Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density, microarchitectural disruption, and increased skeletal fragility, leading to a reduction in the strength of bone that leads to an increased risk of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile, and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization Immobilization Delirium, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis most often presents clinically with frequent fractures and loss of vertebral height. Diagnosis is established by measuring bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types mineral density. Management includes lifestyle modifications, maintaining adequate levels of calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes and vitamin D Vitamin D A vitamin that includes both cholecalciferols and ergocalciferols, which have the common effect of preventing or curing rickets in animals. It can also be viewed as a hormone since it can be formed in skin by action of ultraviolet rays upon the precursors, 7-dehydrocholesterol and ergosterol, and acts on vitamin D receptors to regulate calcium in opposition to parathyroid hormone. Fat-soluble Vitamins and their Deficiencies, and the use of bisphosphonates Bisphosphonates Bisphosphonates are pyrophosphate analogs most well-known for treating osteoporosis by preventing bone loss. Bisphosphonates end in the suffix "-dronate" or "-dronic acid" (e.g., alendronate, risedronate, pamidronate) and bind to hydroxyapatite crystals in bone, inhibiting osteoclast-induced bone resorption. Bisphosphonates.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Osteoporosis is a metabolic bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types disorder characterized by low bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast and increased bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types fragility.
Primary osteoporosis:
Secondary osteoporosis:
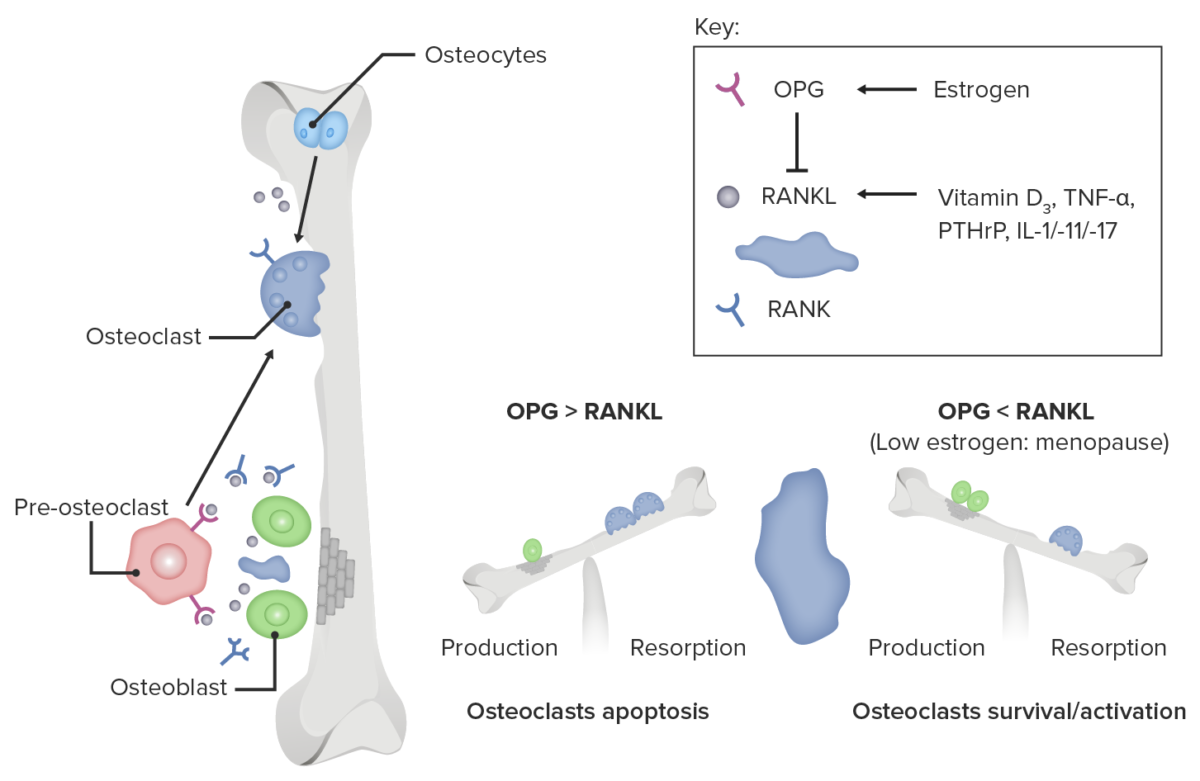
Role of estrogen deficiency in osteoclast activation
Image by Lecturio.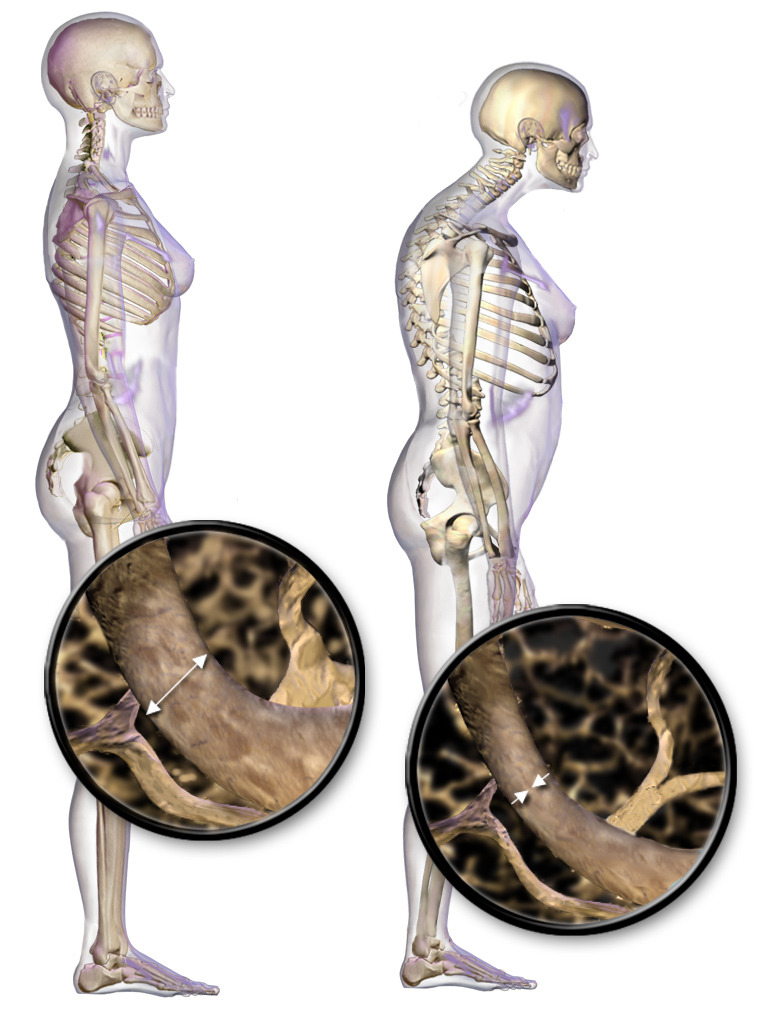
Posture changes and vertebral body bone loss in osteoporosis
Image: “Illustration depicting normal standing posture and osteoporosis” by BruceBlaus. License: CC BY 3.0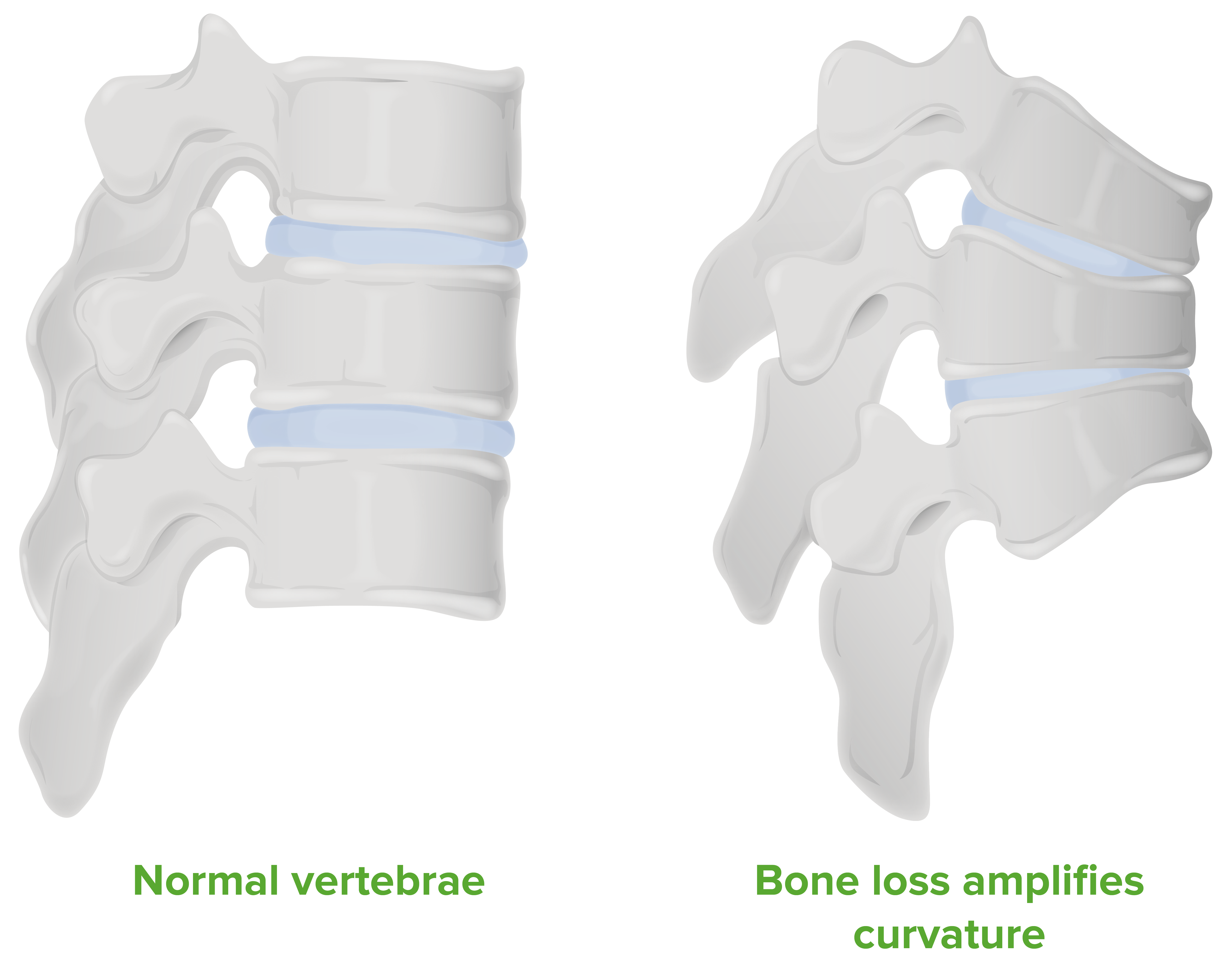
Diagram of the pathological changes seen in a vertebral column with osteoporosis:
Note that the gradual loss of bone density makes the vertebrae collapse, resulting in kyphosis
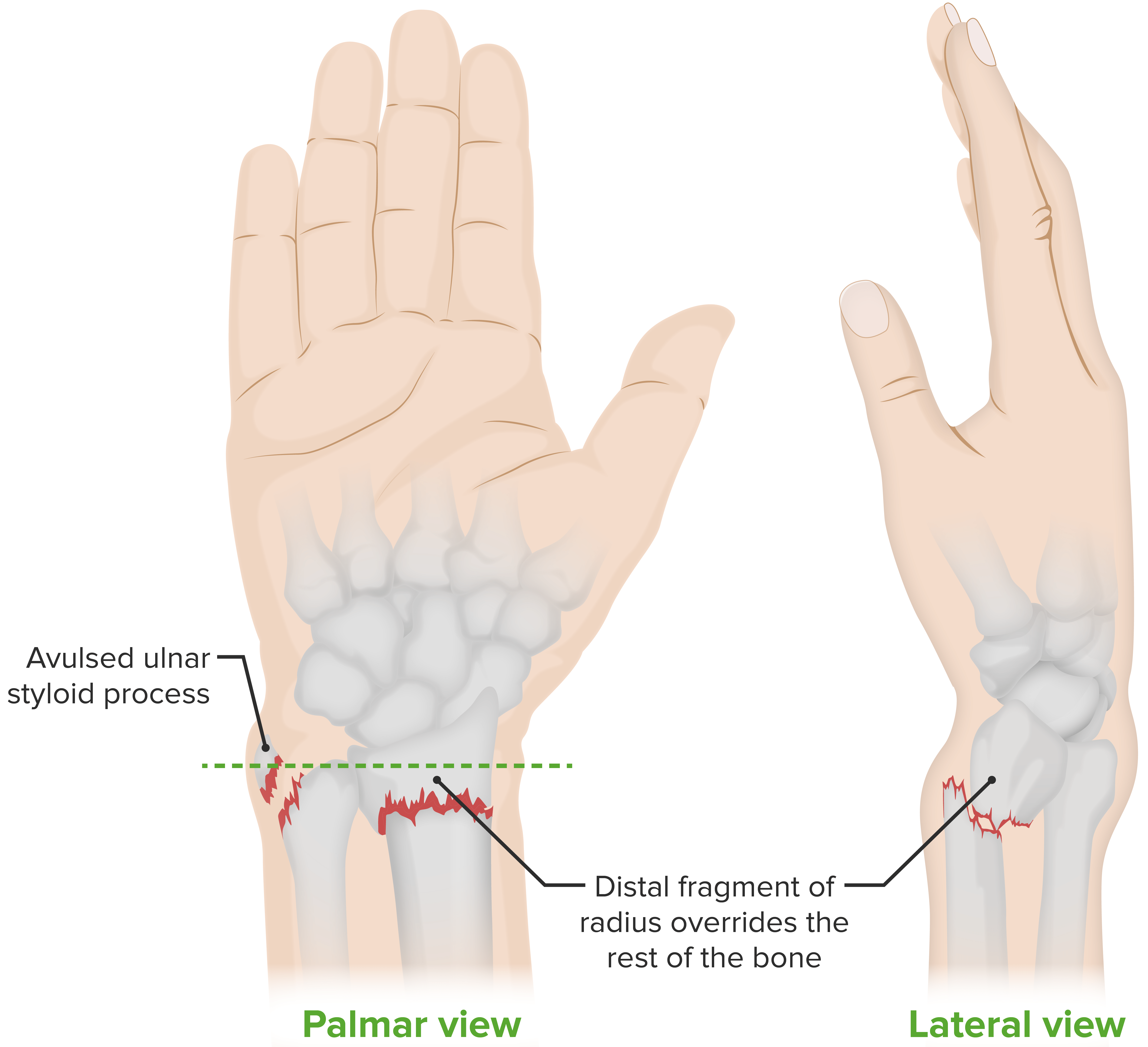
Colles fracture, an extra-articular fracture (i.e., the break is above the wrist joint) of the distal radius, with distal displacement:
This type of fracture occurs most commonly when people fall onto a hard surface and break their fall with an outstretched hand (“FOOSH”). The deformity is commonly known as a “dinner fork deformity.” Falling with the wrists flexed would lead to a Smith fracture, with volar displacement. Ulnar styloid fractures occur in association with ~ 60% of distal radius fractures.