There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves (CNs), which run from the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification to various parts of the head, neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess, and trunk. The CNs can be sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology or motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology or both. Some CNs are involved in special senses, like vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam, hearing, and taste, and others are involved in muscle control of the face. The CNs are named and numbered in Roman numerals according to their location, from the front to the back of the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
| Nerve | CN | Function | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Olfactory | I | Olfaction Olfaction The sense of smell, or olfaction, begins in a small area on the roof of the nasal cavity, which is covered in specialized mucosa. From there, the olfactory nerve transmits the sensory perception of smell via the olfactory pathway. This pathway is composed of the olfactory cells and bulb, the tractus and striae olfactoriae, and the primary olfactory cortex and amygdala. Olfaction: Anatomy ( smell Smell The sense of smell, or olfaction, begins in a small area on the roof of the nasal cavity, which is covered in specialized mucosa. From there, the olfactory nerve transmits the sensory perception of smell via the olfactory pathway. This pathway is composed of the olfactory cells and bulb, the tractus and striae olfactoriae, and the primary olfactory cortex and amygdala. Olfaction: Anatomy) | Sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology |
| Optic | II | Vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam | Sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology |
| Oculomotor | III |
|
Motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology |
| Trochlear | IV | Eye movement ( superior oblique Superior oblique Orbit and Extraocular Muscles: Anatomy muscle) | Motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology |
| Trigeminal | V |
|
Both |
| Abducens | VI | Eye movement ( lateral rectus Lateral rectus Orbit and Extraocular Muscles: Anatomy muscle) | Motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology |
| Facial | VII |
|
Both |
| Vestibulocochlear | VIII |
|
Sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology |
| Glossopharyngeal | IX |
|
Both |
| Vagus | X |
|
Both |
| Accessory | XI |
|
Motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology |
| Hypoglossal | XII | Tongue Tongue The tongue, on the other hand, is a complex muscular structure that permits tasting and facilitates the process of mastication and communication. The blood supply of the tongue originates from the external carotid artery, and the innervation is through cranial nerves. Lips and Tongue: Anatomy movements | Motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology |
| Cranial nerve | Mnemonic 1 | Mnemonic 2 | Mnemonic 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Olfactory | Ooh | Oh | Old |
| Optic | Ooh | Once | Opie |
| Oculomotor | Ooh | One | Occasionally |
| Trochlear | To | Takes | Tries |
| Trigeminal | Touch | The | Trigonometry |
| Abducens | And | Anatomy | And |
| Facial | Feel | Final | Feels |
| Vestibulocochlear | Very | Very | Very |
| Glossopharyngeal | Good | Good | Gloomy |
| Vagus | Velvet | Vacations | Vague |
| Accessory | Ah | Are | And |
| Hypoglossal | Heaven | Heavenly | Hypoactive |
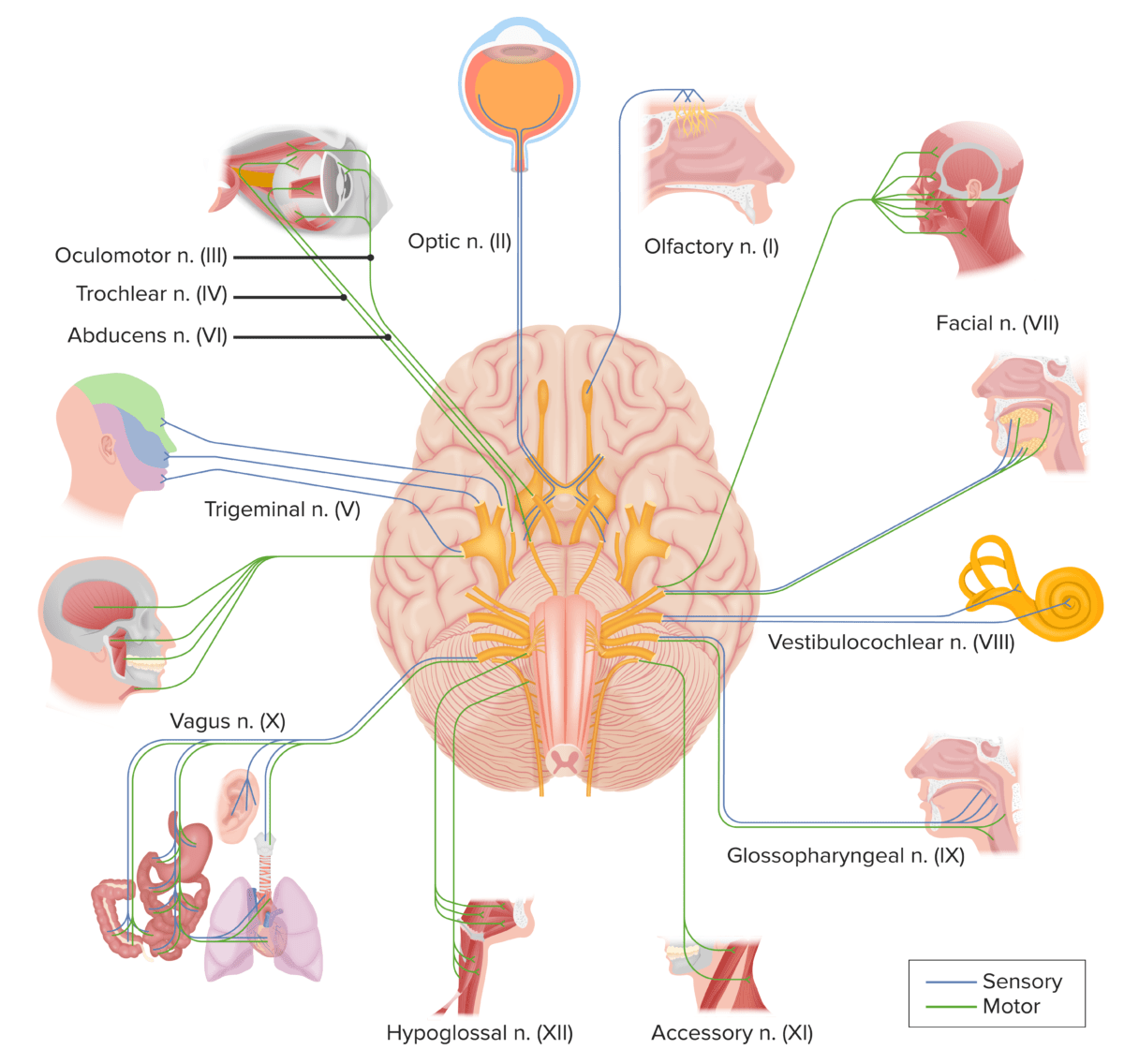
The 12 cranial nerves as they exit from the brain and the primary sites of innervations
n.: nerve
| CN | Sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology, motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology, or both |
|---|---|
| I | Some |
| II | Say |
| III | Marry |
| IV | Money |
| V | But |
| VI | My |
| VII | Brother |
| VIII | Says |
| IX | B ig Ig X-linked Agammaglobulinemia |
| X | Brains |
| XI | Matter |
| XII | More |