Parapharyngeal abscess Abscess Accumulation of purulent material in tissues, organs, or circumscribed spaces, usually associated with signs of infection. Chronic Granulomatous Disease is a deep neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess infection involving the parapharyngeal space. The infection often arises from the nasal sinuses, mouth, or throat Throat The pharynx is a component of the digestive system that lies posterior to the nasal cavity, oral cavity, and larynx. The pharynx can be divided into the oropharynx, nasopharynx, and laryngopharynx. Pharyngeal muscles play an integral role in vital processes such as breathing, swallowing, and speaking. Pharynx: Anatomy. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship often present with spiking fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, dysphagia Dysphagia Dysphagia is the subjective sensation of difficulty swallowing. Symptoms can range from a complete inability to swallow, to the sensation of solids or liquids becoming "stuck." Dysphagia is classified as either oropharyngeal or esophageal, with esophageal dysphagia having 2 sub-types: functional and mechanical. Dysphagia, odynophagia Odynophagia Epiglottitis, trismus Trismus Spasmodic contraction of the masseter muscle resulting in forceful jaw closure. This may be seen with a variety of diseases, including tetanus, as a complication of radiation therapy, trauma, or in association with neoplastic conditions. Tetanus, and neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways. Airway Airway ABCDE Assessment compromise may develop. Diagnosis is made via CT or MRI. Management includes airway Airway ABCDE Assessment stabilization, initiation of antibiotic therapy, and possibly surgical drainage.