturio.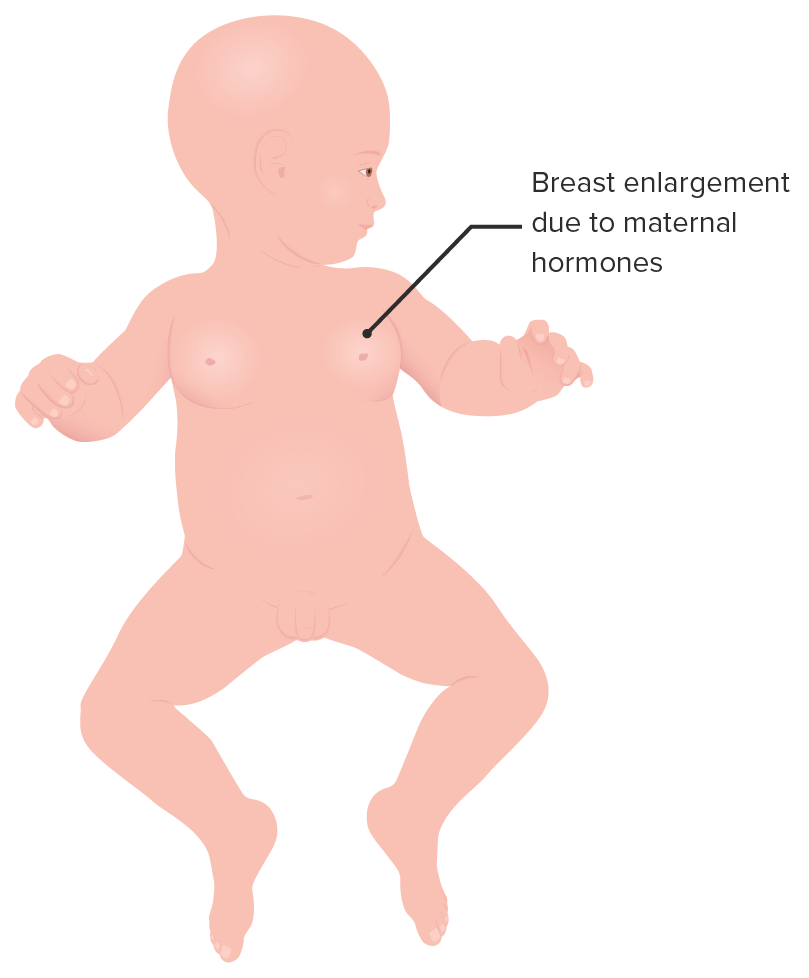
Neonatal gynecomastia
Image by Lecturio.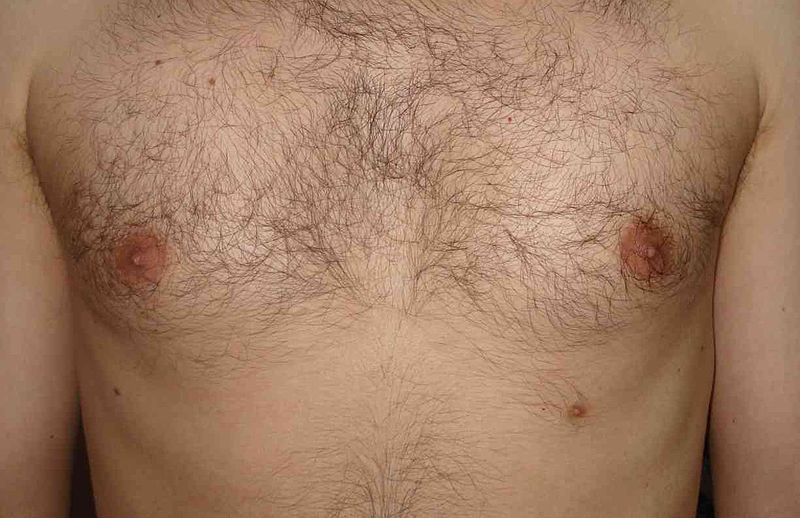
Supernumerary 3rd nipple
Image: “Supernumerary third nipple” by Zureks. License: CC BY 3.0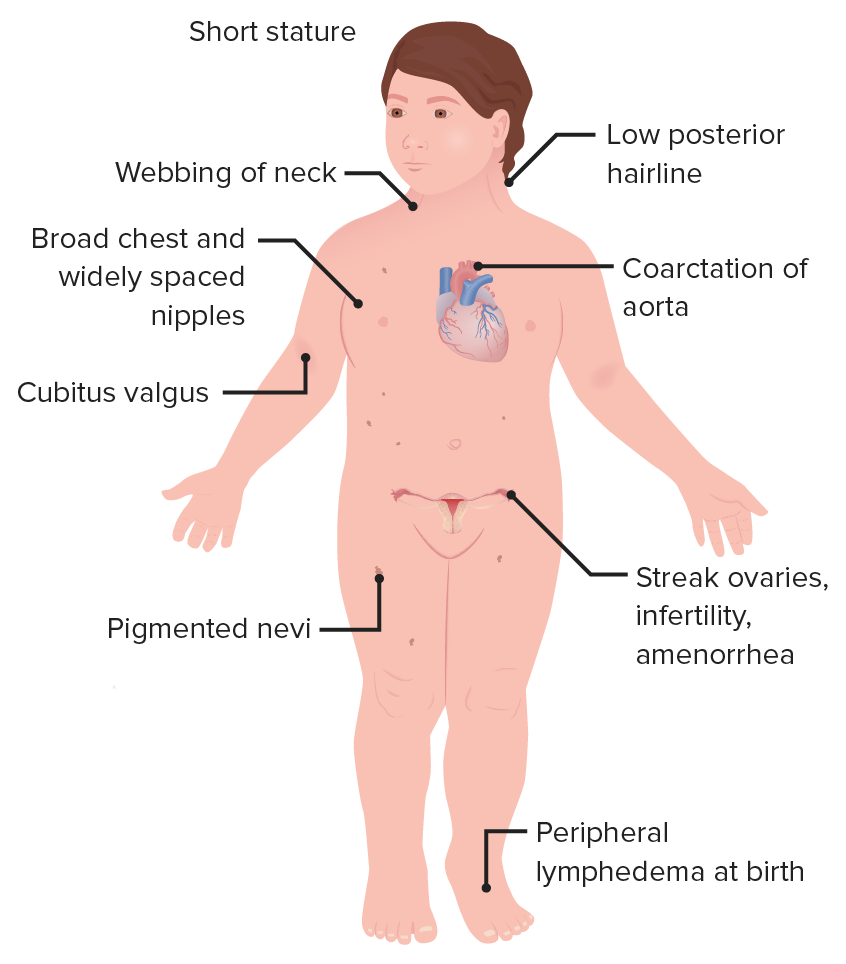
Characteristic features of a girl with Turner syndrome
Image by Lecturio.Auscultate the lung fields bilaterally.
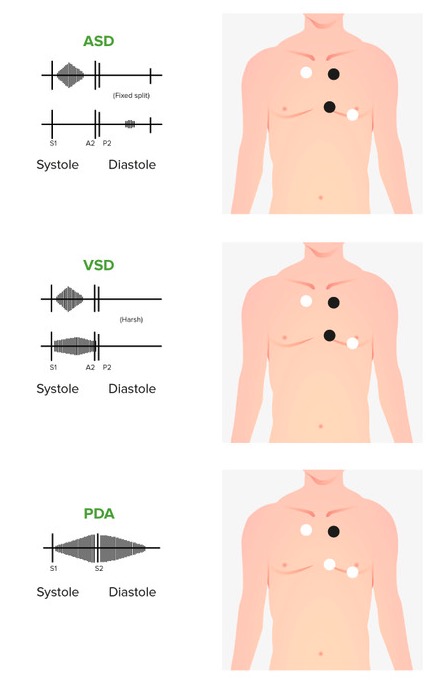
Murmurs of congenital heart disease
