A peritonsillar abscess Abscess Accumulation of purulent material in tissues, organs, or circumscribed spaces, usually associated with signs of infection. Chronic Granulomatous Disease (PTA), also called quinsy, is a collection of pus between the capsule Capsule An envelope of loose gel surrounding a bacterial cell which is associated with the virulence of pathogenic bacteria. Some capsules have a well-defined border, whereas others form a slime layer that trails off into the medium. Most capsules consist of relatively simple polysaccharides but there are some bacteria whose capsules are made of polypeptides. Bacteroides of the palatine tonsil Palatine tonsil A round-to-oval mass of lymphoid tissue embedded in the lateral wall of the pharynx. There is one on each side of the oropharynx in the fauces between the anterior and posterior pillars of the soft palate. Tonsillitis and the pharyngeal muscles Pharyngeal Muscles The muscles of the pharynx are voluntary muscles arranged in two layers. The external circular layer consists of three constrictors (superior, middle, and inferior). The internal longitudinal layer consists of the palatopharyngeus, the salpingopharyngeus, and the stylopharyngeus. During swallowing, the outer layer constricts the pharyngeal wall and the inner layer elevates pharynx and larynx. Pharynx: Anatomy. A PTA is usually a complication of acute tonsillitis Tonsillitis Tonsillitis is inflammation of the pharynx or pharyngeal tonsils, and therefore is also called pharyngitis. An infectious etiology in the setting of tonsillitis is referred to as infectious pharyngitis, which is caused by viruses (most common), bacteria, or fungi. Tonsillitis, an infection caused by group A Streptococci. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship often present with a sore throat Sore throat Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the back of the throat (pharynx). Pharyngitis is usually caused by an upper respiratory tract infection, which is viral in most cases. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, and hoarseness. Pharyngitis, trismus Trismus Spasmodic contraction of the masseter muscle resulting in forceful jaw closure. This may be seen with a variety of diseases, including tetanus, as a complication of radiation therapy, trauma, or in association with neoplastic conditions. Tetanus, and a muffled voice. The infection responds well to drainage and antibiotics. Complications such as the extension Extension Examination of the Upper Limbs of infection to deeper spaces are possible.
Last updated: Jul 21, 2025
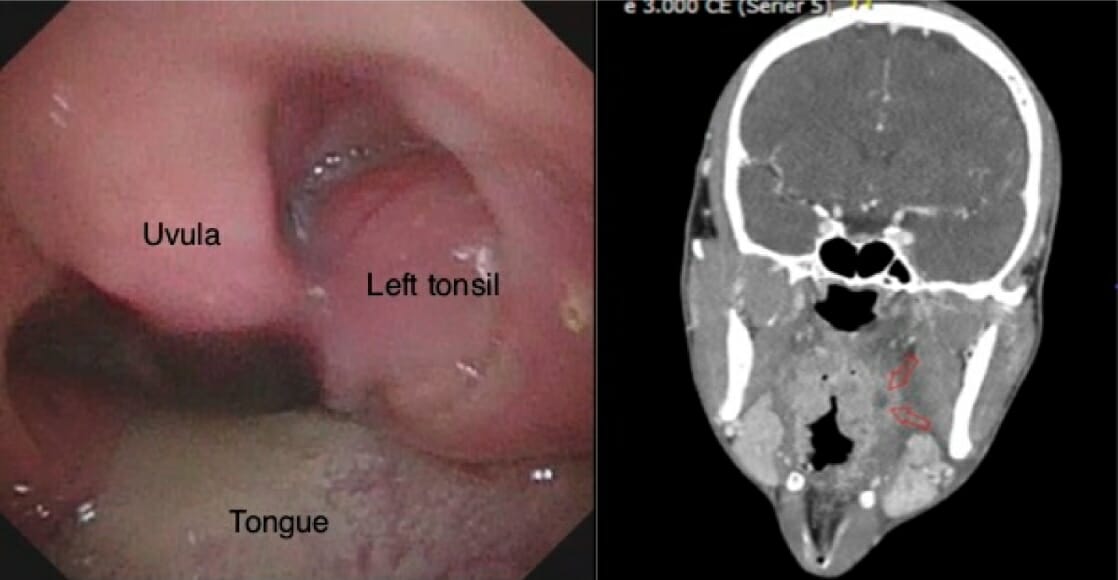
Peritonsillar abscess:
The image on the left shows left-side peritonsillar swelling and uvular deviation on oral examination. The image on the right shows a deep, left-side peritonsillar abscess (red arrows) on the CT image.
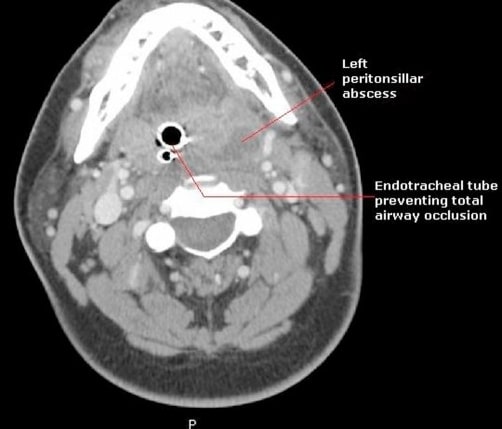
Computed tomography scan showing a left peritonsillar abscess and endotracheal tube preventing total airway occlusion
Image: “Peritonsillar abscess requiring intensive care unit admission caused by group C and G Streptococcus: a case report” by Gupta, N., Lovvorn, J., Centor, R.M. License: CC BY 3.0.The spread of the infection into other parts of the body can lead to serious complications. These include the following: