Trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 13, or Patau syndrome, is a genetic syndrome caused by the presence of 3 copies of chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 13. As the 3rd most common trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations, Patau syndrome has an incidence Incidence The number of new cases of a given disease during a given period in a specified population. It also is used for the rate at which new events occur in a defined population. It is differentiated from prevalence, which refers to all cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency of 1 in 10,000 live births and is more common in women. Most cases of Patau syndrome are diagnosed prenatally by maternal screening Screening Preoperative Care and ultrasound. More than half of the pregnancies result in spontaneous abortions. If pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care reaches term, it is recommended that a specialized center handle delivery and neonatal care. In the neonate Neonate An infant during the first 28 days after birth. Physical Examination of the Newborn, findings include craniofacial and cardiac malformations, severe intellectual disability Disability Determination of the degree of a physical, mental, or emotional handicap. The diagnosis is applied to legal qualification for benefits and income under disability insurance and to eligibility for social security and workman's compensation benefits. ABCDE Assessment, and greatly reduced life expectancy Life expectancy Based on known statistical data, the number of years which any person of a given age may reasonably expected to live. Population Pyramids. Most babies do not survive beyond 3 months. With no treatment available and a null expectancy of survival, the family is given supportive management and resources to navigate through the natural course of the disease.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 13 or Patau syndrome is defined by the presence of 3 copies of chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 13.
“At 13 you enter Puberty”: P as in Patau syndrome or 13 for Trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 13
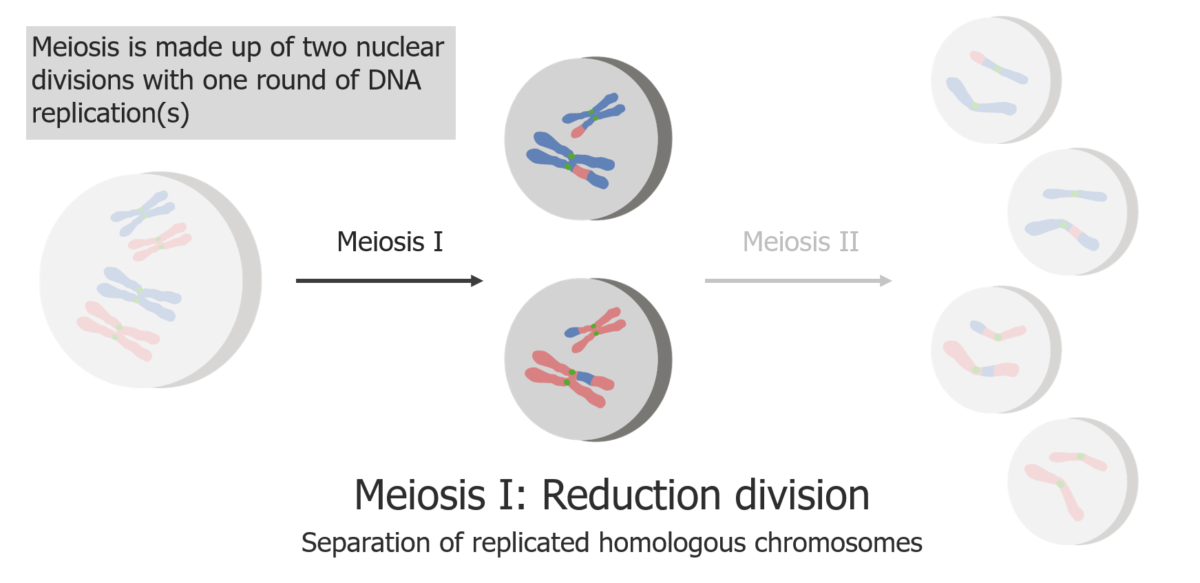
(1) Meiosis I is the separation of replicated sister chromatids.