ASD: atrial septal defect
VSD: ventricular septal defect
PDA: patent ductus arteriosus
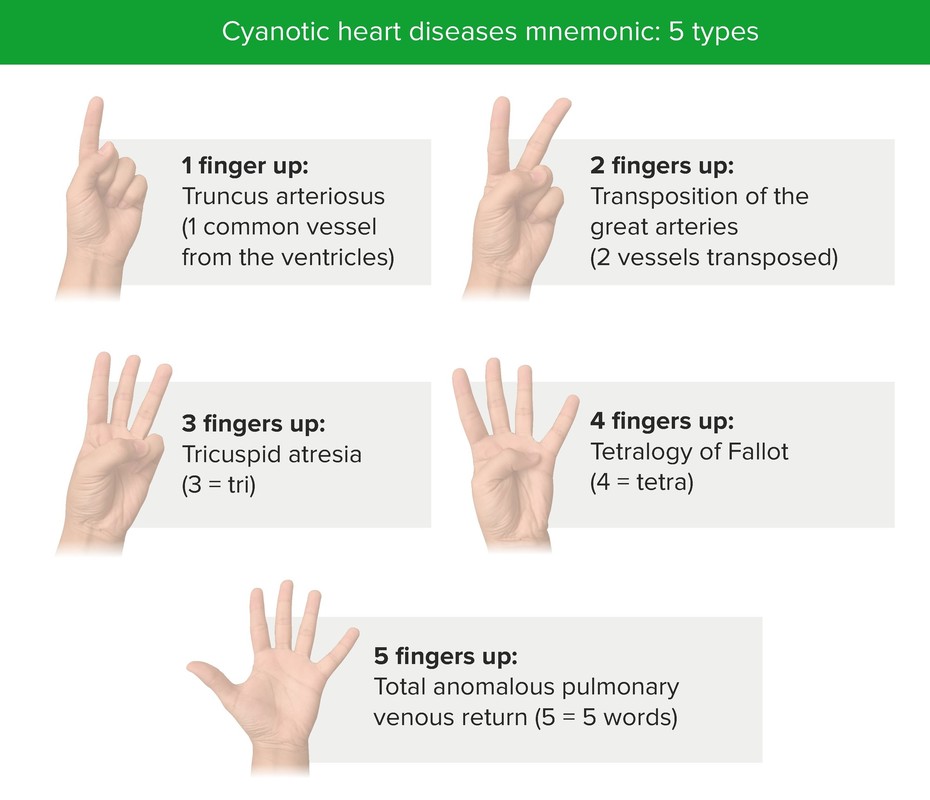
Cyanotic heart diseases mnemonic
Image by Lecturio.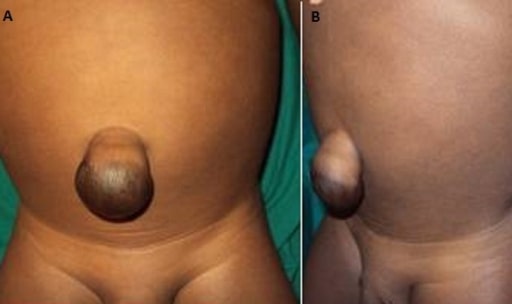
Umbilical hernia in a 2-year-old child
Image: “A and B proboscoid hernia” by Surgeon Department, University Teaching Hospital Center, Yaoundé, Cameroon. License: CC BY 2.0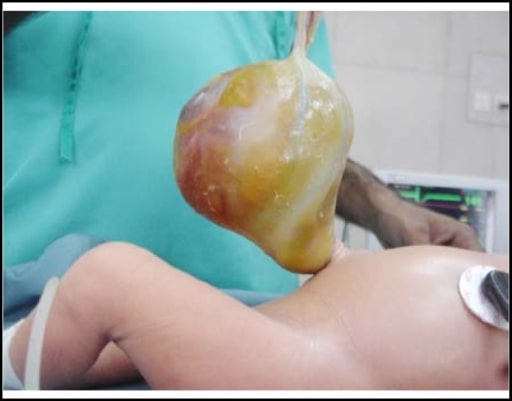
Large omphalocele containing omphalomesenteric duct cyst
Image: “Omphalocele” by Yousuf Aziz Khan, MBBS, FCPS (Paediatric Surgeon), Department of Paediatric Surgery, National Institute of Child Health, Rafiquee Shaheed Road, Karachi – 75510, Sind, Pakistan. License: CC BY 3.0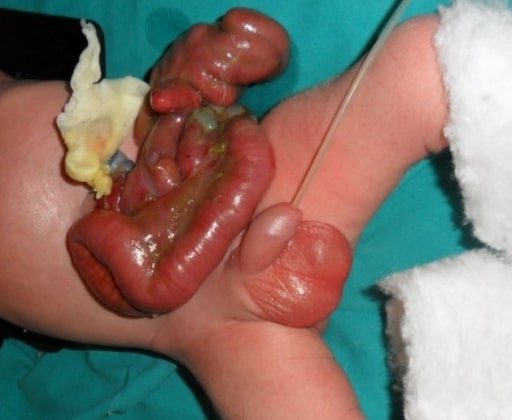
Gastroschisis in a newborn. Note the eviscerated bowel to the right of the umbilical insertion.
Image: “Gastroschis with concomitant jejuno-ileala tresia type III b” by Clinic of Pediatric Surgery, University Clinical Center Sarajevo, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina. License: CC BY 3.0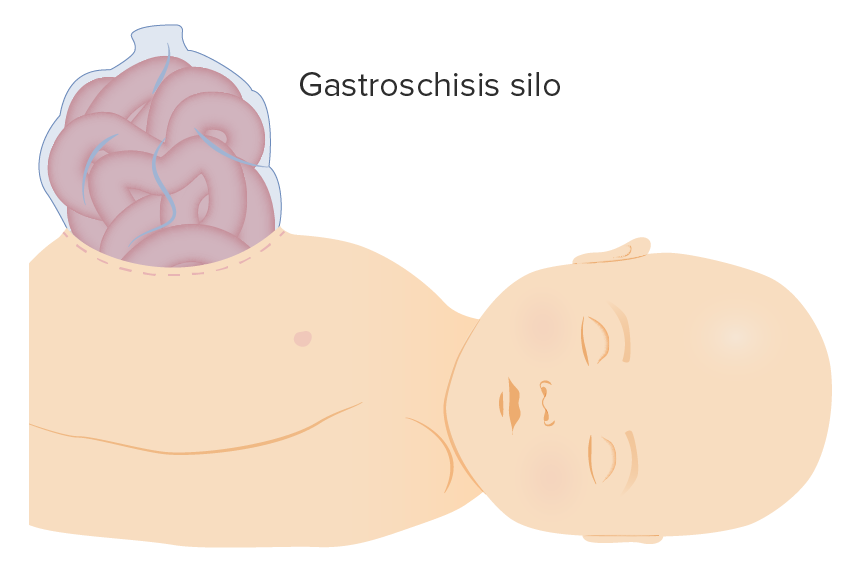
Gastroschisis silo
Image by Lecturio.Inspect and palpate for any congenital defects of the spine Spine The human spine, or vertebral column, is the most important anatomical and functional axis of the human body. It consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and 5 lumbar vertebrae and is limited cranially by the skull and caudally by the sacrum. Vertebral Column: Anatomy.
