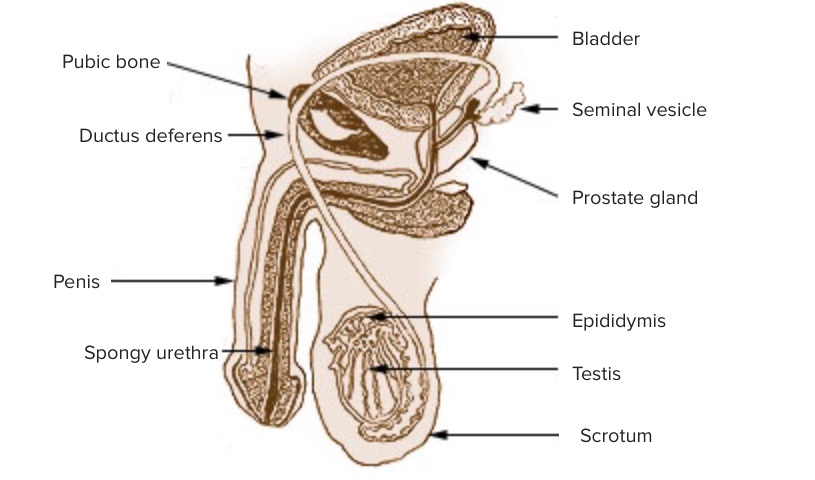
The penis is the male organ of copulation and micturition. The organ is composed of a root, body, and glans. The root is attached to the pubic bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types by the crura penis, which are the extremities of the corpora cavernosa. The body consists of the 2 parallel corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum, which sits beneath the corpora cavernosa and through which the urethra Urethra A tube that transports urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body in both the sexes. It also has a reproductive function in the male by providing a passage for sperm. Urinary Tract: Anatomy passes. The glans is ensheathed by the prepuce or foreskin. The penis is homologous with the clitoris Clitoris An erectile structure homologous with the penis, situated beneath the anterior labial commissure, partially hidden between the anterior ends of the labia minora. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy in females.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The penis is attached to the pubic bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types by the crura penis. This attachment is the root of the penis, and it is located just below the prostate Prostate The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system. The gland surrounds the bladder neck and a portion of the urethra. The prostate is an exocrine gland that produces a weakly acidic secretion, which accounts for roughly 20% of the seminal fluid. gland. The urethra Urethra A tube that transports urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body in both the sexes. It also has a reproductive function in the male by providing a passage for sperm. Urinary Tract: Anatomy enters the penis at the root and travels within the corpus spongiosum on the dorsal aspect of the penis.
Cross-sectional anatomy (sagittal) of the male genitalia
Image: “Illustration of the penis” by US Federal Government/National Cancer Institute. License: Public Domain, edited by Lecturio.The penis consists of a root, body, and glans.
Root:
Body:
Glans:

Erectile tissues of the penis
Image: “Anatomical illustration of the penis structure” by Grant, John Charles Boileau. License: Public Domain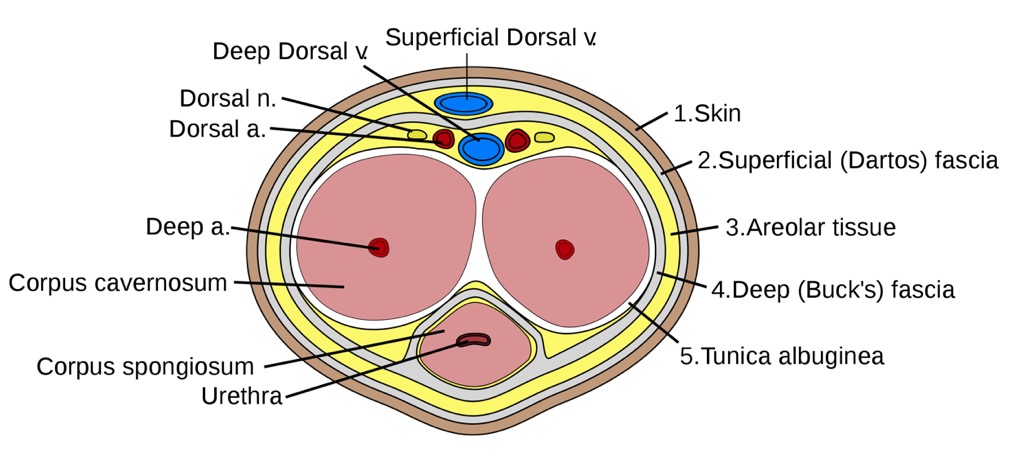
Cross-sectional anatomy (frontal) of the penis
a.: artery
v.: vein
n.: nerve
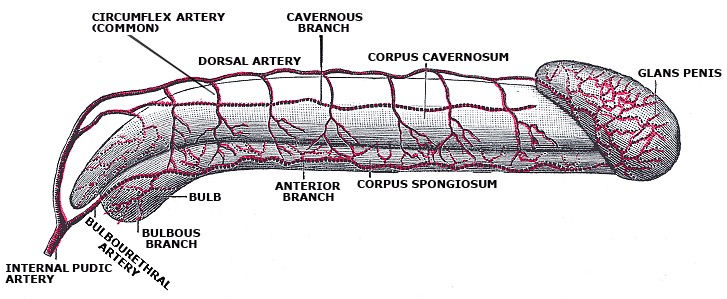
Arterial circulation of the penis
Image: “Arterial supply of the penis” by Gray’s anatomy. License: Public DomainBlood leaving the penis is drained by 1 of 3 venous systems: