A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types and periosteum Periosteum Thin outer membrane that surrounds a bone. It contains connective tissue, capillaries, nerves, and a number of cell types. Bones: Structure and Types and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Clinical presentation varies depending on the cause and location of the injury, but generally includes deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, and inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation. Diagnosis is made clinically and confirmed with imaging, and management may be with splinting or may require surgery.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A fracture is a disruption in the cortex of a bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types.
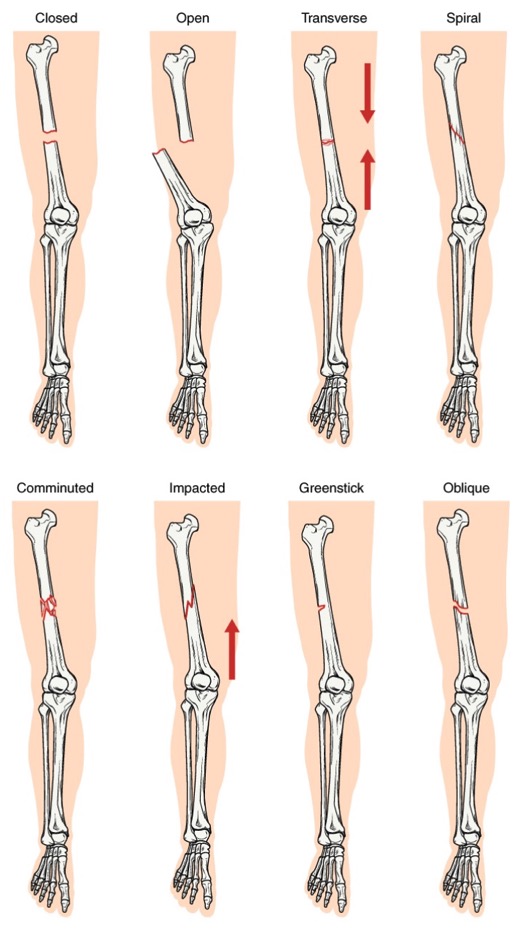
Types of fractures
Image: “Types of Fractures” by OpenStax. License: CC BY 4.0The general principle behind all fractures is that the bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types is subjected to a load that overcomes the bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types‘s bearing capacity, leading to loss of structural integrity.
A thorough history with recent injury or fall details, risk factors for fracture, medications, and past history of a previous fracture are all important.
The diagnosis of a possible fracture is made clinically initially and confirmed on diagnostic imaging.
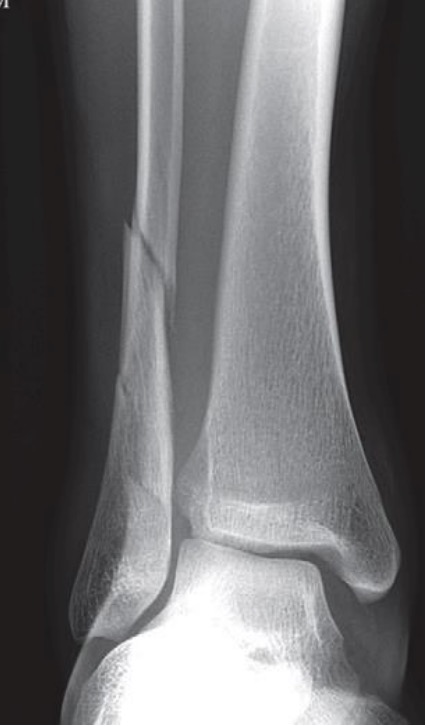
Example of a spiral fracture of the fibula on an anteroposterior (AP) projection of the ankle
Image by Hetal Verma, MD. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0The goal of fracture management by reducing it and allowing the normal healing process to take place is to restore the anatomy, reduce pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and allow the patient to return to the previous level of functioning.
Open fractures require prompt management in the emergency department and transfer to the operating room (OR) for definitive management and hospitalization Hospitalization The confinement of a patient in a hospital. Delirium.