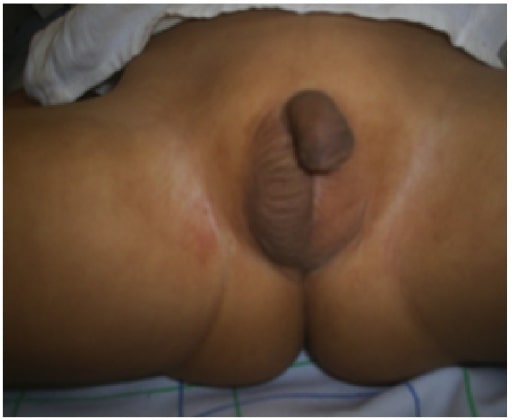
3-year-old child with undescended testes showing nonpalpable left testicle and prepubertal right testicle in scrotal position
Image: “47XYY” by Department of Endocrinology, Mohammed VI Hospital, Medical School, Mohammed the First University, 60 000 Oujda, Morocco. License: CC BY 3.0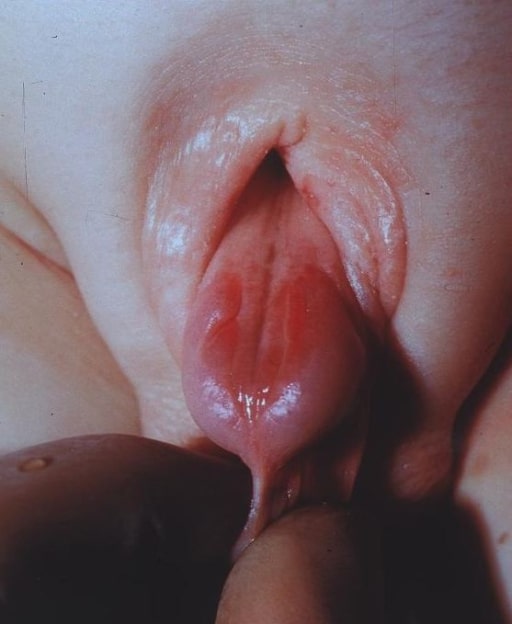
Baby boy with epispadias
Image: “Male baby with epispadias” by Department of Pediatric Urology, University Medical Center Regensburg, Germany. License: CC BY 2.0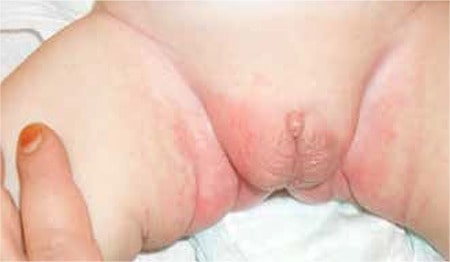
Ambiguous genitalia with bifid scrotum and micropenis
Image: “Bifid scrotum and micropenis” by Kocaeli University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes, Kocaeli, Turkey. License: CC BY 2.5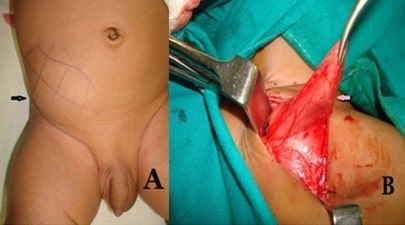
(A) Clinical photograph of a child showing swelling on the right side of abdomen and empty right hemiscrotum
(B) Operative photograph showing the hernia sac containing testis
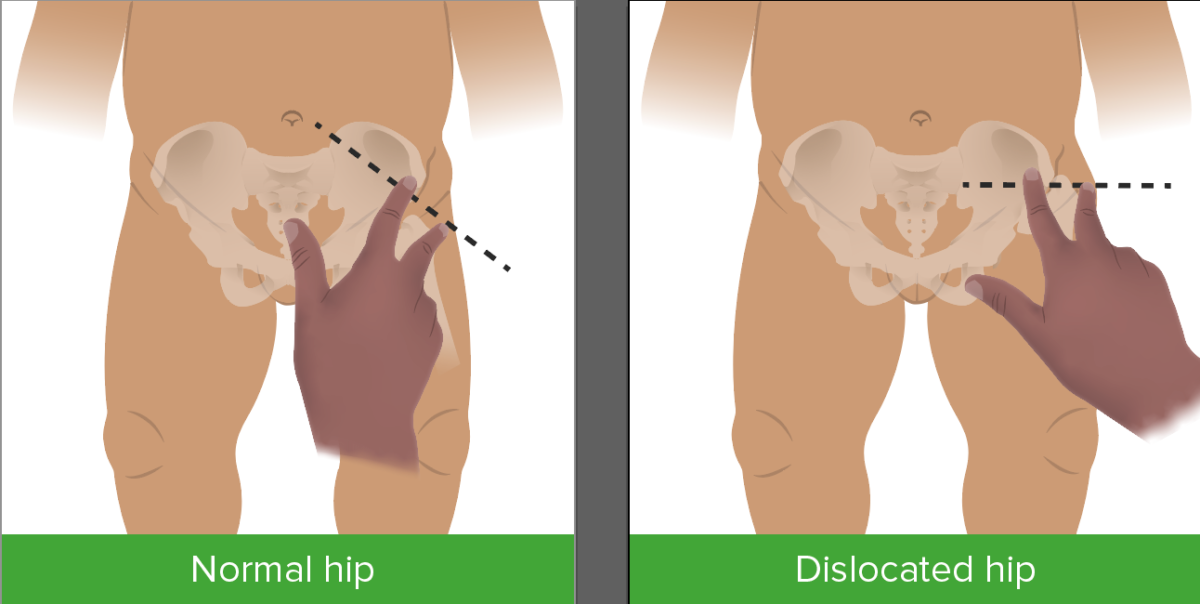
Klisic test for dysplasia of the hip
Image by Lecturio.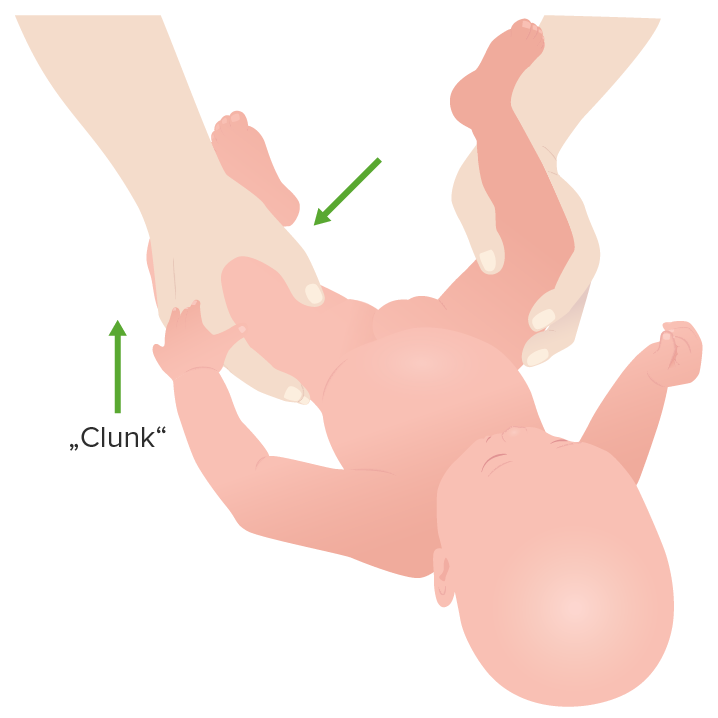
Hip clunk during the Ortolani maneuver
Image by Lecturio.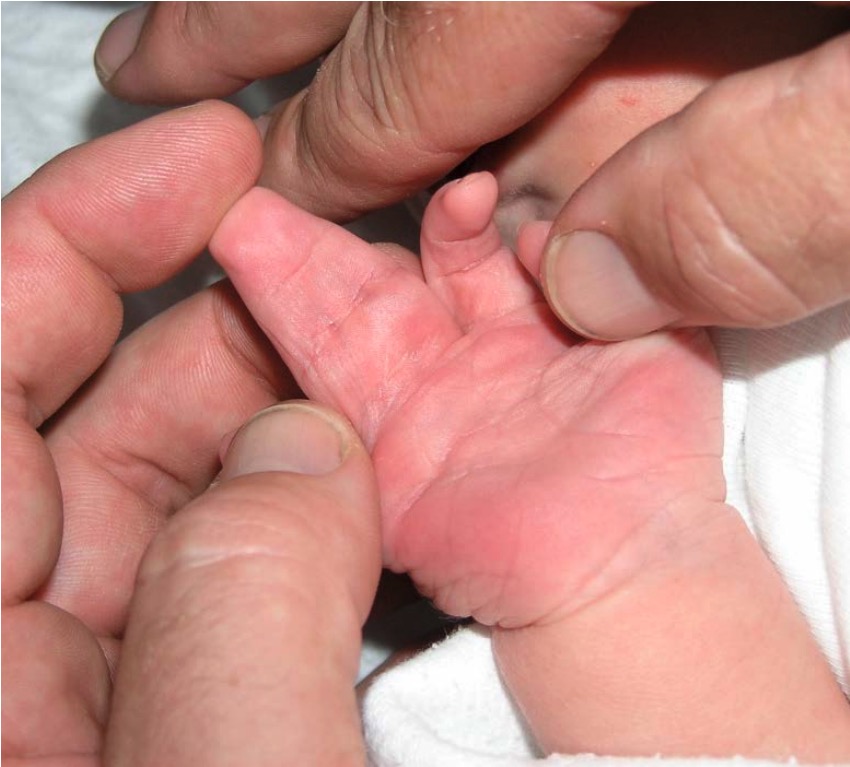
A child with syndactyly
Image by Dumplestiltskin, PD.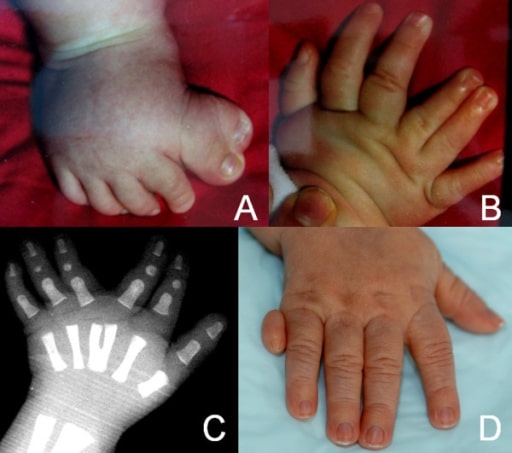
A: Preaxial poly-syndactyly of the right foot
B: Mesoaxial polydactyly of the right hand
C: X-ray of the left hand showing a Y-shaped 3rd metacarpal bone
D: Postaxial polydactyly of the right hand