Image by Lecturio.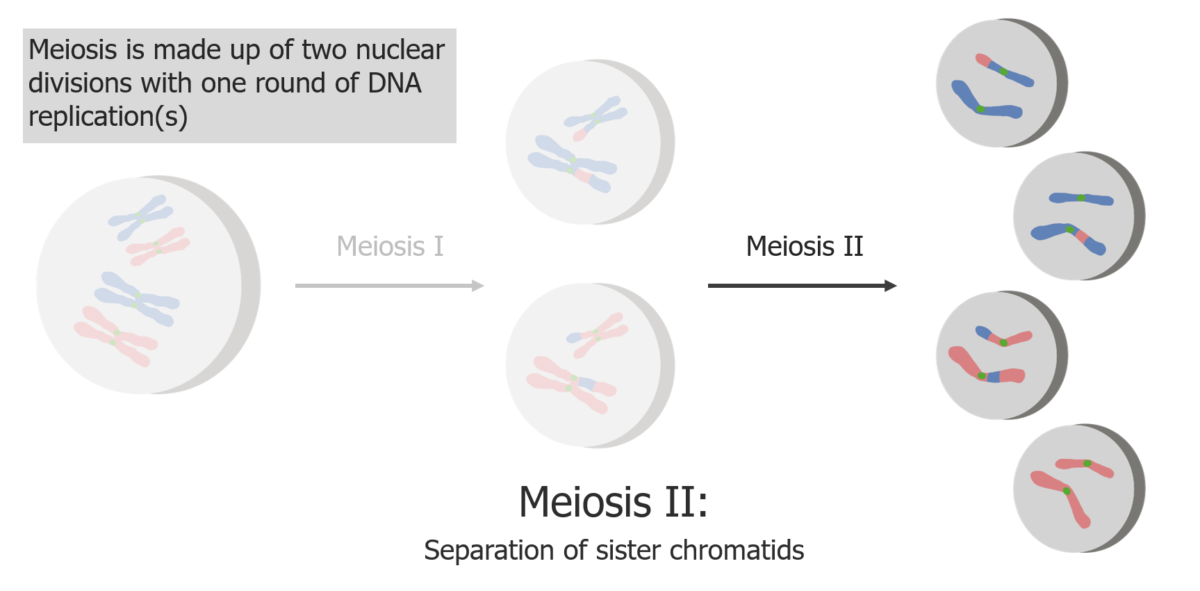
(2) Meiosis II results in the separation of sister chromatids, producing 4 haploid cells/gametes.
Image by Lecturio.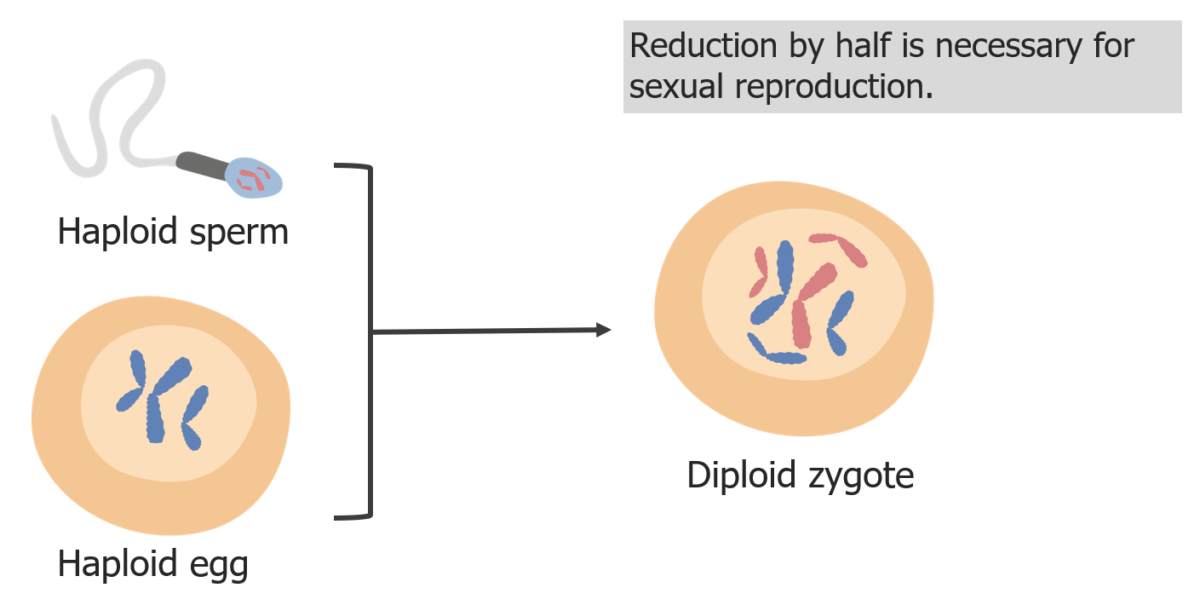
(3) Reduction of chromosomes is needed so that in fertilization, the zygote is diploid.