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Parapharyngeal abscess Abscess Accumulation of purulent material in tissues, organs, or circumscribed spaces, usually associated with signs of infection. Chronic Granulomatous Disease is a deep neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess infection involving the parapharyngeal space.
The layers of the deep cervical fascia Fascia Layers of connective tissue of variable thickness. The superficial fascia is found immediately below the skin; the deep fascia invests muscles, nerves, and other organs. Cellulitis represent the potential routes of spread of infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease.
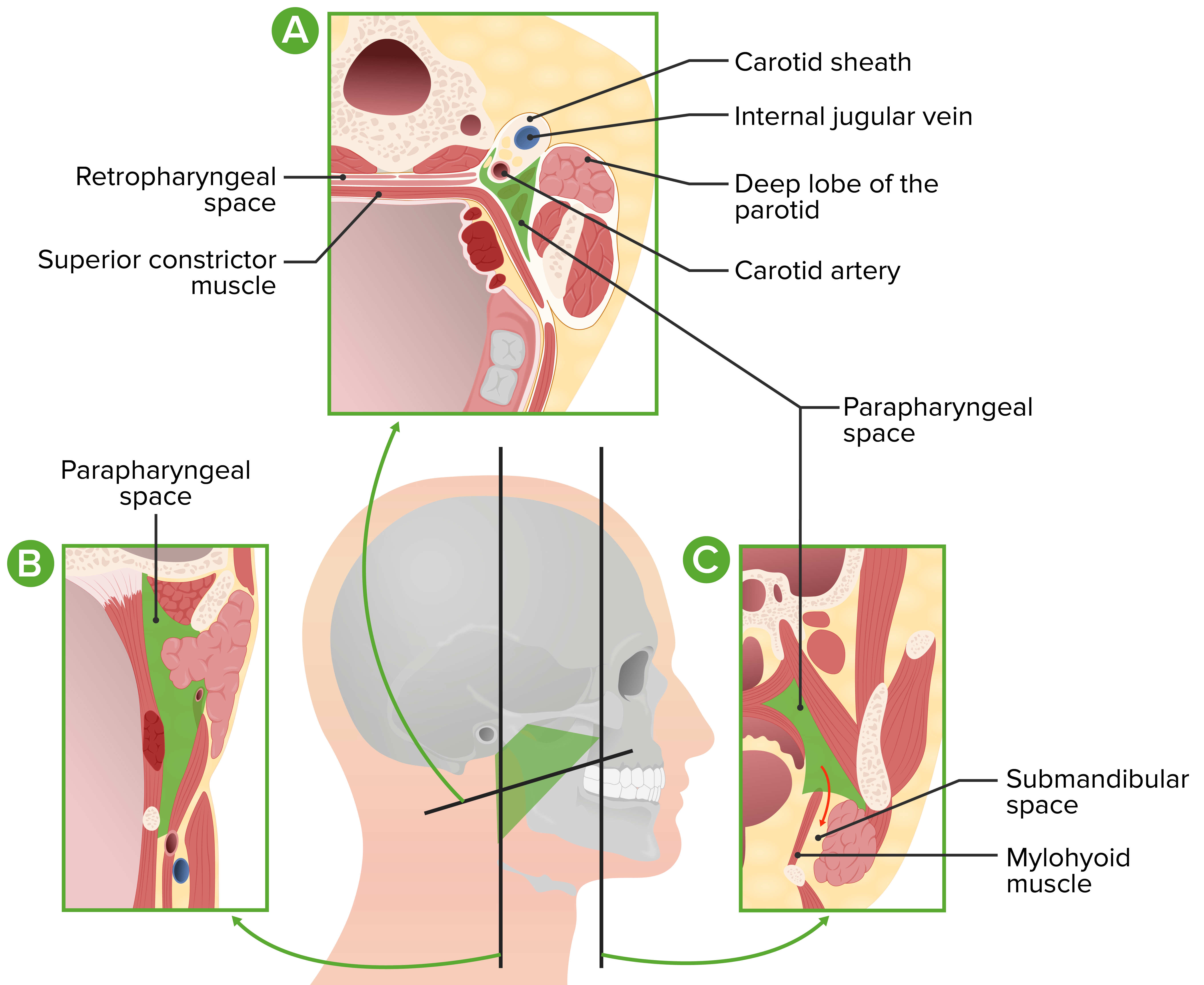
Diagrams demonstrating the anatomical positioning of the parapharyngeal space and surrounding vasculature
Image by Lecturio.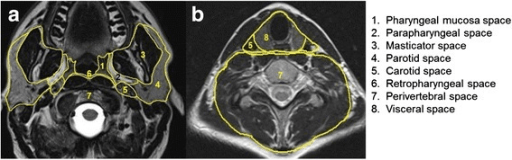
MRI axial cut showing the deep spaces of the suprahyoid neck:
1: pharyngeal mucosa space
2: parapharyngeal space
3: masticator space
4: parotid space
5: carotid space
6: retropharyngeal space
7: perivertebral space
8: visceral space
The initial management focuses on airway Airway ABCDE Assessment stabilization. Infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are polymicrobial and comprise the usual flora from the adjacent source mucosa. Empiric IV antibiotic therapy should be initiated immediately.
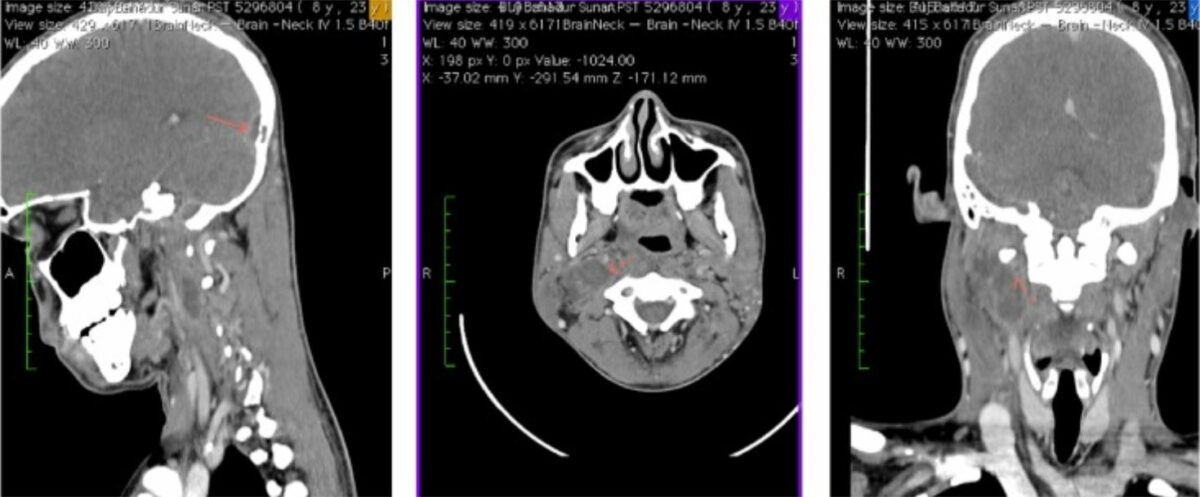
CT scans demonstrate right parapharyngeal abscess and right internal jugular vein thrombosis (arrow in all 3 panels).
Image: “CECT showing right IJV thrombosis with right parapharyngeal abscess and delta sign at the transverse sinus” by Case Reports in Otolaryngology. License: CC BY 4.0