Pertussis, or whooping cough, is a potentially life-threatening highly contagious bacterial infection of the respiratory tract caused by Bordetella pertussis Bordetella pertussis A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria that is the causative agent of whooping cough. Its cells are minute coccobacilli that are surrounded by a slime sheath. Bordetella. The disease has 3 clinical stages, the second and third of which are characterized by an intense paroxysmal cough, an inspiratory whoop, and post-tussive vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia. Pertussis can be prevented by a vaccine Vaccine Suspensions of killed or attenuated microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa), antigenic proteins, synthetic constructs, or other bio-molecular derivatives, administered for the prevention, amelioration, or treatment of infectious and other diseases. Vaccination that is administered as part of most routine vaccinations and usually started at the age of 6 weeks. Diagnosis is based on the clinical history and confirmed by the detection of the organism via culture or polymerase chain reaction Polymerase chain reaction Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). If pertussis is suspected, immediate antibiotic therapy with macrolides Macrolides Macrolides and ketolides are antibiotics that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit and blocking transpeptidation. These antibiotics have a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity but are best known for their coverage of atypical microorganisms. Macrolides and Ketolides should be initiated, even if laboratory confirmation is pending.
Last updated: Apr 30, 2025
Individuals at risk for contracting pertussis and/or severe disease include:
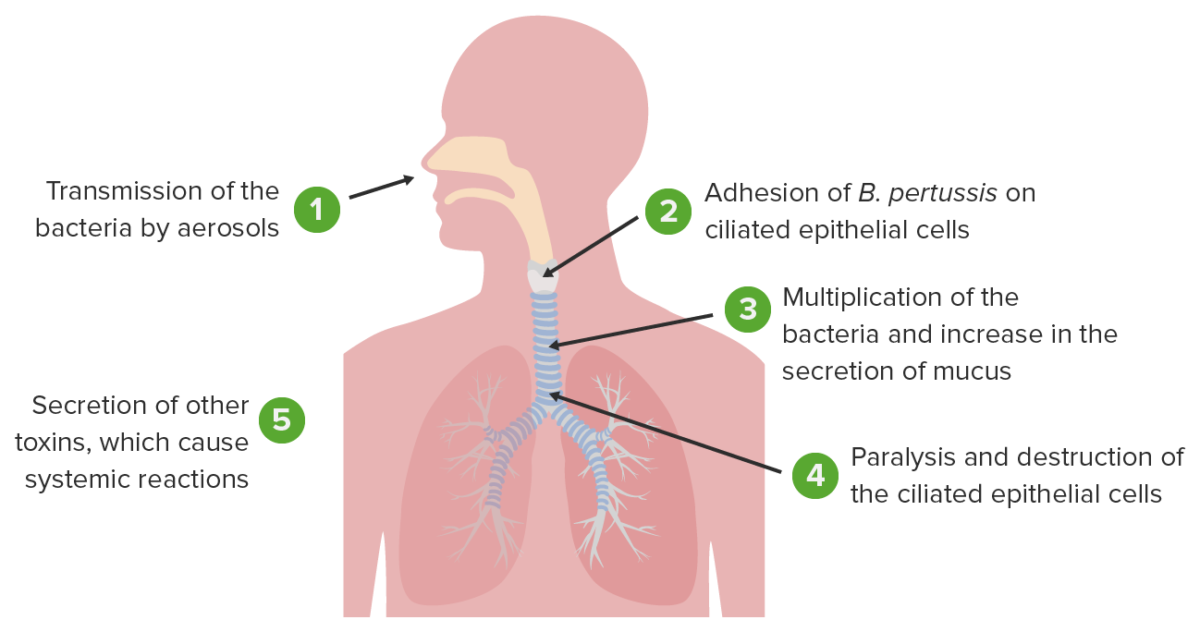
Pathophysiology of Bordetella pertussis causing whooping cough
Image by Lecturio.
Gram stain of the bacteria Bordetella pertussis
Image: “Gram stain of the bacteria Bordetella pertussis” by CDC/Public Health Image Library. License: Public DomainIf the clinical history strongly supports the diagnosis of pertussis, it is highly suggested to initiate antibiotic therapy while awaiting test results.