Image by Lecturio.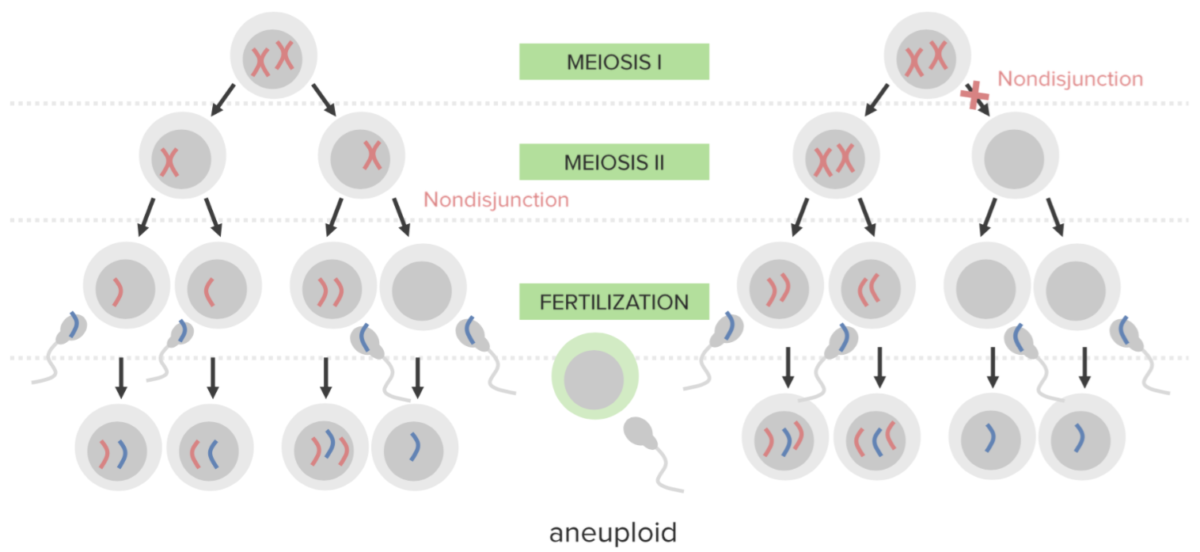
Nondisjunction:
Failure of proper separation of 2 homologous chromosomes or the sister chromatids during cell division.
Nondisjunction results in aneuploidy, a state of chromosomal imbalance.
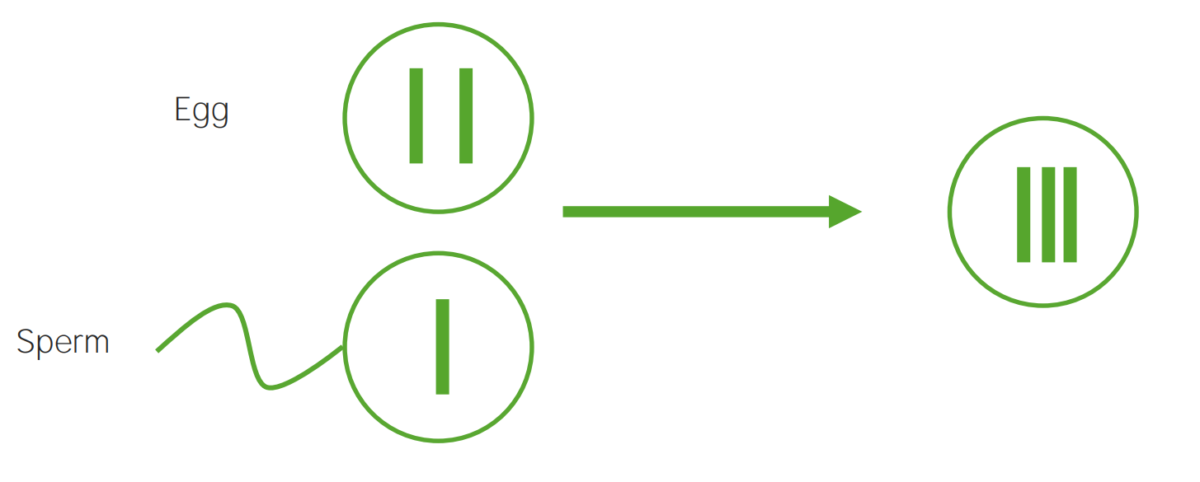
Diagram explaining the etiological mechanism of nondisjunction in trisomies:
An egg that carries 2 copies of the same chromosome acquires another when fertilized (resulting in 3 copies).
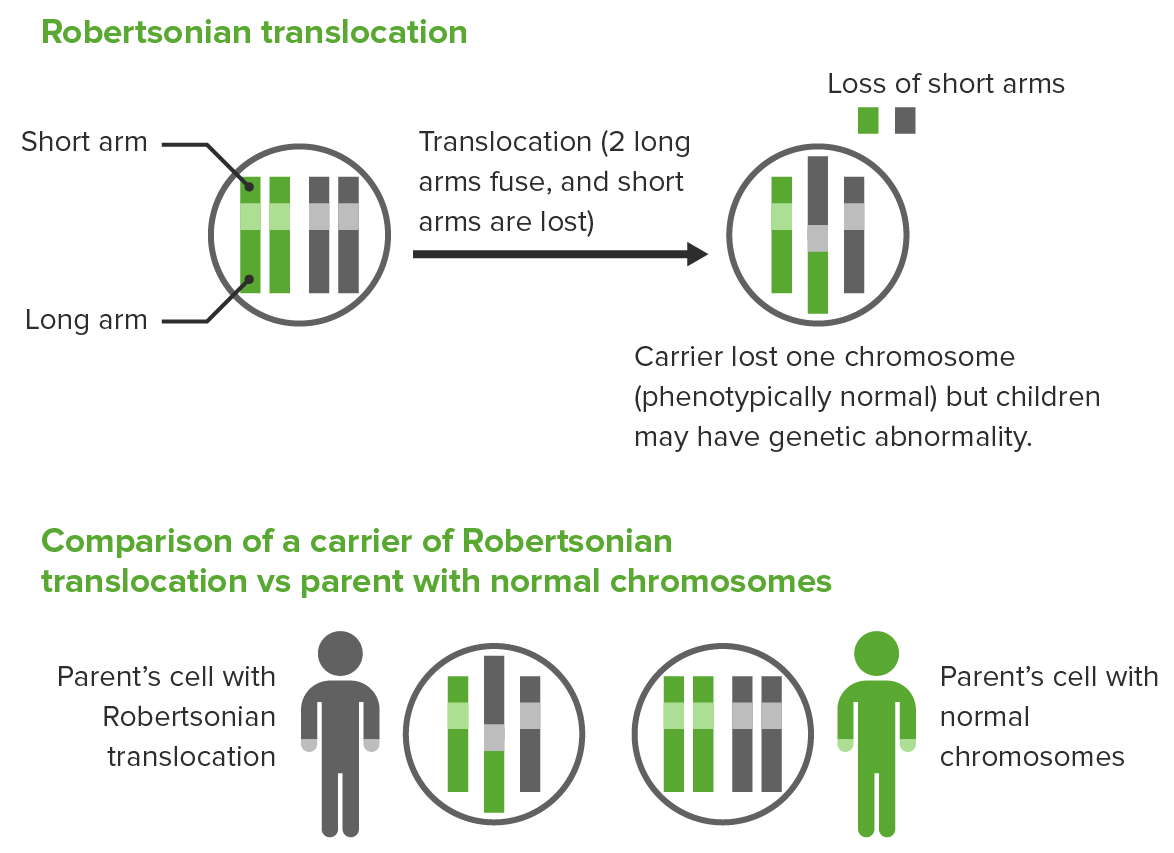
Robertsonian translocation:
The 2 long arms of different acrocentric chromosomes fuse, resulting in the loss of short arms and loss of 1 chromosome.
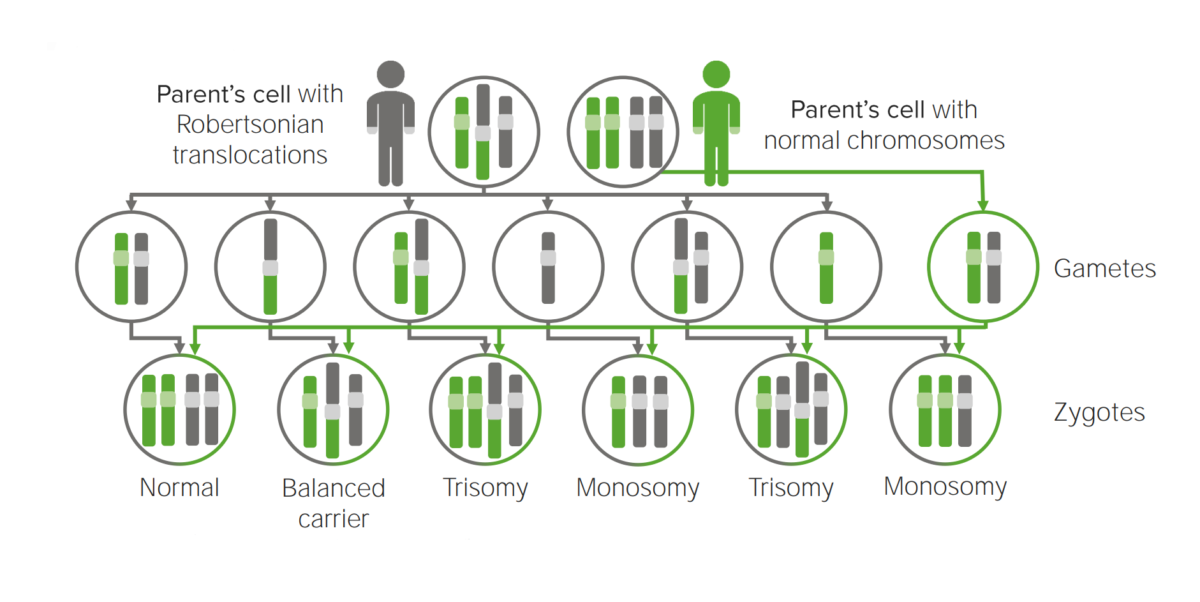
Diagram explaining the etiological mechanism of Robertsonian translocation in trisomies.
Translocation to another chromosome will possibly create a cell carrying 3 copies of the implicated chromosome.
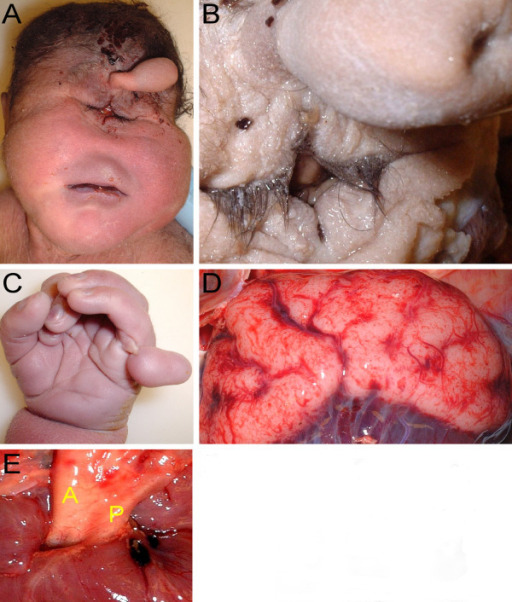
Patau syndrome: 37 2/7 week gestational age male infant with Patau syndrome demonstrating alobar holoprosencephaly with cyclopia.
A) Facial features include sloping forehead with a proboscis superior to a single central palpebral fissure.
B) Close-up of the fused eyelids and proboscis showing a single nostril
C) Polydactyly showing six digits
D) Posterior view of the brain showing indistinct gyri, fusion of the hemispheres, and occipital encephalocele
E) Transposition of the aorta (A) and hypoplastic pulmonary trunk (P)
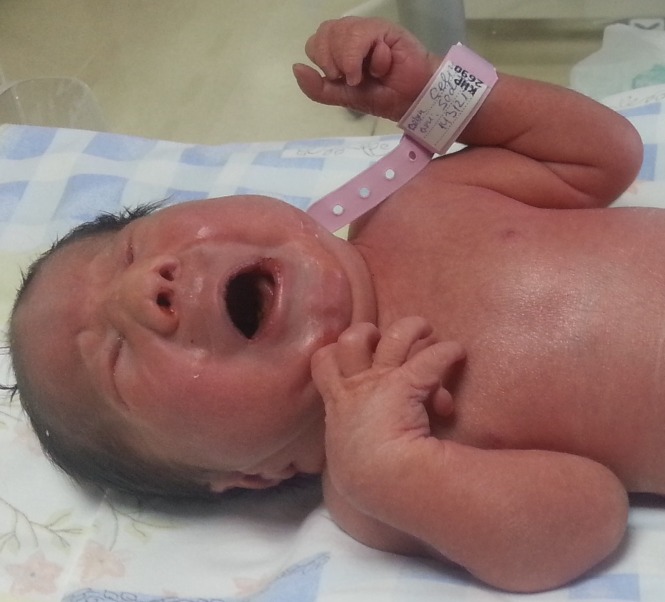
Features of trisomy 13: polydactyly, microphthalmia, low-set ears, and depressed nasal root
Image: “Sacrococcygeal teratoma associated with trisomy 13” by Dorum BA, Köksal N, Özkan H, Karakaya S, Akgül AK. License: CC BY 3.0| 1st trimester | 2nd trimester | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NT | Pregnancy-associated plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products protein-A | β-hCG | AFP AFP The first alpha-globulins to appear in mammalian sera during fetal development and the dominant serum proteins in early embryonic life. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases | Estriol Estriol A hydroxylated metabolite of estradiol or estrogen that has a hydroxyl group at C3, 16-alpha, and 17-beta position. Estriol is a major urinary estrogen. During pregnancy, a large amount of estriol is produced by the placenta. Isomers with inversion of the hydroxyl group or groups are called epiestriol. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins | β-hCG | Inhibin A Inhibin A Glycoproteins that inhibit pituitary follicle stimulating hormone secretion. Inhibins are secreted by the sertoli cells of the testes, the granulosa cells of the ovarian follicles, the placenta, and other tissues. Inhibins and activins are modulators of follicle stimulating hormone secretions; both groups belong to the TGF-beta superfamily, as the transforming growth factor beta. Inhibins consist of a disulfide-linked heterodimer with a unique alpha linked to either a beta a or a beta B subunit to form inhibin a or inhibin b, respectively. Menstrual Cycle | |
| Trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 13 | ↑ | ↓↓ | ↓ | Unchanged | Unchanged | Unchanged | Unchanged |
| Trisomy Trisomy The possession of a third chromosome of any one type in an otherwise diploid cell. Types of Mutations 18 | ↑↑ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ | ↓ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ | Unchanged |
| Trisomy 21 Trisomy 21 Down syndrome, or trisomy 21, is the most common chromosomal aberration and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental delay. Both boys and girls are affected and have characteristic craniofacial and musculoskeletal features, as well as multiple medical anomalies involving the cardiac, gastrointestinal, ocular, and auditory systems. Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) | ↑↑ | ↓↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | ↑ |
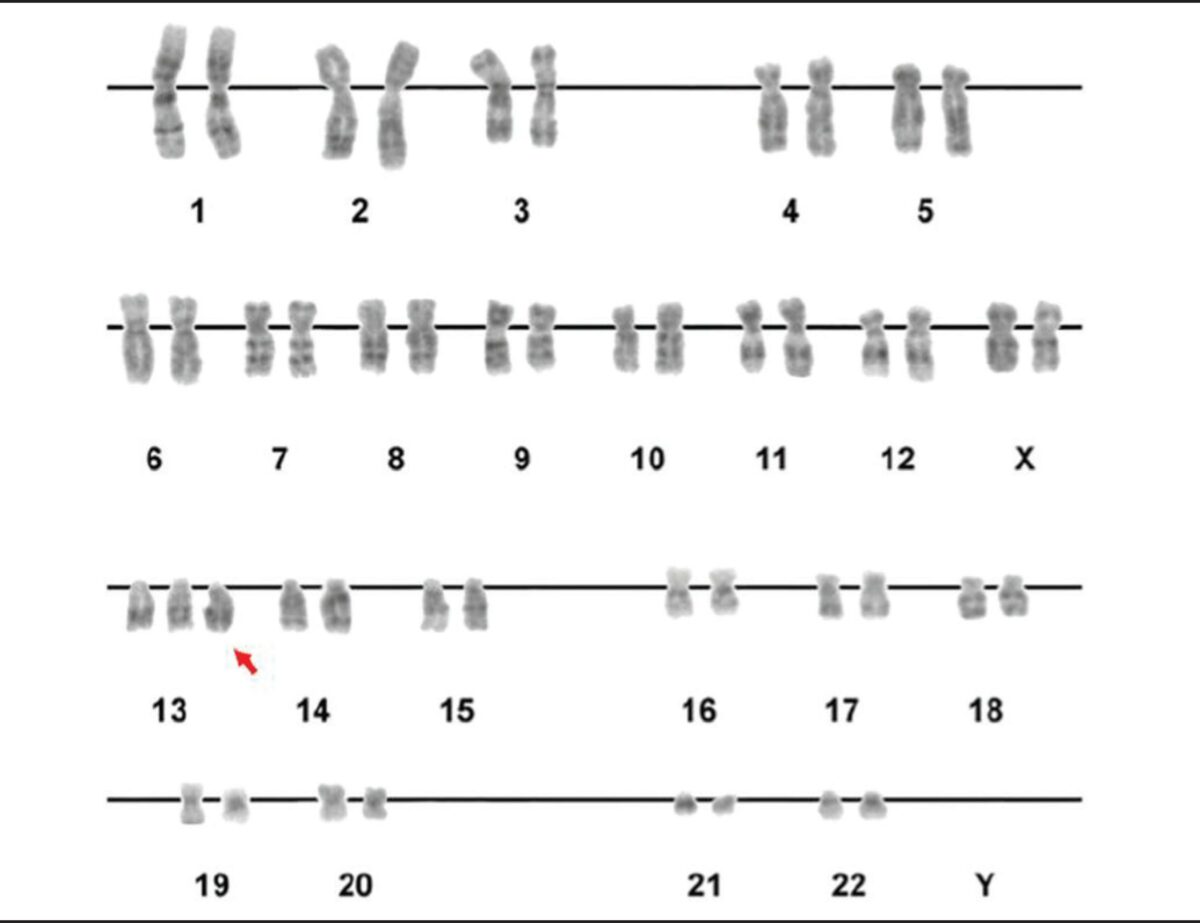
A karyotype showing trisomy of the 13th chromosome (red arrow)
Image: “Figure 2” by Luiza E. Dorfman, et al. License: CC BY 4.0