| Palmar grasp Palmar Grasp Primitive Reflexes | Rooting | Moro | Tonic neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Onset (gestation) | 28 weeks | 32 weeks | 28–32 weeks | 35 weeks |
| Fully developed | 32 weeks of gestation | 36 weeks of gestation | 37 weeks of gestation | 1 month after birth |
| Duration | 2–3 months after birth | Less prominent 1 month after birth | 5–6 months after birth | 6–7 months after birth |
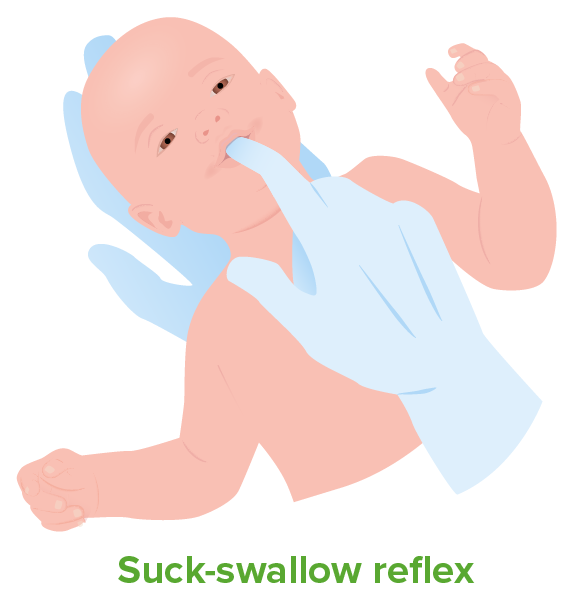
The suck-swallow reflex causes the child to instinctively suck anything that touches the roof of the mouth and simulates the way a child naturally eats.
Image by Lecturio.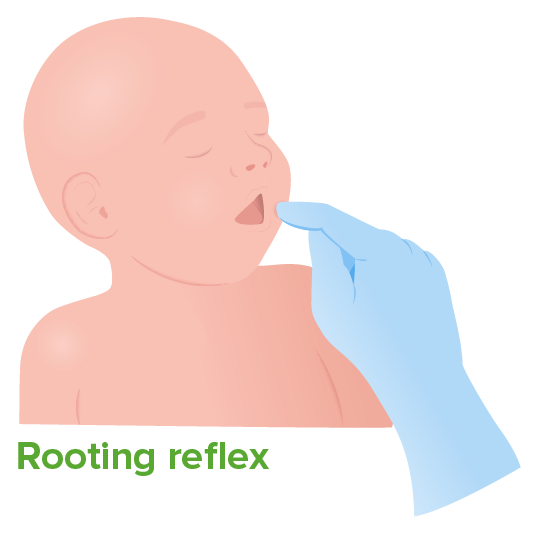
A newborn infant will turn their head toward anything that strokes their cheek or mouth, as they are searching for the object by moving their head in steadily decreasing arcs until the object is found.
Image by Lecturio.
To best observe the Palmar grasp reflex, place the infant on a bed where they could safely fall onto a pillow, and then offer the infant an index finger and gradually lift. The grasp of the finger may be able to support the child’s weight, but they may also release their grip suddenly and without warning.
Image by Lecturio.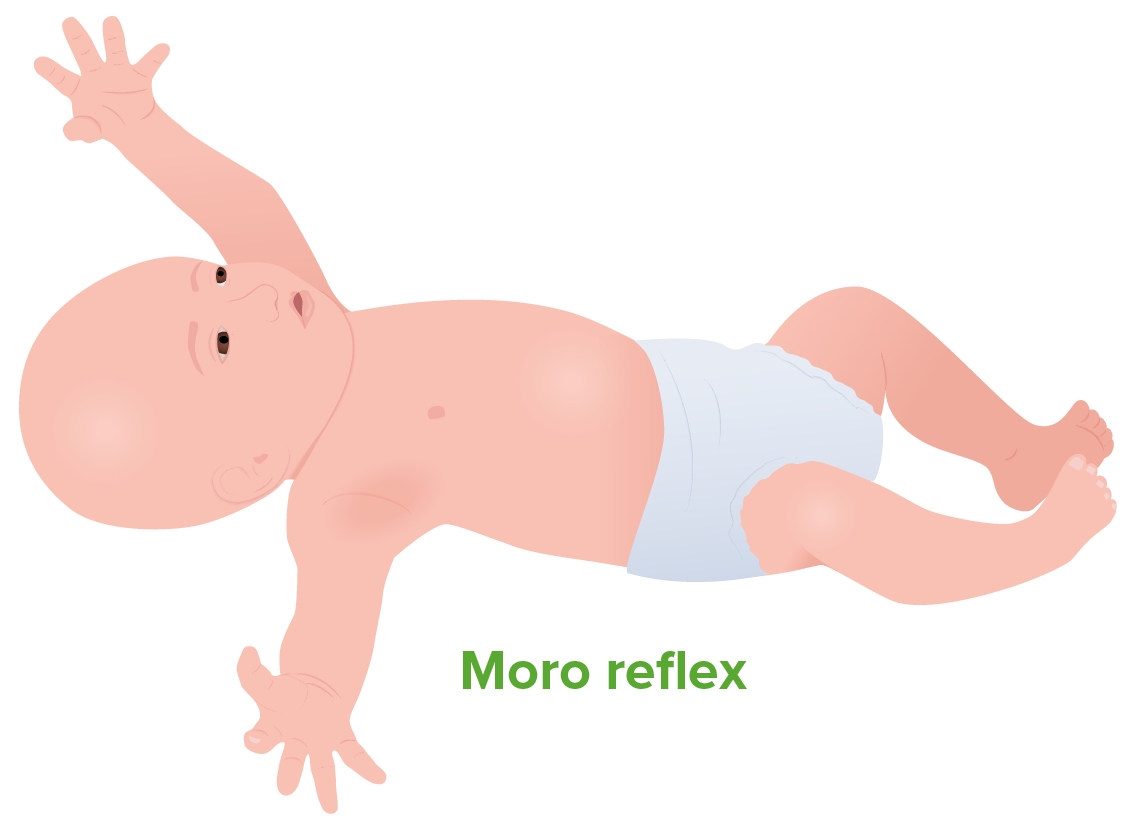
The Moro reflex is initiated by pulling the infant up from the floor and then releasing them:
1. They spread their arms.
2. They pull their arms in.
3. They cry.
The following conditions can be identified or suspected through physical examination of the newborn: